China
4 Chapter Economic Environment
-
-
1 Chapter Introduction
1.1 The history of Japanese companies entering the world
1.2 New business model in China
1.3 Advance scheme through Hong Kong
2 Chapter Basic knowledge
3 Chapter Investment Environment
3.2 Province and region of China
3.5 Investment incentives and regulations
4 Chapter Economic Environment
5 Chapter Establishment
5.3 Establishment of business base
5.4 Procedure after incorporation
6 Chapter Withdraw
7 Chapter Foreign exchange
7.1 Foreign exchange management system in China
7.2 Foreign currency management system of ordinary items
7.3 Foreign exchange control system of capital items
7.4 Foreign exchange control system in bonded area · Hong Kong
7.5 Individual foreign currency control system
8 Chapter M&A
8.2 Laws and regulations concerning M & A
8.5 Challenges after corporate acquisition
9 Chapter Corporate Laws
10 Chapter Accounting
11 Chapter Tax law
11.2 Representative Office Taxation
11.4 Individual Issues in China Domestic Tax Law
12 Chapter International taxation strategy
12.1 International tax relating to entering China
12.2 International taxation strategy
12.3 Individual Issues in International Taxation
12.4 Tax issues related to withdrawal
13 Chapter Transfer Price Taxation
13.2 Individual provision pertaining to transfer pricing taxation
13.3 Transfer price taxation and documentation
13.4 Transfer price survey in China
14 Chapter Labor
14.4 Points to remember when bringing Japanese
15 Chapter International Human Resources Management
15.1 Human Resources Labor Management
15.3 Personnel evaluation system
-
-
-
Economic trend
China was once regarded as a country of BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa), but now it has grown to play a part in the center of the world economy.From the latter half of the 1970's, diplomatic reform and openness of the economy began to restore diplomatic relations with Japan, the United States, Europe and other countries, and in the 1990s it became a major exporting power to be said to be a "factory in the world" with its rich and inexpensive labor force as weapon. Entered the 21st century, joined the WTO in 2001, then held international events such as Beijing Olympic Games (2008) and Shanghai World Expo (2010). Meanwhile, we continued economic growth around 10% per annum and became one of the countries driving the world economy.
■ Changes in GDP and Economic Growth RateThere was also a period of slowing the economic growth rate due to the international financial crisis triggered by the Lehman shock, but China has maintained high economic growth while taking major economic stimulus measures over the past decade. In 2010, I surpassed Japan and became the second largest GDP world. GDP per capita has also increased significantly. However, there is a big gap in the richness of individuals compared with developed countries in Europe and the United States and Japan. In recent years, China has problems such as addressing international negative factors such as the European financial crisis and responding to domestic circumstances such as rich and poor and regional disparity, and from now on it has shifted from high growth to stable growth It is expected to go. In the 11th National People's Congress (NPC) held in March 2012, we set the target for real GDP growth rate to 7.5% in 2012. The policy of withdrawing from the conventional export-dependent high-speed growth model and a policy of evolving domestic demand and converting to a stable growth model that raised quality and efficiency were clearly stated and clear target values per capita GDP Was decided.
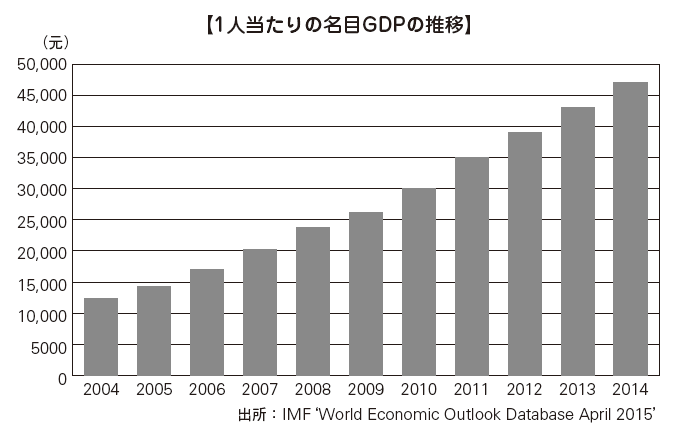
According to the IMF, the real economic growth rate in 2013 was 7.6%, exceeding the Goal Goal, but stopped 8% for the second consecutive year. This is due to the slump in exports to developed countries and the downturn in the economy due to the strengthening of regulations on fund procurement other than bank lending called Shadow Banking (shadow bank). Although the future outlook is difficult to reach, due to the evacuation of domestic demand through the infrastructure improvement, it is expected to remain solid.
Trends in National FinanceThe fiscal finance of China turned to profit once in 2007 as a result of a single fiscal year, but it made a large amount of fiscal expenditure for large-scale economic stimulus measures against the influence of the global financial crisis, and turned to deficit again. However, in terms of GDP, fiscal expenditure remains within 2%. In addition, the ratio of government bonds outstanding for deficits to GDP is generally within 30%, which is considered internationally healthy.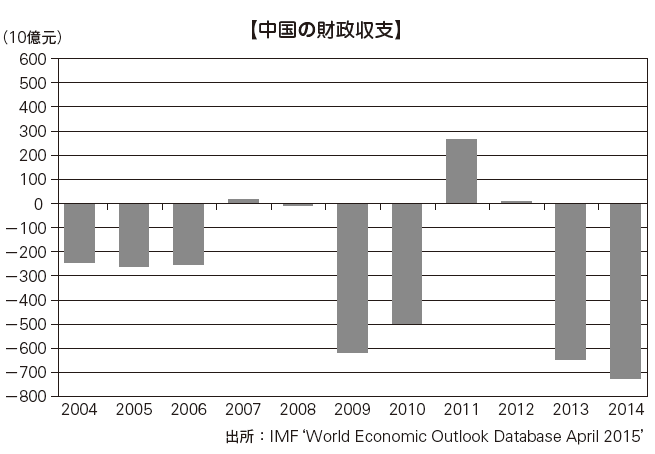
Since fiscal 2010, we are actively implementing fiscal measures, and we are continuing to compensate for the deficit by issuing government bonds within a sound scope. In the future, as we move from high-growth to stable growth, we have risks such as an increase in nonperforming loans accompanying a decline in real estate prices, a deterioration in the financial situation of weak local governments and a corresponding increase in fund procurement costs Although it is considered to be stable for the foreseeable future. It continues to be stable in 2014, with revenues up 8.6% from the previous year and expenditure by 8.2%.
■ Suppression of inflationChina has experienced more than 20% inflation in the 1980s and 1990s, but since the beginning of the 2000s it has been in a state of calm. The inflation rate is lower than other BRICS countries.
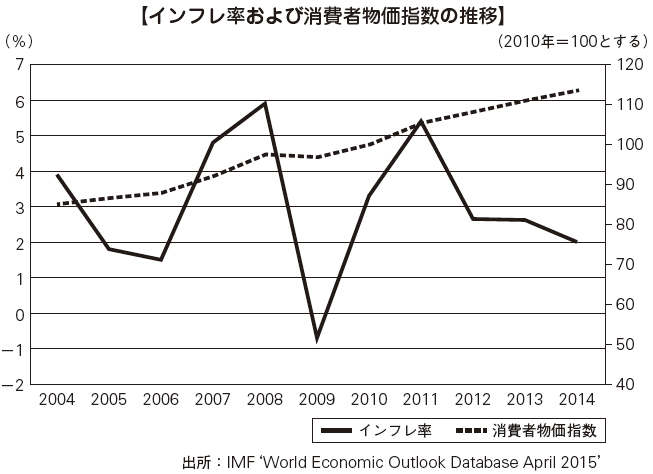
In 2007 and 2008, prices rose by about 5% against the background of high crude oil prices, but turned to negative in 2009. After that, real estate prices stopped high, food prices continued to rise. In order to maintain constant stable growth while maintaining price stability of foodstuffs directly linked to citizen's living while making a heated real estate bubble soft landing (suppress excessive economy and bring it to stable growth) The Chinese government in recent years has been forced to steer hard.The People's Bank of China announced that the official target value of consumer price increase rate in 2014 will be 3.5%, but it reaches the target value in real 2%, and stayed at less than 3%, almost the same level as in FY 2013 It was. The rate of increase after 2015 is still within 3% and it is stable. -
Trade
Since opening up to the external economy, the amount of trade in China continues to expand, continuing further growth in the 2000s, exporting to the total of 26,433.5 billion yuan in 2014. Trading accounts have been continuing to have a substantial surplus at all times because of the strong tendency that they have expanded by processing trade that imports raw materials, processes them, and exports them. Especially the export value from 2002 to 2007 after the WTO accession continued to grow by more than 20% in annual rate, becoming the world's largest exporter.However, due to the impact of the global financial crisis, both imports and exports declined in 2009. From 2010 to 2014, exports and imports both increased and the amount of trade turned to a recovery trend, but due to the European fiscal crisis and deteriorating relations between the Senkaku Islands and Yasukuni shrine visits, It is a trade under circumstances that are more anxious than before. The trade surplus declined consecutively in 2009, 2010 and 2011 but it picked up for the first time in three years in 2012. In 2014, it was about 382.4 billion dollars, an increase of about 47% over the previous year, and recorded a record high.The 12th Five-Year Plan, which was announced at the National People's Congress in 2011, balanced growth policy of the balance of consumption, investment and exports and domestic demand have is hammered out clearly, it has been taken over by the subsequent Xi Jinping, Li Keqiang system I will. In the future, trade in China will be required not only for quantitative expansion but also for qualitative improvement.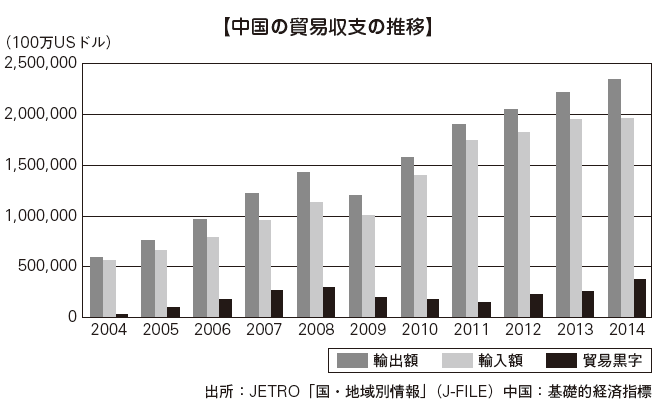
■ Exports by country / regionThe export value by country is the largest export destination of China in 2013 in Hong Kong is US $ 384.7 billion. Next, America is second with US $ 368.4 billion, Japan is third with USD 150.2 billion, Korea is fourth place with US $ 91 billion. Other countries such as Germany, the Netherlands, the UK and other EU countries are also among the top 10 export destinations. The export rate by region is the largest in Asia, including Hong Kong, Japan and South Korea, with 51.2% of total exports, 18.4% in Europe and 18% in North America. Traditionally, China's trading is characterized by importing raw materials and parts from neighboring Asian countries and processing trade in which products are exported to developed countries such as Europe and the United States and Japan. In recent years, export destinations are diversifying while leaving that trend.Exports in 2014 grew steadily, but it is lower than last year's growth rate. Regarding this, the Chinese Customs Administration pointed out that competitiveness due to low cost is being lost. Exports to Japan have been sluggish since the fall of 2012 due to the worsening of the Japan-China relations that originated in the Senkaku Islands issue and others. It is 5.1% lower than in the previous year in 2013, 1% lower than in the previous year in 2014.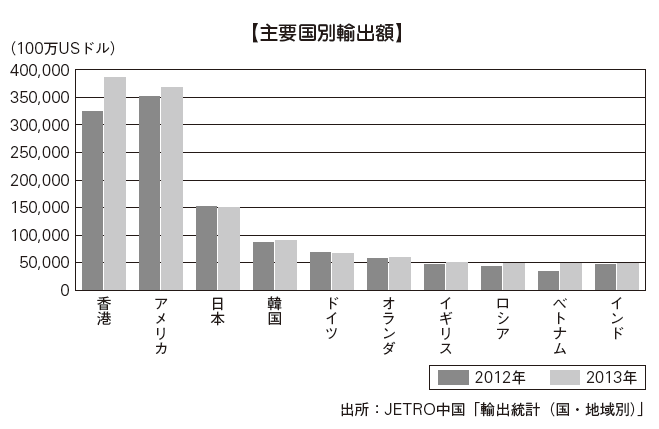
■ Import by country / regionBy country, the largest amount of imports in China in 2013 is US $ 183 billion in Korea, followed by Japan with US $ 162.2 billion, third place Taiwan, fourth place America. Imports of resources such as iron ore and petroleum are increasing, Brazil is ranked 8th, and Saudi Arabia, oil producing country, which is an iron ore producing country, is in ninth place.Looking at the import rate by region, imports from neighboring Asia are as many as 55.9%, Europe is 16.6% and North America is 9.1%. Next, Latin America is 6.5%, Africa 6%, Oceania 5.6%. Diversification of import destinations is proceeding to meet the demand of resources in China domestic industry.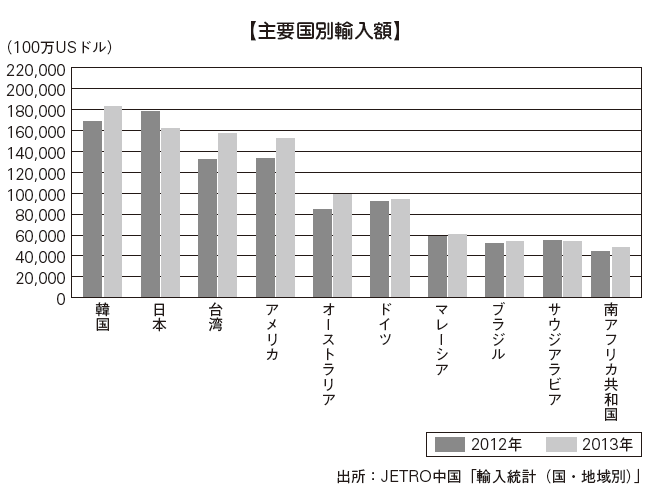
■ Export by Items Looking at the exports of China by item, the overwhelming majority of industrial products are 95.1%. Among them, high-tech products are US $ 601.2 billion, 29.3% of exports, 23.7% of electrical and electronic products, 18.3% of machinery and equipment, etc., and electrical and electronic equipment and machinery-related are occupied mostly.Fiber-related textile, textile products and clothing together totaled 254.8 billion US dollars, 12.3%, which is traditionally one of the major items of processing trade in China, but in the latter half of the 1990s machinery and electrical products were top It has reached the present.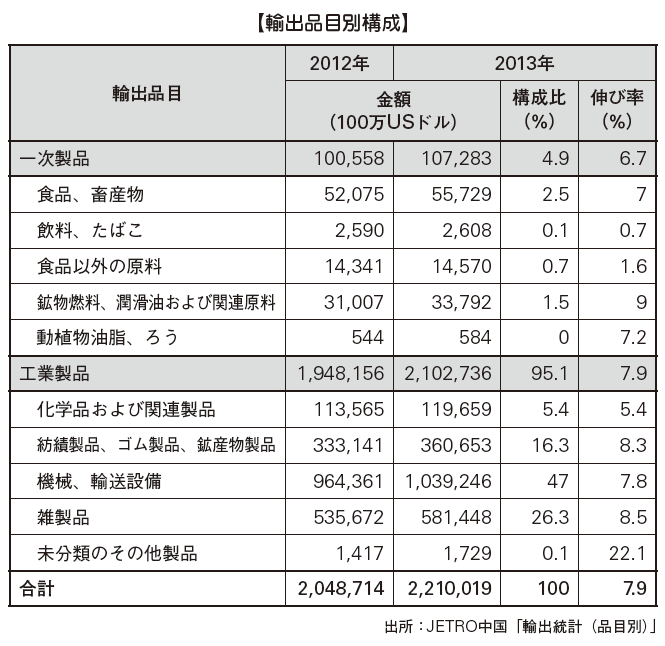
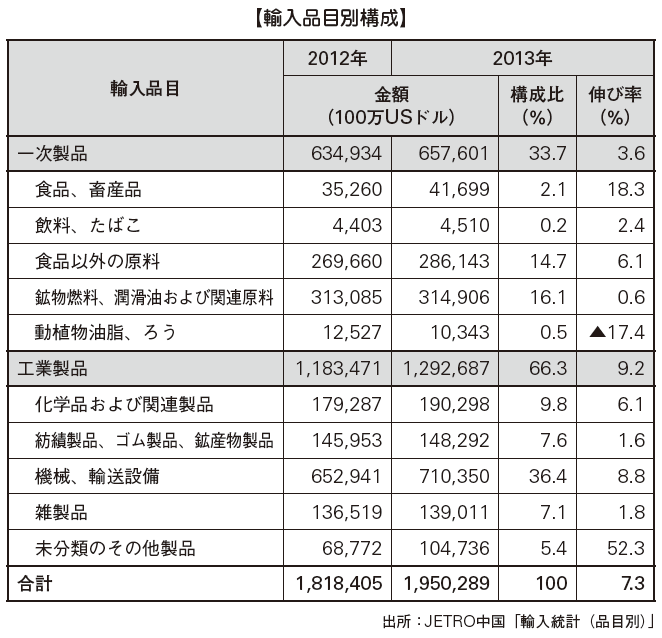
■ Imports by item By import item in China, primary products account for about 33.7% and industrial products account for 66.3%.Many industrial products are electric and electronic equipment, machinery, transportation equipment and so on. Mechanical and electrical products amounted to 7,823 US dollars, accounting for 43.0% of the total export, followed by high-tech products at US $ 506.7 billion at 27.8%.On the other hand, among primary products, imports of mineral fuel, crude oil, amounted to US $ 220.6 billion, accounting for 12.1% of total imports. In addition, we import a lot of metal resources such as iron ore and copper, securing resources is an important key to China's economic development.
-
Industry trends
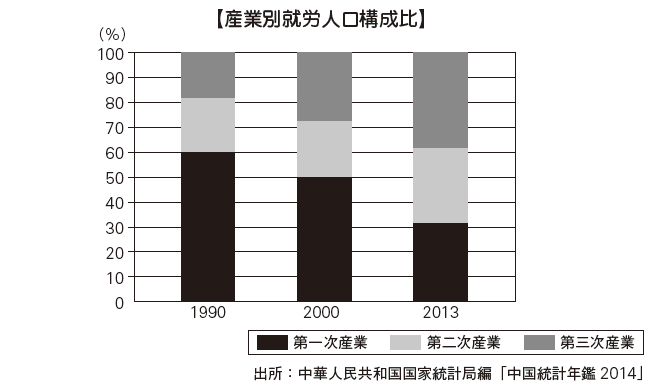
■ Industry Structure in China The industrial structure of China is undergoing a major change. Looking at changes in nominal GDP by industry and changes in composition ratio of working population by industry, the primary industries such as agriculture have drastically lowered both GDP and working population. Secondary industries such as industry maintain a high ratio of GDP of over 40%, and the working population ratio is rising. In the tertiary industry such as the commercial and service industries, both the GDP and the working population have dramatically increased their ratios. Although China has achieved economic growth due to the major changes in such industrial structure, it is also true that the strain caused by the influence is becoming obvious. In future, it is expected that the industrial structure will reach the turning point by carrying out policy change for domestic demand expansion and correction of disparities in rich and poor.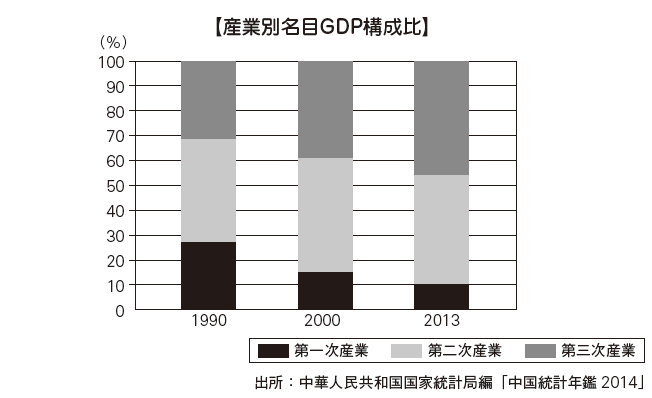
■ Manufacturing industry[Textile industry]Production of chemical fiber is about 41.21 million tons, 2/3 of world production, cotton production and consumption are the best in the world, and China is a major fiber country with an overwhelming international share (as of 2013). However, we are aiming for the transition from "fiber superpowers to fiber dominant countries" before, and we are switching from quantity to quality. The textile industry, which was traditionally representative of China's processing trade, is entering a major turning point. Although we traditionally sell inexpensive labor, we have boasted the world's largest export value for many years but the labor-intensive industries such as the labor-intensive industries such as the labor-intensive industries are seriously hit by shortage of labor and labor costs. There are many manufacturers in the coastal area, but the movement to seek new production bases in the inland areas where labor costs are relatively inexpensive and ASEAN countries is accelerating.[Automobile industry]China's automobile production volume has exceeded that of Germany in 2006, the United States in 2008, and Japan in 2009, becoming the world's largest. Production volume in 2014 is 23.72 million.One of the biggest factors is the dramatic growth in domestic demand in China, although the performance of advanced manufacturers was sluggish against the backdrop of the global financial crisis and the European financial crisis. In the early 2000s, the car was a luxury item that had been limitedly spread to a small number of high income groups. However, in the next few years the income level of the people as a whole increased sharply, and the purchasing power of the middle-income group increased and it became popular rapidly. With the production of many automobiles of less than 50,000 RMB, sales of low-priced automobiles are growing rapidly.China has become the world's leading automobile producer, but the Chinese automobile industry has many challenges. Productivity is only one-third of Japan's. There is also a problem that more than 100 small and medium-sized manufacturers of finished cars are mingling. Since China joined the World Trade Organization (WTO), in addition to the full-scale capital investment by global automakers, there is also a series of domestic emerging capital entry, and despite the expansion of the market, competition intensifies and the deficit Currently there are not many companies.Even though it became the world's largest automobile producer, global automobile manufacturers' worldwide evaluation of technology is low. As a result, manufacturers of Chinese capital actively acquire productivity and technological capabilities along with the acquisition of overseas manufacturers, and have achieved dramatic growth.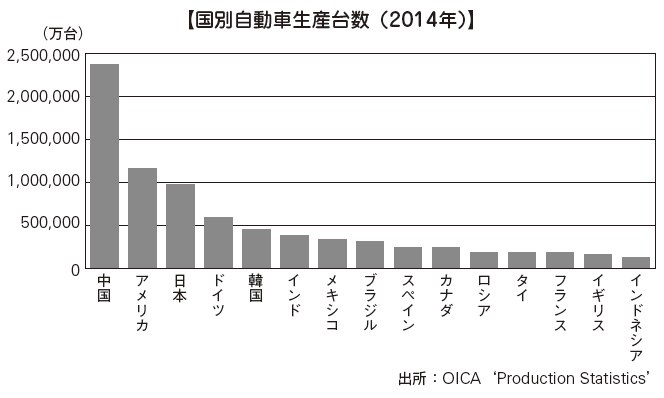
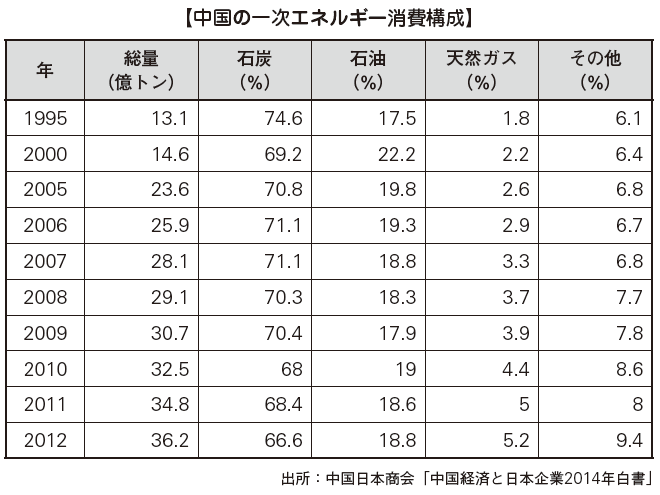
■ Mining and Energy[Coal, oil, natural gas]While China is a producer of fossil fuels, it is also a mass consumption country. For example, crude oil production in 2012 is 4.15 million barrels, which is fourth in the world after Saudi Arabia, Russia and the United States, consumption is also 122.2 million barrels which is huge, second only to the world and the world's second largest oil import It is a country. In addition, although coal production is the world's largest, export volume which was 100 million ton in 2003 decreased to 1/5, which is less than 20 million tons in 2010. This is because we prioritized the response to the sudden increase in domestic demand.According to the table below, China's primary energy consumption composition is mainly dependent on coal. In addition to establishing a stable energy supply system as the foundation of economic growth, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of coal with high CO2 emissions as a challenge for China in countering global warming. Therefore, the Chinese government has strengthened energy diplomacy to secure diversified routes such as oil and natural gas. China's oil and natural gas industry is trying to maintain international competitiveness by consistently implementing oil exploration and processing as a national strategy. As a result, it is largely concentrated in state-owned enterprises such as China Oil Natural Air Group Company and China Petrochemical Industry Group Ltd. which are big companies even from a global perspective.
[Rare metal]China has abundant reserves of nonferrous metals such as zinc and tin, and it is a country where mining is active. Particular attention is rare metals called rare metals. It is used in many products such as mobile phones, personal computers, liquid crystal televisions, hybrid cars, medical devices, solar panels and so on. For example, tungsten with hardness next to diamonds accounts for nearly 90% of world production, and many rare metals such as vanadium and molybdenum are the world's No. 1 in the world. In addition, China accounts for more than 90% of rare earths, which are said to be rare earths. In the midst of continuing global tightening of receipts, rare metal became a problem internationally as the Chinese government took measures such as export restrictions after 1999. Since rare metal production sites are not unevenly distributed compared to reserves, securing new resource transport routes has started in various countries. For Japan, which is the largest exporter of rare earth in China, it is a matter of life and death, so China's response in the future will draw attention.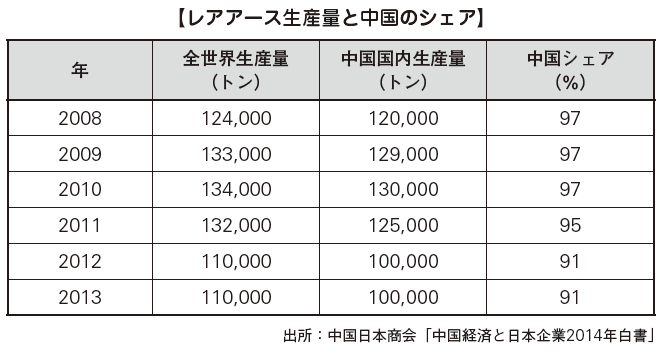
■ AgricultureInternationally, China is the most export industrialized country of secondary products, but in fact, primary industries such as agriculture, forestry and fishery occupy 33.7% (2013) of the employment ratio. Compared with many developed countries in Europe and the Americas, it is a country with a high percentage of working population in the agriculture, forestry and fishery industries.The graph below shows the output of major agricultural products in China converted to monetary value. Of the top ten, beef and poultry are second in the world production rank, but most other agricultural products are No. 1. A huge amount of agricultural products are produced, but many of them are consumed domestically in the largest population of China in the world.The Chinese economy has grown with inexpensive labor force against the backdrop of rural and urban disparities. In the future, we are developing policies to rectify nationwide domestic demand including rural areas and to correct the gap between urban and rural areas. In order to realize that, there are issues such as obtaining the international competitiveness of Chinese agricultural products by improving production efficiency and establishing safety. In 2010 the new food safety law was enforced. A step to get reliable domestic and overseas quality and safety of food at last has begun.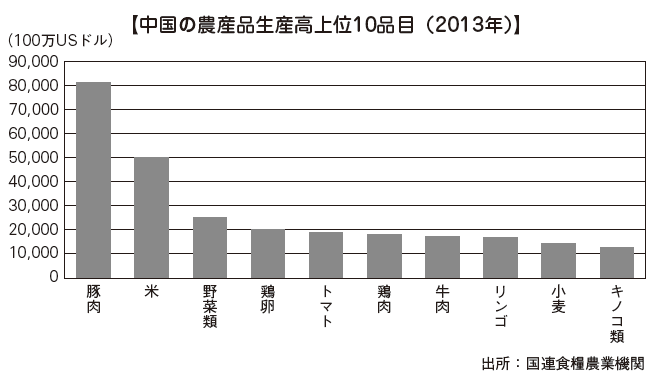
-
-
-
Websites
[1] 産業活動分析
[2] 趙晋平「2010 - 2030 年の中国産業構造の変化動向に対する分析と展望」
[4] 国際協力銀行(JBIC)「中国投資環境シリーズ 総論編」2013年8月
[5] 佐野淳也「貿易統計からみた中国の輸出構造の変化」アジア・マンスリー、2000年11月号
[6] 関辰一「中国自動車産業の現状と課題」アジア・マンスリー、2011年5月号
[8] 日本化学繊維協会「内外の化学繊維生産動向 2013年」2014年3月17日
[9] BP‘BP Statistical Review of World Energy
[11] 日本貿易振興機構(JETRO)
[12] 山下一仁「中国の農業・農村問題」独立行政法人産業経済研究所(RIETI)フェローコンテンツ(2006年1月6日)
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya