China
10 Chapter Accounting
-
-
1 Chapter Introduction
1.1 The history of Japanese companies entering the world
1.2 New business model in China
1.3 Advance scheme through Hong Kong
2 Chapter Basic knowledge
3 Chapter Investment Environment
3.2 Province and region of China
3.5 Investment incentives and regulations
4 Chapter Economic Environment
5 Chapter Establishment
5.3 Establishment of business base
5.4 Procedure after incorporation
6 Chapter Withdraw
7 Chapter Foreign exchange
7.1 Foreign exchange management system in China
7.2 Foreign currency management system of ordinary items
7.3 Foreign exchange control system of capital items
7.4 Foreign exchange control system in bonded area · Hong Kong
7.5 Individual foreign currency control system
8 Chapter M&A
8.2 Laws and regulations concerning M & A
8.5 Challenges after corporate acquisition
9 Chapter Corporate Laws
10 Chapter Accounting
11 Chapter Tax law
11.2 Representative Office Taxation
11.4 Individual Issues in China Domestic Tax Law
12 Chapter International taxation strategy
12.1 International tax relating to entering China
12.2 International taxation strategy
12.3 Individual Issues in International Taxation
12.4 Tax issues related to withdrawal
13 Chapter Transfer Price Taxation
13.2 Individual provision pertaining to transfer pricing taxation
13.3 Transfer price taxation and documentation
13.4 Transfer price survey in China
14 Chapter Labor
14.4 Points to remember when bringing Japanese
15 Chapter International Human Resources Management
15.1 Human Resources Labor Management
15.3 Personnel evaluation system
-
-
-
System of Chinese accounting system
The chart below shows the regulatory system of accounting system in China.
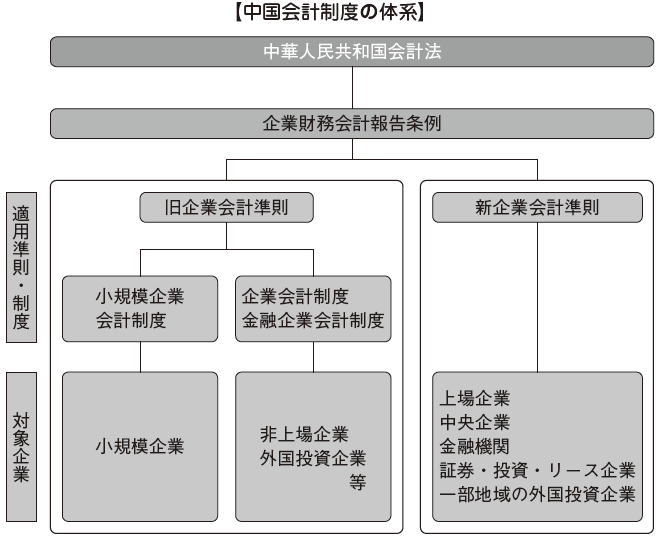
In China, under the accounting law of the People's Republic of China, there are Corporate Financial Accounting Reporting Ordinance and Business Accounting Standards. The corporate accounting rules include the old company accounting rules and the new corporate accounting rules issued in 2000. In addition, there are corporate accounting system, financial company accounting system, small business accounting system as subordinate system of old company accounting rules.
[PRC Accounting Act]The People's Republic of China Act (Accounting Act) is the provision that is the basis of Chinese business accounting. It was enacted to strengthen accounting and tax management system, to achieve growth of economy, maintenance of order of market, prescribing basic matters such as accounting act and accounting processing mainly.Following the enactment of this law in 1985, revision was made in 1993 and 1999 in order to adapt to the market-oriented economy from the conventional socialist economy with the market economy of China.
In the accounting law, attention must be paid to the following provisions.
· The accounting period is January 1 to December 31 each year (Article 11) Unlike Japan, the accounting period can not be specified· Display money can be entered with one type of foreign currency amount only when RMB (12th) booking is entered (except for the RMB accounting report)· In principle, display language is Chinese (22 articles) However, foreign investment enterprises can use other languages (limited to one type) in combination· Internal control and statutory audit are required for certain businesses (Articles 27, 31, 37)
[Corporate Financial Accounting Reporting Ordinance]Along with the amendment of the accounting law in 1999, the State Council of State issued financial reporting regulations as a financial reporting standard in 2000 and has been enacted since 2001.
[Old Corporate Accounting Rules]Corporate accounting rules and corporate finance notification were regulated from 1993 to 1999, and regulations concerning accounting processing and financial management were developed. Along with the development of the capital market, accounting was also stipulated to be compatible with it. Chinese accounting standards are also referred to as Chinese Accounting Standards (CAS). Currently there are old CAS and new CAS. The former corporate accounting rule (former CAS) consists of basic accounting rules and concrete accounting rules. In the basic accounting rules, matters that form the basis of the preparation and reporting of financial statements are specified, and specific accounting rules provide matters concerning individual accounting processing based on the basic accounting rules.
[Corporate accounting system]In December 2000, the Ministry of Finance issued a corporate accounting system as a comprehensive provision for concrete accounting in order to respond to the revisions and promulgation of the Accounting Law and the Corporate Financial Accounting Reporting Ordinance. This corporate accounting system is created based on International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) against the background of China's international development. Financial corporate accounting system is an accounting system created for financial companies, and small business accounting system is accounting system created for small companies (micro and small companies).Initially, this corporate accounting system was applied only to Kabushiki Kaisha, but it was also applied to foreign-invested enterprises including Japanese companies in 2001, newly established companies in 2002 and some state-owned enterprises.
[New Corporate Accounting Rules]In February 2006, the New Finance Ministry of China issued a new corporate accounting rule (New CAS). The new CAS consists of business accounting rules and basic accounting rules and concrete accounting rules (No. 1 to No. 38). In establishing the new CAS, we will promote convergence (convergence) to IFRS and aim to raise the international status of China. The reason why China adopted convergence instead of IFRS 's adoption (direct adoption) is considered to be not only economic burden, but also economic and regulatory system specific to China.The Ministry of Finance of China says that the accounting standards of their country are to be done based on their own economic and legal regulations etc. Furthermore, convergence of accounting standards to IFRS will have mutual impact on IFRS and its accounting standards.This new CAS has obtained EU equality evaluation (EU equivalence evaluation of accounting standard) in April 2012.

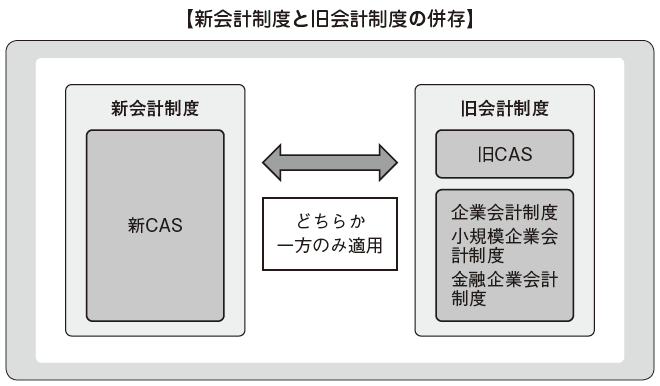 It is important to note that both standards are not applied at the same time.
It is important to note that both standards are not applied at the same time. -
Accounting period
The accounting period of China is a calendar year, it is decided from January 1 to December 31 every year (Article 11 of the accounting law). The deadline for submitting each financial report is as follows.
[Monthly report, quarterly report]In China, monthly reports (monthly balance sheet, profit and loss statement) must be submitted to the tax office within 15 days from the end of the month. Also, after the end of the quarter, submitting the quarterly report and temporary tax payment are required on the 15th day of the following month.Within 45 days after the end of the fiscal year, you will submit a settlement statement and tax return form, which will be the flow of tax payment. After paying taxes, it is necessary to review the tax after receiving the audit of the accounting office.
[Year Financial Statements]The deadline for submission of annual financial statements is as follows: Foreign investment companies' tax returns (address: tax bureaus) are from May to 31 May, joint annual examinations (Address: Industry and Commerce Administration Bureau, Ministry of Commerce, Ministry of Finance, tax bureau, statistics Station, Foreign Exchange Administration Bureau) is stipulated from March 1 to June 30. -
Disclosure system
■ Disclosure based on accounting law Under Chinese accounting law, foreign invested enterprises are obliged to prepare and disclose financial statements and audit reports for all related organizations (Industrial and Commercial Administration Bureaus, Foreign Exchange Administration Bureaus, Tax Bureau, etc.) . Financial statements refer to the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and attached schedule, which are different from those stipulated in the Japanese Corporate Law.
As shown in the table above, China is obliged to prepare and submit cash flow statements to all foreign investment companies. In the attached detailed schedule, it is obligated to attach asset valuation loss reserve detailed schedule, shareholder's equity change fluctuation chart, accrued surplus tax schedule, profit appropriation statement, segment report (listed companies only). Since the financial statements must be submitted separately to the financial authorities of the city, the Ministry, etc., and the format differs for each city and province, it is necessary to confirm whether the form of the financial statements actually submitted before starting the business is correct need to do it. Documents necessary for submission on a monthly basis and submission by year are as follows.

■ Disclosure prescribed by securities law etc.Disclosure system in foreign invested enterprises is regulated by accounting law which is general law. In addition to this, Foreign Investment Corporation needs to comply with relevant provisions of the Securities Regulatory Commission and minimum capital stock ratio and listing review provisions. These provisions are enacted under the Securities Act and the Law of China law in China. The Securities Act is equivalent to the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act in Japan, and companies that publish and issue securities (shares) need to perform listing procedures accordingly.
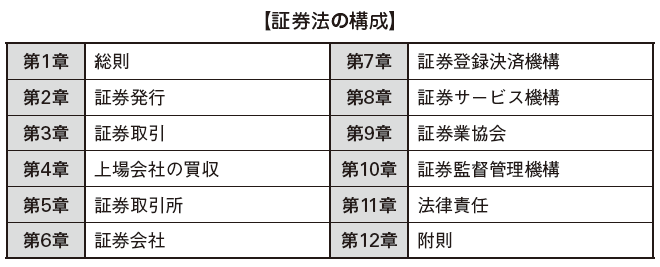
Based on the Securities Law, the Securities Regulatory Committee establishes detailed relevant provisions in the listing of documents to be submitted. Since these provisions have been revised frequently in recent years, renewal of information has become an obstacle in listing.
[Submission of Disclosure Documents]From January 1, 2002, listed companies are obliged to disclose annual, semi-annual and quarterly report based on corporate accounting standards and related communication rules. For the listed stock exchange, the fiscal year is within four months from the end of December, the half yearly report is within two months from the end of June, the quarter is over at the end of March and within one month from the end of September, respectively, the Securities Regulatory Authority and Securities Transactions It is necessary to submit and public notice to the place. In addition, although the annual report needs to be audited by an accounting practitioner (certified public accountant in China), in the case of the semiannual report (interim report), only in certain cases audit by the accountant accounting personnel is required (See P.450 "Audit of listed companies"). Certain cases are as follows.
· The opinion of the audit in the last three years is not an unqualified opinion and when applying for or implementing stock dividends or new shares in the second half· In the first half of the year, if you plan to pay dividends, capital stock of capital reserves, or compensate for deficits and implement it in the second half
[Submission of temporary report]Regarding listed companies, in the event of a serious event that may cause a significant impact on stock prices, submit a temporary report to the Securities Regulatory Commission and listed stock exchanges and publish it There is no doubt. Examples of serious reasons are as follows.
· Significant changes in corporate management policy and scope of management· Decisions on significant investment activities and important property purchases by companies· A serious loss or damage occurred to a company· The occurrence of relatively large changes in the shareholding or corporate control situation of shareholders or substantial rulers holding 5% or more of the company's shares· Decision of company's capital reduction, merger, division, dissolution and bankruptcy motion
[Submission of Consolidated Financial Statements]Similar to Japan, companies that meet certain requirements need to prepare consolidated financial statements including financial statements of subsidiaries and affiliates, as follows.
· Companies that authorized the management of state by the state-owned state administration· Listed company· Foreign trade companies· Other companies that need to submit consolidated financial statements to the outside
Materials to be prepared include consolidated balance sheet, consolidated income statement, consolidated cash flow statement, consolidated appropriation of disposal statement.
■ Revision of related laws and regulations in recent yearsOn March 29, 2010, the Securities Regulatory Commission adopted the Information Disclosure Regulation No. 20"Emerging Markets (Founded Version) Listed Company Quarterly Report Contents and Format" was promulgated. Disclosure details and changes added to the regulations before revision are as follows.
· Disclosure of change factor analysis information and future planning information of profit etc.· Analysis and disclosure of risk factors after revision· Simplified disclosure method
The purpose of the revision is mainly to improve the satisfaction level of investor needs and to reduce disclosure costs. Even in future revisions, the Chinese government will maintain its direction.In recent years, when a foreign investment enterprise applies for listing, it is necessary to establish a foreign investment corporation. Regarding the form of establishment, it is permitted to set up the establishment (how the incorporators undertake all of the established shares) and recruitment establishment (a method for the incorporators to underwrite a part of the incorporated shares and publicly invite the remaining share) It is also possible to establish by application from or transfer of shares. -
Systems related to listed companies
■ Public company information disclosure control valve methodPublic company information disclosure control law was promulgated in 2007. The configuration is as follows.
According to this provision, we have to make periodic reports (including annual reports, interim reports, quarterly reports) as information disclosure obligations of listed companies. The content of the periodic report includes the company's financial accounting report and the financial accounting report must be audited by an accounting firm qualified to engage in business related to securities and futures transactions. In the event of serious fluctuations in the financial situation of the company, we must disclose information in a temporary report.
■ Market typeThere are two stock exchanges in China, Shanghai and Shenzhen, which is characterized by one stock never being traded on two exchanges at the same time. A listed company can distribute two kinds of shares on one exchange. This stock is classified as A shares and B shares, and their roles are as follows.
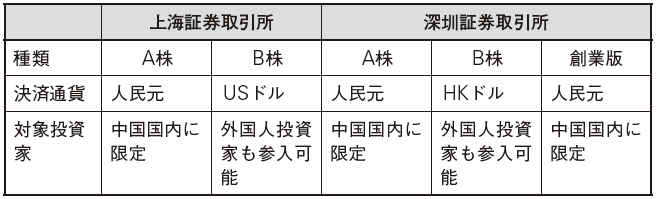
In this way, the types of shares are classified, but as for A shares that are limited to China, there are 1,001 types of Shanghai Stock Exchange and 1,578 types of Shenzhen Stock Exchange, whereas foreign investors also enter There are only 53 types of B shares available on the Shanghai Stock Exchange and 51 on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (the same as at April 2014). In recent years, in addition to international demand, the view that the integration of A shares and B shares or B shares will be abolished from the reduction of the volume of B shares is strengthening.The foundation version is the stock market made for emerging companies. It is set lower than the listing standard of A shares and B shares. For example, of the listing standards for A shares and B shares, the surplus in the last three years is the listing requirement, but the necessary requirement is the surplus in the last two years.
Listing standards of foreign companiesListing standards for A shares in Chinese companies are mainly seeking compliance with related laws and regulations such as the Securities Act of China, Listed Public Offering Publicly Issued Listing Regulation Law and Stock Listing Regulations. In addition to this, foreign companies must meet the following requirements.
· Foreign investment enterprises scheduled to listen to change to foreign investment corporation in advance· Annual review for three years before application for listing· More than half of the five founding people are Chinese· The share of foreign capital after listing is not less than 10%· If the shares owned by foreign investors after listing are less than 25% of the total shares, they must return a certificate of approval by a foreign invested enterprise
■ Listing of foreign companies to ChinaForeign companies listed A shares are mainly Taiwanese companies.There are not a few Japanese companies aiming to list A shares, but in some cases it can not be realized for the following reasons.
· The localization of Japanese companies could not be made smoothly· A joint venture between Japanese companies and Chinese companies failed
Although it is a reality that there are many difficult points in terms of management strategy for an equal joint venture, it can be said to be an indispensable factor in comparison with successful cases.
■ Delisting criteria Although the delisting standards of the stock exchanges in Japan are primarily concerned with stocks (volume, market capitalization, trading stocks, shareholders, etc) and matters relating to debts, etc., more rigid provisions for China than in Japan Yes. According to the new delisting provisions of the Shanghai Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Securities Exchange announced on June 28, 2012, in addition to the delisting provision equivalent to Japan, the operating income fell below 10 million Yuan for the second consecutive year In case of listing provisional suspension, in the case of third consecutive year it is delisting. -
Accounting book
■ Preservation of books The Accounting Law requires that records and records of the financial condition and business performance of one accounting period be recorded in a certain format. The retention period of each accounting document is as follows.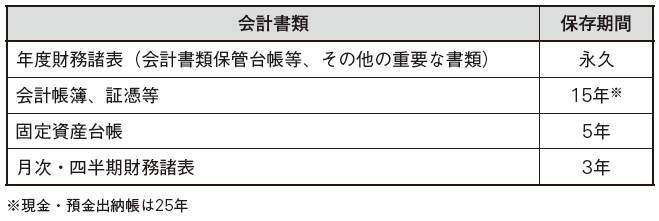
■ The creation of books based on the accounting law, the Auditing and Accounting Law stipulates its methods, etc. concerning the preparation of books of accounts. Certain accounting personnel are required certain requirements.
[Matters concerning control, inspection and supervision, etc.]In order to prevent errors and fraud of accounting books, it is necessary for the internal control to be effective and functioning effectively (Article 27 of the Accounting Law). Accountant and dispenser are forbidden to concurrently hold work other than accounting such as checking and managing accounting data (Article 37 of the same law). Therefore, in principle, it is necessary for the company to have two accounting managers (accounting staff, accounts payors) who perform accounting related business.In the case of a company whose personnel is not well established, it is possible to outsource general accounting, but since cash management and deposit management must be done in-house, one teller is required at the very least. If accounting managers can not come to work due to sudden illness etc., the problem is that accounting can not be done. Those who do not qualify for accounting in China can not process accounting in China. It is necessary to obtain accounting work qualifications for those other than the current accounting staff in advance. Also, because it is also possible to ask the accounting office for substitute assistance, small businesses or companies that have just founded them often request accounting services from outside accounting firms.Bank procedures can not be done if accounting tellers can not come to the office. In cash withdrawal from banks in China, the person who registered in the bank in advance must have an identification card. If only the accounts payor is registered as a person in charge at the bank, it is impossible to withdraw cash from the bank, so it is important to register in advance those who are not accountants.
Under the accounting law, certain entities are obliged to undergo statutory audits (Article 63, 165 of the Companies Act). As government inspection items, in addition to the state of the accounting data, the accuracy of the contents, etc., inspection of requirements of accounting personnel and other necessary items related to accounting are cited, and inspections are carried out each time. In spite of such statutory audit, if illegal acts or the like are discovered, it is stipulated that the entity and the individual have a charge of accusation, and the government must strictly observe the charges of the whistleblower and accusation contents.
[Penalty for illegal acts etc]Penalties due to illegal acts are classified as follows according to the contents and acting parties (Accounting Laws 42 to 45).
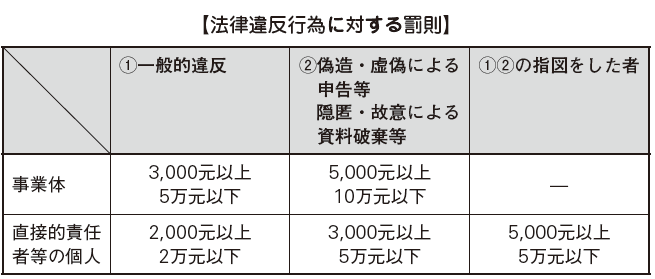
-
Voting system
We adopt the voting system in China. The vote is issued by the seller at the time of conducting business activities such as commodity trading, provision of services, etc., which the buyer acquires. Not only will it become a transaction voucher of payment receipt but also it will be a tax evidence. Without formal vote in China, tax treatment can not be accepted. Purchasing of votes can only be done at the tax office. A company that has registered for taxation at the tax bureau acquires a voucher purchase manual, and will take the procedure to purchase the voucher accordingly. When purchasing votes, prepare necessary documents (voucher purchase application form, applicant's identification card, last voucher after use) and submit it to the tax office in advance. Votes will be issued in a few minutes.
For companies to receive votes, it is necessary to hire an accountant and follow ongoing training, but many companies respond by outsourcing to reduce costs and time. -
Accounting system
It is said that China's accounting system differs from city to city, and it is one obstacle to entering China. The reason is that the accounting system is fluctuating every year, there is a possibility that it may not correspond to the prescribed form in the same form as the previous time, there is the Ministry of Finance for each city and province, the form of financial statement There are circumstances such as differing etc etc. Also, in China, when using software for accounting tasks, it is necessary to notify the Finance Bureau of the jurisdiction. The government has officially designated an accounting system that can be used for financial reporting, and the following software manufacturers release software is adopted.
· INSPUR (Lushi)· KINGDEE (Kim Butterfly International)· NEWGRAND (New Chuo University)· SAP / UFIDA (friend)· ORACLE
Although some accounting software released by other manufacturers is also accepted, since books, accounting evidences, and financial statements are required to be created in Renminbi and Chinese, at a minimum they can respond to them (Article 12, Article 22 of the Accounting Act). -
Structure of financial report
Regarding account books, it is necessary to report financial reports on a certain period, such as annual or semi-annual period. The structure of the financial report, the method of making it, and other matters are stated in the Corporate Financial Accounting Report Ordinance. Financial reports are required to be reported for the fiscal year, semester, quarter and month. Also, the required documents will vary depending on the content to be reported. For the reported fiscal year, the semiannual financial statements require comparison data for two terms (Article 6, 7, 13 of the Corporate Financial Accounting Report Ordinance).
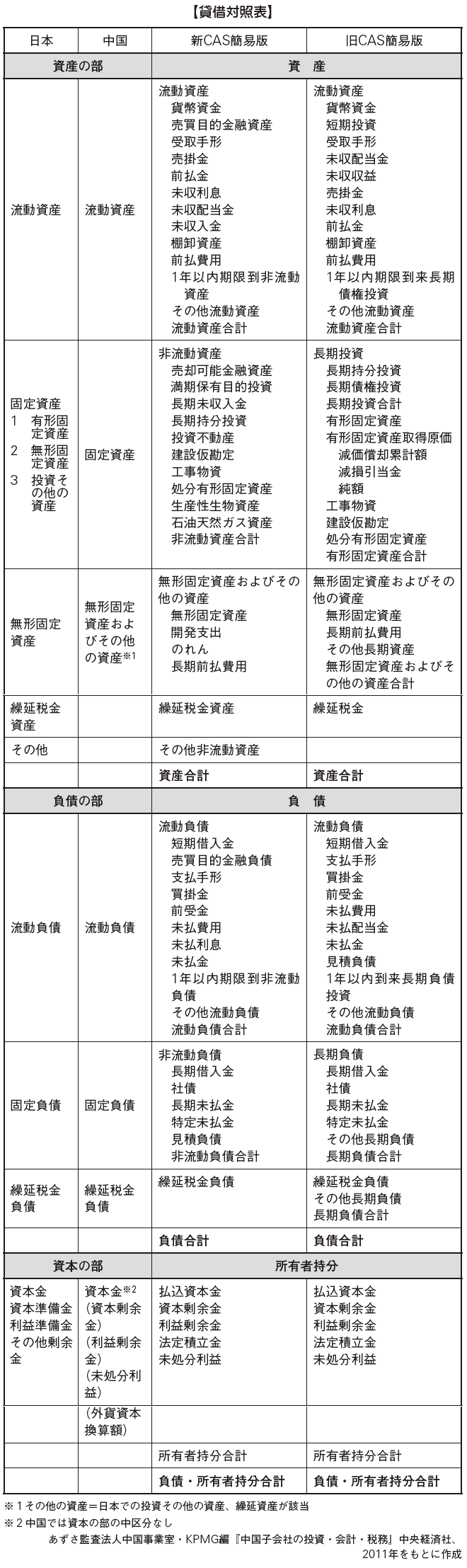
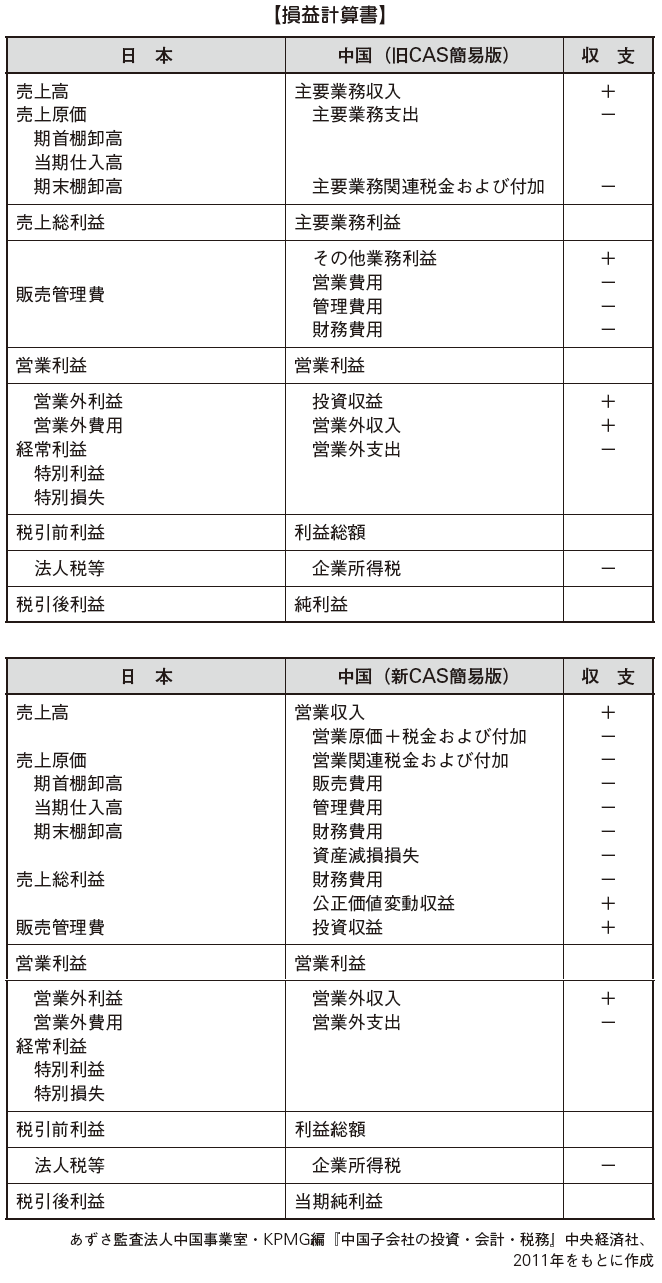
[Balance sheet]The balance sheet (asset and liability table) is a statement that shows the status of all assets, liabilities, and net assets at a certain point in time to clarify the financial condition of the company (Article 9 of the Corporate Financial Accounting Report Regulation). The style is almost the same as that of Japan, but the land of the ground (land use right) will be treated as intangible fixed asset, etc., partly.
[Profit and loss statement]The profit and loss statement (profit table) is a statement that shows all revenues and corresponding costs and profits / losses during one accounting period in order to clarify the business performance of the company (corporate financial accounting Reporting regulations Article 10).Those that correspond to gross profit in Japan are treated as main business income. Since non-operating income and non-operating expenses in China are part of extraordinary income and extraordinary loss, there are no items corresponding to ordinary income.
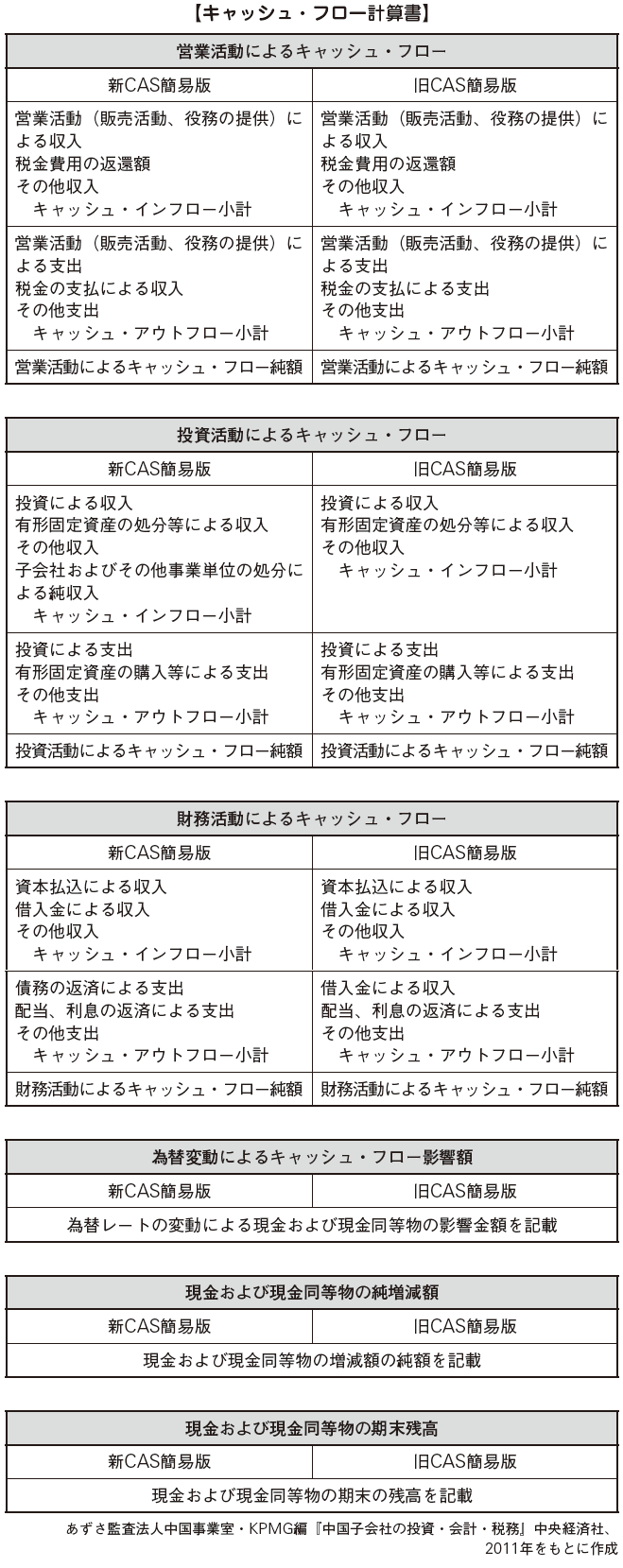
[Cash flow statement]Cash Flow Statement (Cash Flow Chart) refers to a statement that shows the status of cash flows in one accounting period by a certain activity category (Corporate Financial Accounting Reporting Ordinance 11).The cash flow statement should be categorized by activity category and must be listed by item. Although it is basically required to prepare by the direct method, the cash flow from operating activities requires an indirect notation (see former CAS Cash Flow Statement Article 24, 25, New CAS No. 8, Article 8, 16).
· Sales activities: sales activities, taxes, other transactions other than investment and financing activities· Investment activities: Purchase and construction of tangible fixed assets, other investment activities· Financing activities: Payment of capital, borrowing / repayment of funds, other financing activities
[Supplied schedule]The attached schedule refers to the statement prepared to complement the contents of the balance sheet, income statement and cash flow statement (Corporate Financial Accounting Report Ordinance 12).
· Profit appropriation statement· Other supplementary schedule (asset impairment loss etc.)
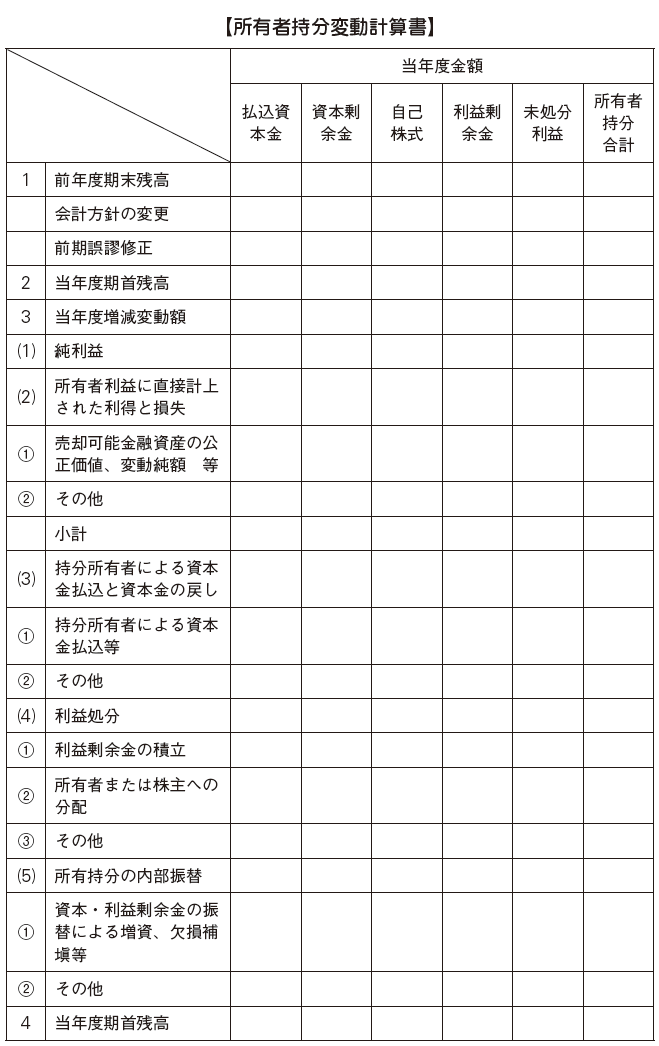
[Owner's Equity Interest Changes]Owner's equity change chart is the statement of changes in shareholders' equity, etc. in Japan, which is the statement of change in owner's share in the current period. Requests that the following items be stated in the new CAS 30 rule.
·Net income· Gains or losses directly recorded in owner's equity· Dividend and appropriation of appropriation· Increase / decrease of each owner's equity item
[Notes to Financial Statements]Notes on financial statements are statements that describe important accounting policies, estimates, and other items that require explanations to supplement the understanding of the contents of financial statements (Article 14 of the Corporate Financial Accounting Reporting Ordinance).It was positioned as a component of the financial statements from the new CAS and is a description containing the attached schedule of the old CAS. The notes on the company's situation (description of the company's outline, etc.), the notes of the financial statements (basic policy of preparation, accounting policy, estimate etc.) and dividend are stated.
· Matters concerning not meeting the basic premise of accounting treatment· Matters concerning important accounting policies, accounting estimates, changes thereof· Other matters (contingent and subsequent events, matters concerning related parties, merger / division etc)
[Financial situation manual]The Financial Status Description refers to a description that explains matters concerning the company's business situation, profits, funds etc. (Corporate Financial Accounting Report Ordinance Article 15).
· Basic matters concerning the management situation of the company· Matters concerning realization and disposal of profit· Others (funds, matters that have a significant influence on financial statements, etc.)
[Submission of report]Documents to be submitted vary by period.
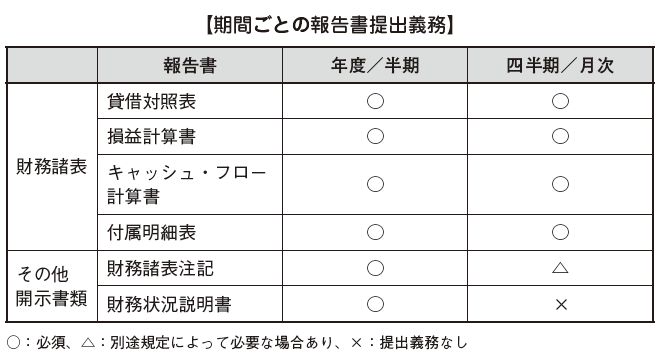
Changed from old CAS to new CAS, the following differences occurred.
· Owner equity change chart is a component of financial statements· Notes on financial statements are treated as components of financial statements in new CAS Included schedule is included in explanation of important items in note
-
-
-
中国のIFRSへの取組
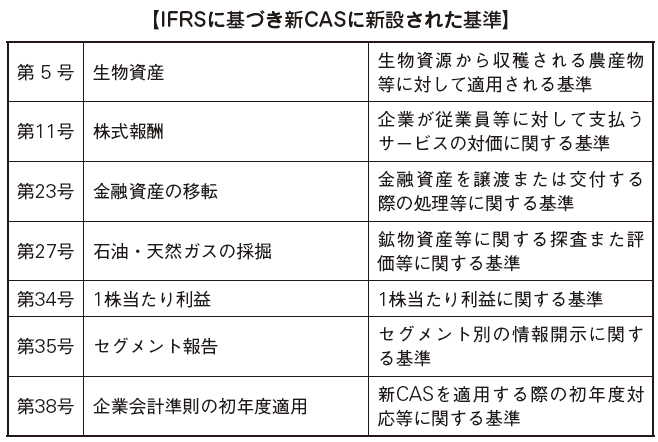
In China, we adopt a position to converge rather than adopt (directly adopt) IFRS. Reasons for convergence include the relationship between politics, economics, laws and regulations and the like peculiar to China, and the fact that it is practically difficult to adopt it directly from consideration of the burden of the economic community.The response to IFRS is progressing in order, and the new CAS also has a common section with IFRS. What we must be aware of is the difference between the new CAS and IFRS.Below are the same scores of new standards and new CAS and IFRS after the new CAS. -
Old CAS, New CAS and IFRS
Currently in China, the old CAS and the new CAS coexist. New CAS is forcibly applied to some regions and companies of more than a certain size, but many companies including foreign investment companies have adopted the old CAS. It is expected that each company will shift to a new CAS in the future.Companies applying the new CAS should understand the differences from IFRS and Japanese standards and make accurate modifications when consolidating accounting work. Although convergence to IFRS is progressing, there are over 100 items of differences when comparing the new CAS and IFRS.
-
Consolidated accounting system in China
In the corporate accounting system (promulgated in 2000), if there is a subsidiary that is considered to have substantial control even if the investment ratio is more than 50% or less than 50%, the parent company can prepare the consolidated financial statements of the entire corporate group It is compulsory. Regarding this substantial control judgment, we will consider potential shares such as convertible corporate bonds and warrants.Until now, companies that are compelled to prepare consolidated financial statements are limited to companies that have authorized the management of the state's state-owned assets management authority, some companies such as listed companies, and the necessity of creating foreign investment enterprises Was unclear and was interpreted as practically unnecessary. However, as the creation of consolidated financial statements was clarified in the new CAS, foreign investment companies need to prepare their consolidated financial statements when applying the new CAS.When preparing consolidated financial statements, procedures such as consolidation and elimination are required as in Japan. In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the following points.
[Settlement date and accounting period]The closing date and the accounting period of the consolidated financial statements must be the same for parents and subsidiaries. In case of mismatch, we will adjust and create it according to the closing date of the parent company (both parent company and subsidiary assumption in China). It is also necessary to be aware that there are no provisions equivalent to Japan's three - month rule.
[Accounting policy]The accounting policies of the consolidated financial statements need to be unified, and if they do not match, they are adjusted and created according to the closing date of the parent company (premise assumed in China both at the parent company and the subsidiary company). However, if importance is low, you can use it as it is without adjusting it.
[Individual financial statements]In the individual financial statements, the investment in subsidiaries of the former CAS is accounted for by the equity method, but the cost method is applied in the new CAS. Therefore, companies that newly apply the new CAS from the old CAS need attention.
-
-
-
Audit system
In China, companies are required to prepare financial statements at the end of each fiscal year and to have an audit of the accountant office / audit corporation according to the law (Article 165 of the Companies Act).Foreign investment enterprises must submit the annual financial statements to relevant organizations by attaching the audit report issued by the accounting accountant by April 30th from the settlement date (December 31). -
Audit system and internal control in China
■AccountantChina employs an accounting system that allows accounting practices only for persons with accounting qualifications (Article 38 of the Accounting Act). The accountant will do from booking to tax return. The qualification equivalent to a certified public accountant in Japan is an accountant accounting professional, qualified as an accounting practitioner. Accounting professional refers to the person in charge of financial accounting within the company.In order to conduct accounting work within the company as an accounting practitioner, it is necessary to pass the accounting qualification examination. After passing, you will receive certain continuing training in addition to registration registration. In 2013, the Accounting Employment Qualification Control Law was revised and enforced, and there were some changes such as continuing educational management of unit system and paperless of examination, but when accounting work is outsourced to accounting office etc, accounting qualification possession If it does not hire a person, it is amendment to the extent that it does not affect the practice.The level of the examination has three levels of elementary, intermediate, and advanced, and accounting professionals are classified into four groups: accounting professionals, accounting professionals, accounting consultants and accounting personnel. Accounting as an Accountant Employee qualifications can be acquired by passing the elementary level and then appointed as Assistant Accounting Professional by taking certain practices. The accounting professional is an intermediate examination passing examination, and the luxury accountant needs the government certification in addition to passing the luxury examination.If the company conducts accounting practices etc. to persons without accounting qualifications, a penalty of 3,000 to 50,000 RMB will be imposed and will be subject to administrative penalty.

■ Notebook Accounting professional system[Note Accounting Professor]Qualified people equivalent to certified public accountants in Japan are called accounting practitioners in China in China. In order to be an accounting professional, after passing the papers accounting master examination, it is necessary to apply to the papers Accounting Professional Association, receive continuous training and meet certain requirements of practical experience and more.Note When you select accounting professionals, it is often that you usually ask the local accountant office. Therefore, it is important to work closely with the local accountant office, the staff of the parent company, and the audit corporation of the parent company. It may be possible to unify the audit corporation of parents and subsidiaries according to circumstances.Notebook The Accounting Professional Association was established in 1988 as an accounting professor's industry organization. Note The Chinese government department responsible for the Accounting Professional Association is the Finance Bureau and the Ministry of Civil Affairs. The association is engaged in the establishment of professional ethics, the accounting master's examination and implementation of the continuous training system, the examination of registered accounting office, etc. as the main work.
[Notebook work of accountant]Note The main task of accounting professionals is divided into audit work and non-audit work.
Audit work (Notebook Accountant Law Article 14)· Audit corporate financial statements and submit audit reports (including clearing financial statements)· Verify company capital at company establishment and submit investment inspection report· Conduct audits on company merger, division, liquidation and submit related report· Conduct other audit work as stipulated in laws and other administrative regulations· Other reviews, etc. for consolidated accounting etc.
Non-audit work (Article 15 Accountant)· Accounting consulting service· Accounting entries and substitution for preparing tax returns· Asset valuation service (However, valuation of state-owned assets is carried out by a valuable note asset evaluator)
[Notes Tenure of Accounting Professional]Notebook The term of accounting is usually one year and reappointment is also possible. Election is based on a resolution of the General Meeting of Shareholders, but if you do not re-appoint or dismiss it, you must make a public notice to the relevant publications and notify the relevant agencies. In addition, it is also necessary to give notice to the Accountant beforehand and to give opportunities for excuses at the general shareholders meeting.
Audit by foreign invested enterprisesThe auditing system of foreign invested enterprises includes internal audits by internal corporate auditors and external audits by external accounting accounting professionals (investment audits and annual audits are conducted by external accounting ledger). Furthermore, since 2006 the new corporate law came into effect, it is obliged to establish auditor (equivalent to corporate auditor of Japan) and supervisory board (equivalent to the board of corporate auditors of Japan).
[Investment verification]For companies established by law in China, shareholders must receive investment inspections by the investment inspection organization after paying out the investment funds and receive investment inspection certificate (Article 29 of the Company Law). Foreign invested enterprises are obliged to verify investment at the investment stage (Article 29 of the Chugai Joint Venture Company Act Implementing Ordinance, Article 22 of the Chugai Business Collateral Corporate Law Implementation Law, Article 32 of the Foreign-owned Enterprise Law Implementing Regulations).Investment verification is a procedure to verify that both foreign and Chinese sides verify that foreign invested enterprises are surely making money, spot, etc. contribution. It is legally obligatory to obtain investment verification report from the accountant office in compliance with the law.In the case of capital investment, we receive investment verification within 60 days after investment and we will receive investment verification report within 10 days after verification is completed. The company holds the document and makes it evidence of investment. Careful attention is necessary because capital investment is also necessary when making capital increase etc. (Submission destination is Industrial and Commercial Administration Bureau, Foreign Exchange Administration Bureau, etc.).
[Yearly audit]Under the Companies Act of China, it is stipulated that the company must prepare financial statements at the end of the fiscal year and receive an audit of the accountant office according to the law (Article 165 of the Companies Act). Foreign invested enterprises are obliged to receive annual audits at the end of every fiscal year (Article 79 of the Chugai Joint Venture Company Act Implementing Ordinance, Article 46 of the Chugai Regional Cooperative Enterprise Law Implementing Law, Article 60 of the Foreign-owned Enterprise Law Implementing Regulations).There are accounting audits and foreign currency audits for fiscal year audits. Foreign invested enterprises must submit audit reports to the relevant financial institutions with annual financial statements attached to the fiscal year financial statements between April 30th and the end of the fiscal year (December 31st) (The submission destination is Industrial and Commercial Administration Department, Foreign Exchange Administration Bureau, Taxation Bureau, Total 6 Departments). Foreign invested enterprises will ask the accountant office to receive an audit report by the due date of the annual financial statements. In addition, we can also receive voluntary audits for consolidated accounting etc. of our parent company. For listed foreign-invested enterprises, it is obligatory to submit interim reports in addition to annual financial statements. However, with respect to the interim financial statements included in the interim report, it is unnecessary to audit the accounting auditor except for certain cases (see P.450 "Audit of listed companies").
Accounting auditThe accounting audit is to report the financial statements prepared by foreign independent investors in a voluntary independent third-party accounting book on the appropriateness of their financial statements based on relevant laws and regulations. An accounting audit report will be issued after the accounting audit.
Foreign currency auditForeign currency audit is an independent independent third-party accounting practitioner who reports on the foreign currency balance situation of the inspected company. A foreign currency audit report will be issued after the end of foreign currency audit.
■ joint annual inspectionJoint Annual Inspection (Union Yearly Opinion) is a joint inspection by foreign enterprises invested enterprises jointly by the Industry and Commerce Administration Bureau, Foreign Exchange Administration Department, Tax Bureau, Commerce Department, Finance Department and Customs etc.
The procedure of the joint annual inspection is as follows. The company receives the joint annual inspection report at the Industrial and Commercial Administration Bureau, fills in necessary items, attaches other necessary related documents, and sends them to each joint annual inspection participation department I will send it. Documents to be submitted vary by region. After that (after several weeks), the result will be notified from each joint inspection participation department after paying the annual inspection fee.In case of failure, the company must take corrective measures and improvement measures within the time limit specified by the government official. In addition to sanctions by law if appropriate response is not taken, business license may be canceled if the content is serious. Even if you pass, certain limitations will be added if you are certified as a Class B Company.In some areas, the introduction of the annual inspection by the Internet is being promoted and there are cases where it is not necessary to go directly to the government agency, so it is important to check the instructions of each local government before proceeding. The Joint Annual Inspection Report needs to be submitted to each relevant organization from March 1 to June 30 of the following fiscal year. However, if there is a legitimate reason, it is possible to extend the deadline for up to 30 days after obtaining the approval of the relevant agencies. Newly established companies will be participating from the following fiscal year.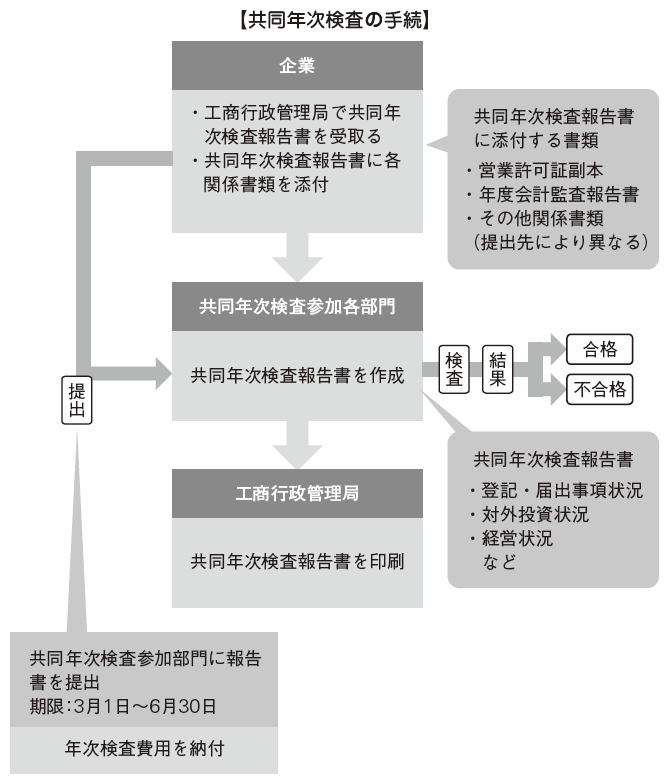
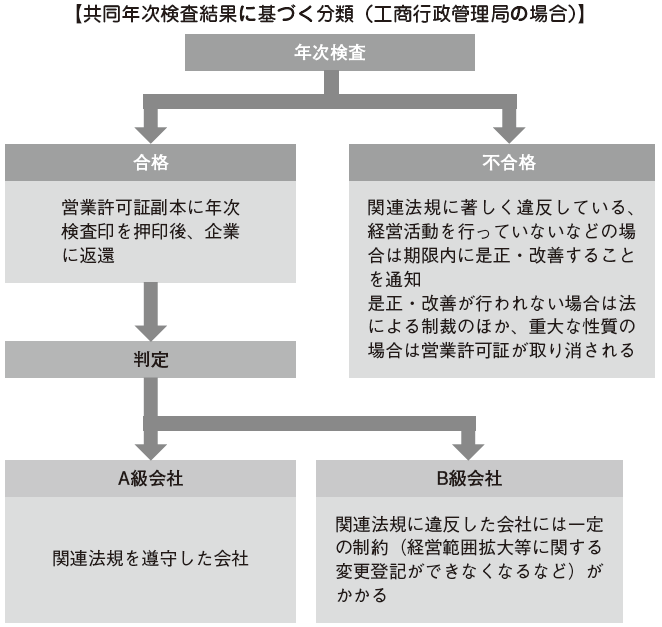
■ Audit of listed companies[Accounting audit] In addition to annual financial statements, listed companies are obliged to submit interim reports. However, with regard to the interim financial statements included in the interim report, no accounting auditor is required, except in the following specific cases.
· The audit opinion in the last three years was not an unqualified opinion (opinion of an accountant judged to be appropriate in all important points of the financial statements), and application or implementation of stock dividends or new shares was issued in the second half Case· In the interim period, dividends, capital stock of capital reserves or supplementary deficitIn the case of implementation in the second half
Listed companies are also supervised by the China Securities Regulatory Commission, in addition to the accounting auditor's note.
Submission scopeIn addition to preparation of individual balance sheet, income statement and cash flow statement, preparation of consolidated financial statements is required.
Submission DeadlineWhile the deadline for submission of annual financial statements is within four months from the end of the fiscal year, the deadline for submitting the interim financial statements is within two months from the end of the first half.
[Internal Control Audit]Internal control audit is implemented for listed companies, guaranteeing the truth and completeness of compliance of corporate management and management, asset preservation, financial reporting and related information, improvement of management efficiency and effectiveness, improvement of corporate development strategy We are aiming to realize (see page 454 "SOX Act of China").
■ Risk managementIt is important to consider various country-specific country risks in China when doing business in China. Specifically, there are uncertainties about the future of exchange rate fluctuations, relationships with joint venture partners, infringement of other intellectual property, boycottes due to anti-Japanese emotions, and lack of legal system.It is also important to consult with specialist consultants and legal experts on country risk, and it is also important to deal with companies withdrawing business due to lack of internal control of Chinese subsidiaries, It is necessary to pay attention to the current situation that there are many.Below, from the perspective of maintenance and operation of the internal control of the Chinese subsidiary, we will touch on risk management in doing business in China.
[Response to risk]Responding to risks can be divided into activities to avoid risk beforehand and correspondence after risk occurrence. In any case, it is necessary to work with the head office in cooperation with a Chinese subsidiary.
Activities to avoid risk in advanceIn order to avoid the occurrence of risk, we must have all stakeholders recognize our company's basic policy on risk response, not only to the management level of the company but also to the employee level. On the other hand, it is necessary to construct and maintain an internal control system for risk aversion. In addition, it is important to prepare manuals to ensure that the internal control system is operated, to periodically check whether they are properly operated and to establish them in companies.
Response after risk occurrenceIt is most important to solve not only the solution to the risks that occur but also the risk quickly. Especially for risks that can not be predicted beforehand, it is important to prepare for minimizing damage, such as maintaining an emergency contact network with the headquarters, not by only subsidiaries.
OtherIn Chinese subsidiaries, documents are usually created in Chinese. Therefore, when preparing a report to the parent company it is necessary to translate it into Japanese (or English). There is also a way to create the report itself from the beginning in Japanese (or English), but it is thought that it is desirable to create it in Chinese to promote the development and operation of the internal control by the local staff.Importance of Chinese subsidiaryIn conducting financial reporting by the parent company, depending on whether the subsidiary in China considers importance or not, the response to internal control assessment and maintenance will change.If a subsidiary in China is included within two-thirds of consolidated sales from the top of sales of each consolidated group company, the Chinese subsidiary is recognized as an important business base. In this case, in addition to enterprise-wide internal control, it is necessary to evaluate financial accounting reporting process, business process, general control over IT. Even if it does not correspond to an important business base, if it is judged that importance and risk (management, accounting, legal risk, etc.) exist in individual business processes, in addition to companywide internal control, settlement financial report Process and business processes may need to be evaluated. In this case, the points that the Chinese subsidiary should deal with are as follows.
· Clarify matters required by the parent company and clarify matters to be addressed by the Chinese subsidiary· Understand the internal status of internal control of subsidiaries, grasp the status of external audits, also grasp the status of external audits, and also grasp the subsequent countermeasures, etc.· Based on the above, devise plans for work required for subsidiaries
In addition, it is important not only to strengthen the coordination to cooperate with the parent company, to reconfirm and understand the policy of the parent company, but also to raise the importance of internal control to Chinese local staff.
■ Chinese SOX ActIn China, the internal control system has been expanded since the 1990s. Independent audit standards No. 9 was promulgated in 1996 and the basic concepts of internal control (organizational structure, procedure method, internal supervision) were clearly stated. Thereafter, provisions concerning internal controls were established under each related laws such as the Company Law, and from 2001 onwards, the Internal Accounting Control Code was published from the Finance Bureau one by one, and the basic framework of internal control has been established.However, following the publication of the Internal Accounting Control Code, due to frequent false accounting and misconduct at the securities market, in 2006, the Securities Regulatory Commission adopted the "Regulations on Issuance and Listing Management" On the other hand, the Shanghai Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Securities Exchange also announced the internal control guidelines of the listed company, and this rule came into effect in 2007.Furthermore, the Finance Bureau, the Securities Regulatory Commission, and other committees jointly strengthened provisions on internal control of the company, and the following efforts are made to contribute to the development of a fair securities market.
2006 Company Internal Control Committee established2008 Corporate Internal Control Basic Code promulgated (enforced in 2009)Prompted issuance guidelines for corporate internal control in 2010 (enforced in 2011)
The Chinese version SOX law refers to the company's internal control basic norms and the company internal control management guidelines.The internal company's internal control of the Chinese formed in this way was established based on the internal control framework of the American Treadway Committee Organizing Committee (COSO), similar to the US corporate reform method (SOX law) Therefore, it is called Chinese version SOX Act or C (China) -SOX.
The main norms concerning corporate internal control are as follows.
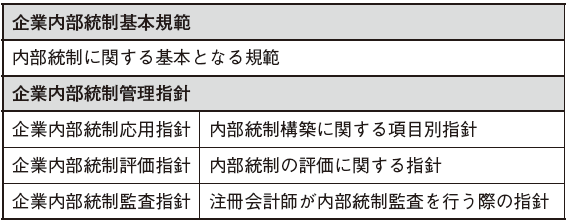
[Corporate Internal Control Basic Code]It describes the basic matters such as the definition and scope of internal control that companies should observe. It consists of all seven chapters of Article 50. Below, I will describe the contents of the internal control.
significanceInternal control is a process that is implemented by the company's Kaoru Kai, the board of directors, the senior management and all employees and aims to achieve the control objectives. Its objective is to strengthen and standardize corporate internal controls, enhance corporate management level and risk prevention capability, promote sustainable development of enterprises, protect socialist market economy and the interests of society masses It is in that.
rangeAlthough it is enforced for listed companies, it is also recommended to apply to large and medium size companies (it can also be applied to small companies). Internal control companies need to periodically evaluate the effectiveness of internal control in accordance with the situation of internal supervision and to prepare their reports.
Control targetWe aim to guarantee the truth and completeness of compliance of corporate management control, asset preservation, financial reporting and related information, improve management efficiency and effect, realize the company's development strategy.
Basic componentInternal environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, internal supervision.
Regarding whether or not to provide internal control audit work and consulting work at the same time, in Article 10 of the Basic Code of Internal Control for Internal Control,Accounting professional office providing salting service should not provide internal control audit services to the same company at the same time ". Since the internal control audit needs to maintain independence and consulting work may hinder its independence, simultaneous provision of both work is prohibited.
[Corporate Internal Control Management Guidelines]Corporate internal control management guidelines consist of corporate internal control application guidelines, corporate internal control evaluation guidelines, and corporate internal control audit guidelines. For each guideline, there are descriptions concerning the construction of items by internal control items, guidelines when internal organizations such as the Kura Kai or the like evaluate internal control of the company, and note on guidelines for accounting auditors to conduct internal control audits.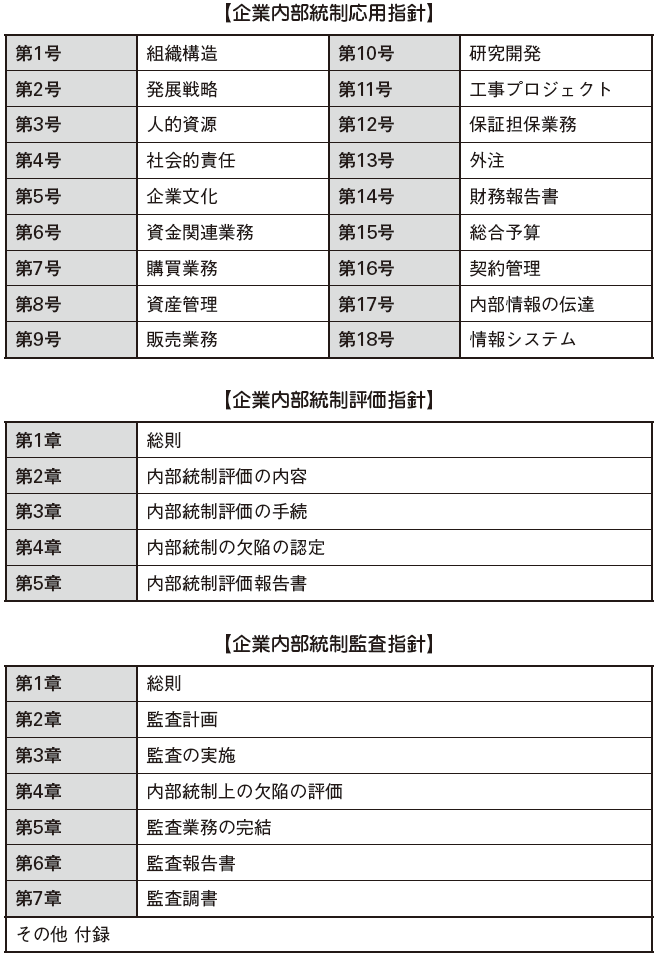
In addition, the following points are noteworthy regarding the corporate internal control management guidelines.
Standard date of internal control evaluation reportIt is necessary to submit December 31 as the base date within 4 months after the base date (Corporate Internal Control Evaluation Guideline Article 26).
Outsourcing of internal control evaluationA listed company in China needs to prepare a self-assessment report for fiscal year concerning the evaluation of the effectiveness of its internal control. However, regarding the effectiveness of the report, it is stated that evaluation can be entrusted to accounting professors and others. Also, it is prohibited accounting practitioner to audit the internal control to the same company (Article 14 of the internal control evaluation guidelines).
Note Integrated implementation of audits of financial statements and internal control audits by accounting professionalsEven in China, it is possible to carry out audits of financial statements and internal control audits as a unit from the viewpoint of the effectiveness and efficiency of audits. The point that it may be carried out alone is in contrast to the United States and Japan.
Audit method, objectNote Accountant's internal control audit is conducted by top-down approach, and direct opinions are expressed for internal control itself. The deficiency classification of internal control evaluation is divided into three stages of serious defects, important defects, general defects (Article 4 of the Internal Controls Evaluation Guidelines).
These features are based on the guidelines on internal corporate internal controls in China based on the US SOX Act, COSO report, etc., but the practical burden is large, the theory and practice are divergent Is the current situation.
-
-
-
Websites
[1] JETRO中国「ビジネス関連法」
[2] 上海茂木咨詢有限公司「業務案内」
[3] 中国監査コム「中国の会計制度」
[5] Y'sConsultingChina「中国ビジネスQ&A」
[7] 上海ビジネスフォーラム「中国と日本の会計相違点②発票制度」
[8] 福田崇男「ココが違う、中国のIT事情複雑な会計ルール、商習慣にも差」日経コンピュータ、2008年4月25日
[9] 伊藤久明「連載:IFRSとは何なのか(1)ここから始まる国際会計基準」IFRS国際会計基準フォーラム、2009年6月29日
[10] 黒田健二、萱野純子「中国ビジネス・ローの最新実務Q&A第31回中国の株式市場における問題(その1)」
[11] 萱野純子、山上祥吾「中国ビジネス・ロー最新実務Q&A第38回独資企業の実務(2)」
[12] 経済産業政策局企業会計室「企業会計制度をめぐる動向」2013年11月
[13] 高﨑博「中国ビジネスQ&A中国子会社を連結する際の留意点」2013年6月
[14] 税務会計情熱ねっ島 「中国の外商投資企業の決算・税務申告等手続スケジュール」2005年6月
[15] TMI総合法律事務所「TMI中国最新法令情報」2013年4月
[16] 森・濱田松本法律事務所「2005年10月27日証券法の大改正」2005年10月27日
[17] 毛衛兵「中国上場企業(製造業)における株式所有構造と株主価値との実証分析」2011年11月
[18] 王昱「中国における四半期報告の会計基準と開示例」2002年8月
[19] トムソンロイター「中国、外国企業の国内上場認可に向け作業=証券監督管理委」2010年1月14日
[20] 曲軍「中国証券市場の動向―外国企業の上場承認に向けて―」2011年7月
[21] 福澤広一朗、奥村豊、川上泰央、中村義明、溝淵友裕「中国に進出した日系中小企業の成長モデル~上場による資金問題解決策~」
[22] 高革慧「中国上場会社の情報開示:継続開示義務に関する規定」2007年3月15日
[23] 神宮健、李粹蓉「中国の企業会計・監査制度―新基準導入で企業情報開示の改善へ―」2007年
[24] EICネット「中国、上場企業に義務化する環境影響情報開示への指針につきパブリックコメントを募集」2010年9月14日
[25] 清河雅孝「中国における上場会社の不正な情報開示の民事責任(一)」2006年3月
[26] 齋藤尚登「中国:上場廃止プロセスの迅速化・透明化株式市場の健全化には株式発行制度の改善も不可欠」2012年7月2日
-
Babiliography
[1] 高部一郎監修、有限責任あずさ監査法人中国事業室・KPMG編『中国子会社の投資・会計・税務〈第2版〉』中央経済社、2014年
[2] 監査法人トーマツ編『中国の投資・会計・税務Q&A(第5版)』中央経済社、2013年[3] 近藤弘監修『中日対訳中国企業会計準則』中央経済社、2007年
[4] 近藤義雄『ポイント解説!中国会計・税務』千倉書房、2011年
[5] 近藤義雄『中国現地法人の企業会計制度日中対訳』日本国際貿易促進協会、2008年
[6] 近藤義雄『中国現地法人の企業会計制度解説』日本国際貿易促進協会、2002年
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya