Singapore
10 Chapter Labor
-
-
1 Chapter Importance of Management by Regional Headquarters
1.1 Importance of Asian market
1.2 Regional management of the Asian market
1.3 Comparison of countries as headquarters
2 Chapter Regional Headquarters System and Utilization Examples
3 Chapter How to Utilize Regional Headquarters
3.1 Method of Consolidating Profit by Dividend and Making it as Reinvestment Base
3.2 Utilization as a Finance Company (Loan Function)
3.3 Example of Utilization of Efficiency by Consolidating Settlement Functions
3.4 Example of Reviewing Supply Chain Functions and Risks
4 Chapter How to Make Regional Headquarters
4.1 How to Set Up a Regional Headquarters
4.2 Singapore as a Business Base
4.3 Corporate Law in Singapore
5 Chapter Overseas Relocation of Head Office Functions
5.1 Head office relocation to low tax rate country
6 Chapter M&A
6.1 Trends in M & A in Singapore
6.2 Points to keep in mind when doing M & A
6.3 Laws and regulations concerning M & A
6.7 Investment regulatory environment of Singapore
7 Chapter Accounting
7.1 Accounting System in Singapore
7.2 Accounting Standard in Singapore
7.3 Disclosure System in Singapore
7.4 Accounting Audit in Singapore
8 Chapter Tax Risk of Regional Headquarters
8.1 Tax · Haven Countermeasure Tax System
8.2 Foreign Subsidiary Dividend Income Non-inclusion System
8.5 Taxation of Country of Residence and Double Taxation by Source Taxation
8.6 Tenuous Capital Tax System
9 Chapter Tax
9.2 Personal income tax in Singapore
9.3 Corporate income tax in Singapore
9.6 Singapore withholding system
9.7 International tax in Singapore
10 Chapter Labor
10.1 Work environment in Singapore
10.3 Social Security System in Singapore
10.4 Points to keep in bringing Japanese to Singapore
11 Chapter Q&A
-
-
-
Working Environment
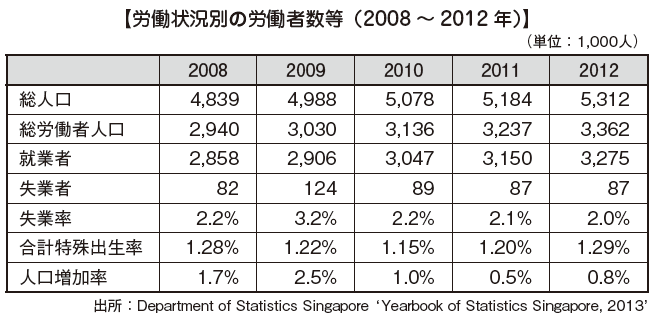
■ Working Population
The total population of Singapore as of 2014 is about 5,470,000 people, of which the labor force population (over 15 years old) is about 3.53 million and the employed workers is about 3.44 million.
The birthrate is very low, about 1.3 people. The population growth rate is also very low at 0.61%, especially the birthrate is low enough to be located at 189th of 194 countries in the ranking of World Health Statistics 2015 (World Health Statistics 2015). It is about 1.4 people and it is 179th place. With regard to the decreasing birthrate, the difficulty of this is to increase the labor force population.
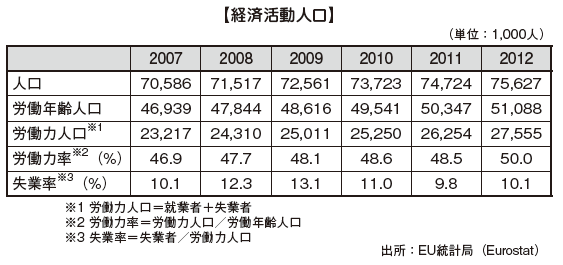
■ Working Population by Industry
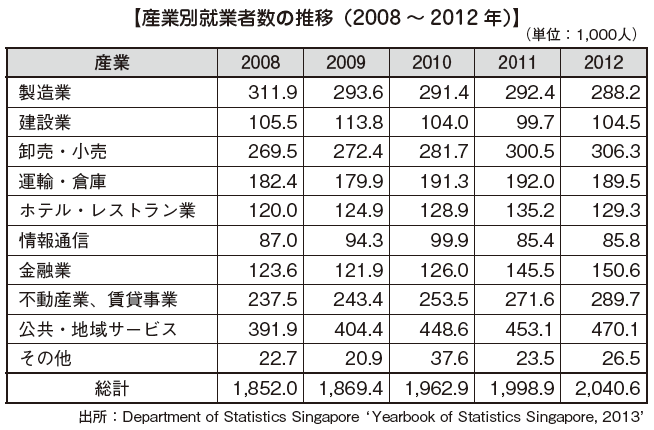
Looking at the employment structure of general workers by industry, the number of workers engaged in the service industry is the largest, and the total is 82%. Also, workers in the manufacturing industry are on a downward trend, but the service industry is on an upward trend.
■ Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate in Singapore has been on a downward trend since 2001 and has raised to 4.7%. After that, although it fell to 2.2% in 2008, the number of unemployed people increased mainly in the manufacturing industry from the misery of external demand due to the global economic downturn in 2009, again deteriorating to 3.2%. Despite of these circumstances, in recent years Singapore, the working population has been on an increasing trend, peaked at 3.2% in 2009, and it is decreasing again, and it has settled to 2.0% in 2014.
■Industry Wage
In Singapore, the minimum wage is not stipulated by law and wages. It is depending on the negotiations between employers and workers. Wages are determined primarily by job function and occupation and there are gaps due to academic qualifications, and skills.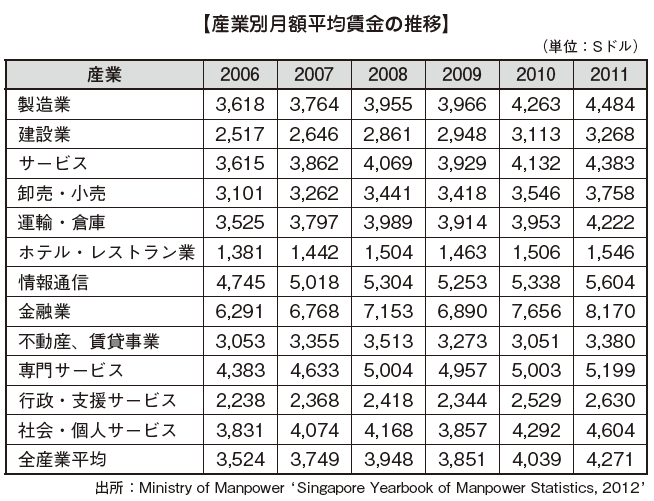
■ Comparison of Wages with Other Countries
The average wage in Singapore is higher than the other Asian countries. Looking at the wage changes, the nominal wage has been increasing the rate in 2000 and at high at 6.6%, but it has been decreased with the economic deterioration in 2001, and it became 0% in 2002. However, due to the subsequent economic recovery, the economy recovered to the 3% to 4% levels in 2004 and 5.9% in 2007. Due to the impact of the Lehman shock, there was also a scene of -0.4% in 2009, but it was 5.9% again in 2011, and it is steadily growing.
Labor market in Singapore is in demand. In changing jobs in Singapore is more in common than in Japan. The number of years in service of each employee is short due to the current situation of employment is that the job offers are not often relatively.
In conjunction with the recovery of the economy, the number of employed people continues to increase and the number of employed persons reached 2.86 million who increased by 8.6% from the same month of the previous year as of June 2008. However, due to the economic slowdown since the latter half of the same year is manufactured industry and recorded as significant decreased in particular. Also, as a result of the Asian economic crisis that began in 1997, the Singapore government faced a situation in which employment did not grew even if the Singapore economy was on a recovery trend, so the Singaporean government announced last September 2003 that Singapore employment training (SWDA: Singapore Workforce Development Agency) has been settled up, and they are planning and implementing vocational training policies while working closely with an industry.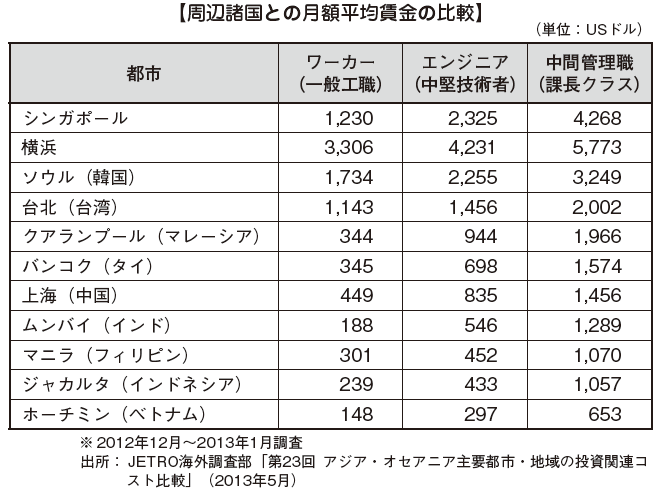
-
Labor Disputes with Labor Unions
■ Labor Union etc.
The labor union in Singapore has a very high social status. Workers have the right to freely organize trade unions and to engage in collective bargaining with employers. Unlike Japan, union shop system is not adopted. There are 66 registered union members in 2012, with about 610,000 members. These 66 unions are under the umbrella of the National Trades Union Congress (NTUC) in Singapore. In addition, there are three associations (Singapore Airlines Pilot Association, Singapore Transport Vessel Labor Union Association, Singapore Film Industry Association Association).
NTUC has a strong function as a cooperative and operates several supermarkets, insurance companies, travel agencies, taxi companies, etc. to improve the lives of their members. As a partner of the administration, they have established a position to actively cooperate in improving the productivity of companies necessary for economic development and it is extremely close to an administration.
■ Trade Union Law
The Labor Union Law is established for the purpose of maintaining labor-management relations between companies and workers as well in which they contributing to the corporate, Singapore economy, and improving the work conditions etc. Under the trade union law, registration methods and workers' rights are stipulated and labor unions shall register with the Registrar within one month of establishment.
In addition, according to the Labor Law, union members are generally accepted as plans for labor disputes and acts that relates to them. However, penalties shall be imposed on acts such as delivery of money within the union.
Details of the number of labor unions (members) and employer groups (members) in Singapore between 2008 and 2012 are as follows.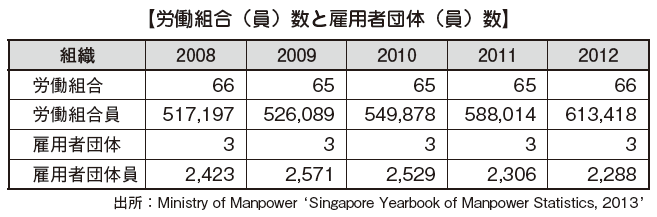
■Procedure for Resolving Labor Disputes
Labor and management disputes are left to arbitration by the Ministry of Labor. If the Labor and Management are unable to solve, they voluntarily solve it. If can no longer resolved, the Labor and Management shall pass through to the Labor Arbitration Court.
■ Conditions of Labor Disputes
There were 38 projects appended to the arbitral tribunal in 2003, but thereafter it decreased with the economic recovery, and in 2007 it was 16 projects. The reason strikes are rare in Singapore is probably due to the successful government regulation but the bigger factor is that since independence has continued to grow rapidly, labor conditions have improved year by yea. Therefore, the standard living of the employees has been improved as they say.
■ Points of Labor Dispute
There are many strikes when labor disputes were made. It is said that it shall be exercised by the majority of votes cast by the members secretively. However, the purpose of the strike is limited to the labor conditions of the partners and other things such as sympathy strikes and political strikes so these are illegal and prohibited. Therefore, the wage hike, service conditions, disbursement compensation, bonuses or rewards, incentives, and shift work duties etc. are the objects of the strike. Most labor disputes occurred in the manufacturing industry followed by finance, insurance and real estate.
However, since 1986 no strikes have found in Singapore. It is said that this peaceful labor-management relationship has greatly contributed to the Singaporean economy. -
Employment Practices and Labor Management
In Singapore, they do not often conduct entry tests for prospective graduates. Jobs will be held as appropriate through Conn, Agent, Newspaper Advertisement or in the Internet. It is common for recruiters to decide their acceptance or rejection only by regular job interviews with jobseekers. Also, there are no employment formalities or new recruitment training, and there are many things to start work from the start date of employment.
In Singapore, job hopping is in a normal state in terms of salary, work content, future potential, etc. For them it is usually to change job if there is a better opportunity. The recruiters and job seekers believes that job hopping is normal. They do not think negatively but they think it as an experience. The frequency of job is high when it is in demand and the rate of retention of the employees tends to increase when misery occurs.
■ Holidays
Holidays in Singapore are announced annually by the Department of Labor and companies shall be given a rest to the employees and they shall get paid. If the annual paid leave day acquired by the employee and if the holiday overlap, the company shall be given the employee a holiday on transfer.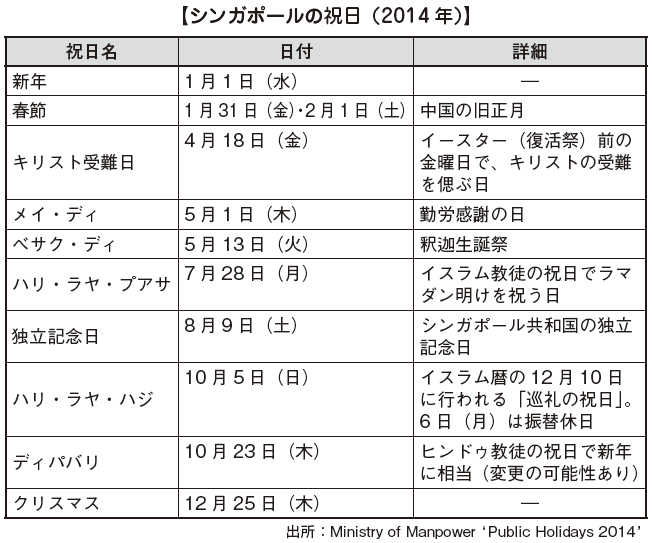 Please note that the premium wage rate when working a employee on a public holiday shall be doubled.
Please note that the premium wage rate when working a employee on a public holiday shall be doubled.■Benefits
For Japanese companies, there are many companies setting benefits not legally stipulated such as commuting allowance, housing allowance, and medical insurance etc. However, there are few cases where local companies set such allowances. If it is necessary to hire good people in the field, it is necessary to set wages and welfare benefits corresponding to that, so that they need to investigate other companies in advance and determine welfare benefits etc. at an appropriate level.
-
-
-
Latest News & Updates
【Changing various childcare leave in 2017】
On November 10, 2016, the revised bill of the Child Development Co-Savings Act was officially passed at the National Assembly of Singapore and from January 1, 2017 Maternity Leave (maternity leave) and Government-Paid Paternity Leave (father's childcare leave) From July 1st it was decided to change about Shared Parental Leave (distribution of maternity leave to male spouses). The changes will be described below.
[Maternity Leave]
It is for unmarried female employees that there is a direct impact on this change.
(Current system)
If you are a single woman and you meet the following conditions, you have been allowed 12 weeks of Maternity Leave (salary for 8 weeks is company burden, unpaid for the remaining 4 weeks).
· When the child is Singaporean nationality
· If you are working continuously for more than 3 months at your current company before your child is born
On the other hand, in addition to the above two conditions, 16 weeks of Maternity Leave (salary of 8 weeks is government burden, remaining 8 weeks company burden) is legal if legally married.
(Changes from January 1, 2017)
Even if you are not married, you will be granted a Maternity Leave of 16 weeks as well as legally married.
[Paternity Leave]
(Current system)
Current Paternity Leave allowed male employees who satisfied the following conditions for a week for Government-Paid Paternity Leave (GPPL), which the government bears a salary.
· When the child is Singaporean nationality
· When you are married legally with a mother of a child
· If you are working continuously for more than 3 months at your current company before your child is born
* The employer can extend and further allow one week's vacation.
(Changes from January 1, 2017)
The consent of the employer is unnecessary, and GPPL will be accepted for two weeks. The father's childcare leave acquisition rate is 38% in 2014 and 42% in 2015.
[Shared Parental Leave (childcare leave distribution to male spouses of maternity leave)]
(Current system)
The current Shared Parental Leave is to distribute a week to male employees who satisfy the following conditions out of 16 weekly maternity leave allowed for women.
· When the child is Singaporean nationality
· Child's mother has the right of Government-Paid Maternity Leave (GPML)
· When you are married legally with a mother of a child
(Changes from July 1, 2017)
Distribution for one week has been allowed until now, but up to four weeks will be accepted by this amendment.
[Other Adoption Leave (Adoption Leave)]
(Current system)
The current Adoption Leave allows a 4 week vacation that the government will bear the salary if the conditions are met.
(Changes from July 1, 2017)
After July 1, 2017, the 12-week Adoption Leave will be accepted, the government will bear the salary for the 8 weeks and the company will bear the remaining 4 weeks. However, in the case of adoptions adopted after the third adopted child, the government will bear all 12 weeks.
[Company response]
Since the start of KETs in 2016, employment law and CDCA changes are frequent. We need to grasp information on these law revisions and manage employees according to compliance.
First of all, it is necessary to change various regulations of the company to those conforming to these revisions. -
Employment Law in Singapore
In Singapore's employment law, general work conditions of workers are enacted, such as dismissing workers, paying salaries, clarifying rights and obligations between labor and management. Most recently, the law was revised in 2015, but the employment law shall be revised in the future. Based on recent wage increases, the nature of workers 'protection is planned to be strengthened, such as changing the scope of workers' allowances for overtime work.
What they shall pay attention to as a feature of Singapore's employment law is that not all workers are covered by the Singapore Employment Act. Certain standards have been established as to whether the employment law is within or beyond the scope of the employment law. For workers falling outside the scope, the employment law itself is not applicable and allowances for overtime work and allowance for holiday work, Granted Paid etc. are not applicable. In the case of hiring workers falling outside the scope of the employment law, it is necessary to prepare a contract for remuneration and welfare individually agreed between the company and the workers.
Whether employment law is applied or not is based on "Employment relationship". In the Employment Law, it is classified as a person in "Employment Relations" or Independent Contractor (Independent Contractor), or a person not in an employment relationship, and in the latter case of Independent Contractor it is merely a service contract, so employment relations There is no application of employment law without it.
However, even those with employment relationships will be exempt from the next workers.
Seafarer
· Stay at home
· Managers, senior positions, workers who fall under the obligation of confidentiality
· Other officials designated by the government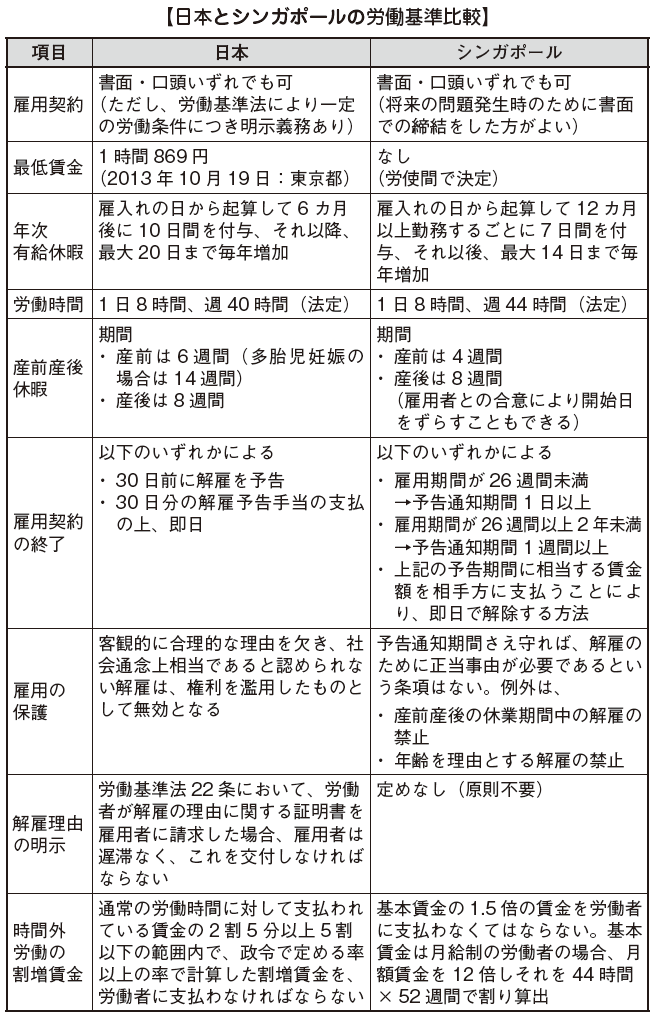
■Working hours
In principle, Singapore's statutory working hours are up to 8 hours, legal work hours per week are up to 44 hours. If you work more than 6 hours in a row, your company shall always have a break time. However, if the number of working days per week is 5 days, they can extend the working hours of the day to 9 hours. Even in that case, the statutory working hours of the week remain unchanged at 44 hours.
In case of working a worker beyond the statutory working hours of the day or the statutory working hours of the week above, it is necessary to pay 1.5 times the basic wage as a premium wage.
■ Holiday
The company shall give the worker a statutory holiday at least one day a week. Legal holidays are called Rest Day, and many cases are set on Sunday, but you can also set a legal holiday on a day other than Sunday. In Singapore and in Japan, there are a lot of companies taking a two-day weekend system, in that case, for non-holidays on statutory holidays, called Non-Working Day or Off Day, a Rest Day which is a legal holiday and It is clearly distinguished.
If workers are made to work on Rest Day, which is a statutory holiday, the company is supposed to pay twice the normal wage as an extra wage. However, if workers are worked on Non Working Day or Off Day, the same handling as overtime work is stipulated, so the company only has to pay 1.5 times the normal wage as a premium wage It will be. -
Legal System on Wages
Regarding payment of wages, it is said that salaries must be paid at least once a month. If the working period of the worker is less than one month, the salary is calculated on a daily basis on a daily basis, and if the working hours per day is less than 5 hours, the wage for half a day Will be recorded.
There is also a provision for the payment date of wages, and it is said that it is within 7 days from the day when the wage calculation period has ended. Therefore, if you set the wage calculation period from the beginning of the month to the end of the month, payment date of wage shall be set by the 7th day of the following month. In addition, when dismissing workers, it is necessary to pay wages of workers within 3 business days from the date of dismissal.
In the event that there is an offer of retirement from the worker side, it is necessary to pay wages on the retirement date, but if the offer of retirement is made after the advance notice period decided between labor and management, from the retirement date If it is within 7 days, it is possible to pay wage late. -
Employment Contracts and Employment Rules
■Employment Contract
In Singapore, employment contracts are signed in writing or verbally. However, many companies have signed contracts in writing to avoid conflict. Regarding the period, it is the agreed period between the employer and the employee, and the contents of the labor contract are the work content of the worker, the working hours, the paid leave, the employment period (start and end), compensation, bonus, and raise etc. Also, when using Japanese labor contracts as they are, there are many cases that do not match the labor laws and practices of Singapore.
■ Employment Rules
In Japan, when employing 10 or more employees, it is mandatory to prepare employment rules, but in Singapore there is no obligation to create employment rules regardless of the number of employees employed. However, in operation, there are many cases where the workers' rights are clarified by stipulating employment rules.
■ Termination of Employment Contract, Protection of Employment
Unlike Japan, in Singapore, unilateral dismissal notification may be able to terminate employment without a reason.
For workers who are not covered by the employment law, employers and workers set labor conditions, rights and obligations under labor contracts through mutual agreement, so that employment contracts, employment contracts End will be done. On the other hand, when dismissing a worker who is subject to the employment law, you must comply with the provisions of the Employment Act. Therefore, you must notify the other party in writing.
-
-
-
Central Reserve Fund
The Central Provident Fund (CPF) is a compulsory savings scheme in which both employers and workers make a certain amount of money in individual accounts, and the CPF Management Department (Central Provident Fund Board) I manage it. Monthly wage payment, Singaporean citizens whose receipts exceed a certain amount, and holders of permanent residence (excluding some people) are obliged to join the CPF.
Insurance premiums to be accumulated by CPF are calculated by multiplying monthly salary of workers by a certain percentage, and employers and workers will bear responsibility.
The pension system in Japan is an intergenerational dependency system, and pension benefits to pensioners are a mechanism supported by pension insurance premium payers, which is said to be the working generation, but the CPF in Singapore has become a funding system As a rule, pension benefits to pensioners shall be paid in principle from the insurance premiums paid by themselves during the active period.
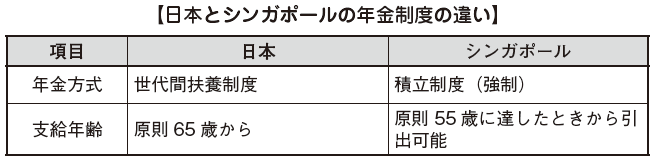
■ Target
A company employing even one worker must register with the CPF and workers with an obligation to pay CPF premiums are limited to Singaporeans or Singapore Permanent Residents. Usually, there is no obligation to join the CPF for those working in Singapore as an assignee from Japan.
■ Calculation of premiums the Basic Wage
In principle, all remuneration paid by the company will be the basis for insurance premium calculation. In addition to regular wages, this includes wages for overtime work, various allowances and bonuses. However, disposal allowances are not included in the basis of insurance premium calculation.
Basically, both labor and management are obligated to pay CPF premiums, and the insurance premiums for workers under 55 are 37% of monthly salary. The breakdown is that the employer will bear 20% of the monthly salary of the workers and the workers will contribute 17%. Also, if the workers are between the ages of 61 and 65, the employer contribution ratio is 12% and the worker contribution ratio is 13%. For employees aged 66 and over, the employer contribution ratio is 7.5% and the workers contribution ratio is 5%. This burden is reduced because it is based on a policy that encourages employment of older workers.
■ Account
Basically every month from the wages of workers, a fixed amount is deducted as a CPF insurance premium and it is transferred to the CPF account. Specifically, subscribers' CPF accounts are as follows.
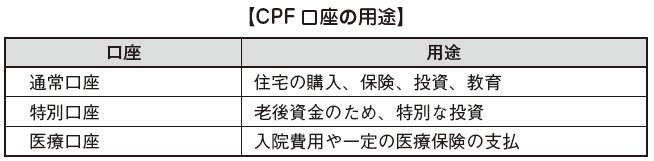
Interest accrues for CPF insurance premiums accumulated in accounts. In principle, subscribers can receive benefits on a monthly basis from CPF insurance premiums accumulated in CPF accounts as pensions from the age of 55, but unlike the Japanese pension system, The benefit received shall be the sum of CPF insurance premiums and interest paid by you.
■ Withdrawal from CPF
If they move from Singapore domestic to overseas, they can withdraw from CPF, and if they withdraw, they can withdraw all the CPF premiums they have accumulated so far. If the withdrawal person emigrated to Singapore again and acquired Singapore's permanent residence right, it is necessary to pay the CPF insurance fee withdrawn when he / she withdrew beforehand to the CPF account.
-
Labor Compensation Ordinance
■Scope of application
The Work Injury Compensation Act is a compensation system for labor accidents of workers. Revision was made in 2008, expansion of coverage and increase of compensation were done. The subjects of the Workers' Compensation Compensation Act will be persons (including foreign workers and part-time workers) who have contracted employment contracts excluding self-employed persons, independent contractors, military personnel, police, domestic workers and etc.
In the event that a worker is physically injured in connection with work, he / she can receive compensation set forth in the Workers' Compensation Compensation Act regardless of employer's negligence. Workers who received compensation based on the Workers' Compensation Compensation Act are said to be unable to compensate damages for employers or third parties who caused the accident that caused the physical injury in principle .
Compulsory insurance subjects for labor accident compensation are as follows. Employers are also obliged to compensate against accidents of workers other than those subject to compulsory insurance. Therefore, even for office workers with monthly salary totaling more than 1,601 S dollars, it is common to join workers' compensation insurance.■Main compensation contentsThe insurance payment will be paid within the following range stipulated by the Industrial Accident Compensation Act.
Employers are also obliged to compensate against accidents of workers other than those subject to compulsory insurance. Therefore, even for office workers with monthly salary totaling more than 1,601 S dollars, it is common to join workers' compensation insurance.■Main compensation contentsThe insurance payment will be paid within the following range stipulated by the Industrial Accident Compensation Act.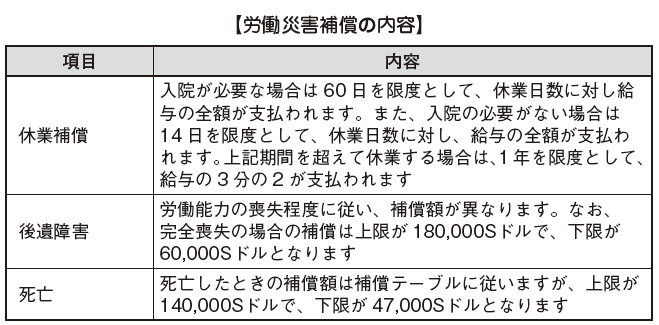
-
-
-
Latest News & Updates
* Amendment of Qualifying salary of EP visaOn 26th July, MOM (Ministry of Manpower) announced the change of minimum salary amount of EP visa. Details are as follows.[Contents]1. From 1 January 2017, the qualified salary of the EP applicant rises from S $ 3,300 to S $ 3,600. This change is a general update in response to the rise of local wages, maintaining the quality of foreign workers and strengthening so as to complement the work force of the local people.2. MOM labor policy framework is formulated to meet the economic personnel demand, it is intended to produce a better occupation increased to maintain the competitiveness of companies, more in Singapore. The previous increase in qualified salary was made in June 2014, with a change from S $ 3,000 to S $ 3,300 in that case.3. This amendment will be effective from January 1, 2017, and EP issuance standards are limited to persons who are deemed to have sufficient minimum salary of S $ 3,600 or more, other appropriate criteria and work experience. As before, more experienced employees are required to set salaries appropriate for their work experience and abilities.4. In this amendment, MOM grants certain consideration to foreign workers who have already owned EPs if their effectiveness expires in the following periods.a. Before December 31, 2016: Under the revised standards, upgrading of the EP shall be allowed up to three years.b. From 1 January 2017 to 30 June of the same year: Under the revised standards, EP renewal shall be allowed up to a maximum of one year.c. After 1 July 2017: The renewal is permitted in accordance with the standard of this revision and it is allowed up to 3 years.5. The employer recommends that the Self-Assessment Tool (SAT) confirm that the applicant of the EP meets the application criteria, and the SAT according to this revision will be released by November 2016 .[scope]
The minimum salary stipulated by MOM is for the new graduates to the last, and it is desirable that the application fee for EP is set high for employment history and ability as described above.
It was a view that S $ 4,500 - 5,000 was the minimum line for about a year in the past year, but from this revision it is considered that companies should consider that this line will rise. As a measure of the Singaporean Government, we strongly encourage the recruitment of Singaporeans as before, and it is very important for companies to carefully plan the hiring schedule of local human resources.
* Trends in Singapore employment visa issuance regulation
Singapore government, the aim of the labor force foundation "Singaporean Core in the Workforce," centered on the Singapore national, composed of two-thirds of the gross domestic labor force by Singapore citizens (and permanent residency holders) in the future We aim to be a goal. Towards this goal, in July 2015, relates to acquisition application of Employment Pass (EP) that have been issued to many expatriates of foreign-funded enterprises, "Quality" of the applicant in the issuance examination, that is, the knowledge and experience MOM is announced if it emphasizes more importance. This is because if you adopt a foreign worker, by having the knowledge and experience over the Singaporean people of the same conditions in educational background etc. to be the condition of issuing EP, the adoption of Singaporean citizens There was an aim to promote.
In addition MOM, compared with other companies in the same industry, to companies proportion of Singaporeans have been lower "Weak Singaporean Core" as a percentage of the employee structure, (1) Singapore citizens and equality standards the adoption of foreign workers We are also asking for submission of explanatory materials, such as (2) whether they are actively engaged in nurturing Singaporean national workers who have been enrolled in the past.
2. Warning Letter
Singapore Ministry of Manpower (MOM) issues a warning letter (Warning Letter) to companies in cases where it is said that Singaporeans received unequal treatment from companies at the time of recruitment or personnel affairs , Suggesting that measures that can not receive a work visa in the future are taken.
3. Triple WeakIn addition, in April 2016 MOM for companies, without adopting despite Singapore citizens went Job, If it is not possible to clarify the reasons for adopting the foreign workers and, of Singapore citizens We announced that we will conduct a more rigorous review at the time of application for EP issuance if we can not specifically show plans to act aggressively in nurturing.
Specifically, it lists the following three factors concerning companies that will sponsor EP and announces that it is an important consideration factor for EP issuance review.
(1)
Percentage of Singaporean citizens (and those who hold permanent residence) in all employees
(2)
In the case that the proportion of Singaporean citizens (and holders of permanent residence) is low, we will strive to foster (foster and strengthen) personnel affairs in the future that will become "Singaporean Core"
(3)
Economic and social contribution to Singapore
For companies that are judged to be "weak" in all three consideration factors, we also announced that they will affect the existing EP holder and the application for new EP acquisition.In addition, TAFEP closely watches the adoption trend of companies that are occupied by foreign workers, more than half of employees with monthly salaries of more than 3,300 dollars. Currently, about 100 such companies are subject to TAFEP's survey. -
Foreign Work Permit
As a general rule, all foreigners working in Singapore shall apply for either Employment Pass for Management / Professionals or Work Permit for Low Skill.
■ Employment License for Management / Profession
Foreigners with monthly wages over $ 3,300 will be eligible for employment permits for management and professionals.
In applying for employment permission for the fundamental application qualification requirement is that in principle, that they have a university graduation qualification recognized by the Singaporean government. The Singapore Ministry of Human Resources Development (MOM: Ministry of Manpower) has ceased publication of accredited universities, but the Employment Permit and S Pass self-assessment tool are available on the website (https://services.mom.gov.sg/sat / satservlet) and recommend self-assessment prior to application.
In order to obtain an employment permission, recommendation and guarantee by a local company is required. Therefore, in the application form there is a column to describe about the employer, and if the worker is to be repatriated, the employer will bear the cost. As well as reviewing the applicant, MOM investigates the employer's credit and decides to issue an employment permit.
Once it is decided to issue an employment permit, a provisional permit is mailed and you will be applying for the first time within the validity period (6 months) of this permit. The term of validity of the employment permit by initial application is up to two years, and up to five years upon renewal will be granted. If your application is rejected, you can re-apply within one month. In this case, it is necessary to explain to MOM a document explaining the skill of the applicant, what the employer needs for this applicant, what kind of contribution can be made, etc.
■ Intermediate level skilled worker's license
Intermediate level skill certificate for skilled workers (S Pass) has minimum basic monthly salary of more than 2,200 S dollar, has equivalent educational and technical qualifications as technical college, related work experience and it shall be qualified as an application and also shall be positioned as a lower permission than the above employment permit.
■ Work Permit for Low Skill
For low-skill work permits, there is a Work Permit for foreign skilled and unskilled workers with monthly basic salary less than 2,200 dollars. In the permit it will be for low income people.
Both S Pass and Work Permit are obligated to pay monthly foreign employment tax and skill development charge in order to manage the number of workers.
■ Personalized Employment Pass (PEP)
Previously, if the holder of the above various permits went off, they have to leave Singapore. Therefore, a system called Personalized Employment Pass (PEP) was introduced so that even if permission holders left the job, they can continue to work in Singapore. With this system, even after the owner of the license has left the job, you can continue to stay in Singapore (up to 6 months) and search for a new employment place.
■ Foreign Workers Employment Act
Singapore has a policy of actively accepting foreign workers to compensate for labor shortages. The Foreign Workers Employment Act is not the purpose of restricting foreign workers but the law established for the purpose of protecting foreign workers such as welfare of foreign workers and maintenance of effective work visas. Of course, regulations have been done, and the work of foreign workers who do not have working visas is prohibited. Employment violating this law will be fined or imprisoned, or both. -
Social Insurance of Expatriates
■ Continuation and loss of the insured person's qualification for social insurance
When you go overseas from Japan, the handling differs depending on whether the employment relationship with companies in Japan continues (enrollment to enrollment) or does not continue (transfer to second year).
In the case of being registered and being dispatched from part-time or part-time salary from the secondary company, the insured qualifications such as health insurance, welfare pension insurance, employment insurance etc. continue even while they are in abroad.
Meanwhile, in the case of a transfer to a transferring company that terminates an employment relationship with a Japanese employer on a secondary basis and establishes an employment relationship with an overseas subsidiary, the employment relationship with the employer of the employee is terminated, so that health insurance, welfare pension insurance, employment is insured qualifications such as insurance will be lost.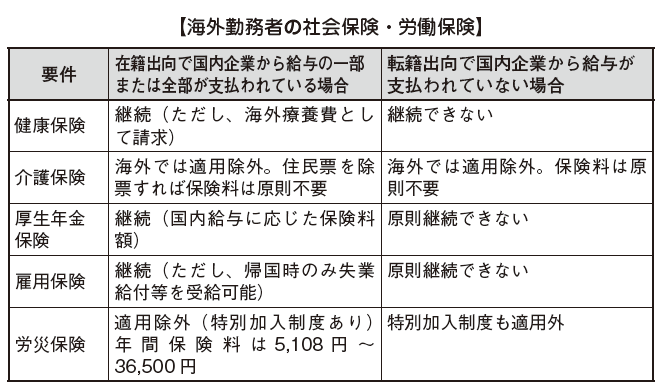
■ Optional Subscription of the National Pension
In the case of a transfer to another company, they cannot continue the insured qualification of the employee's pension insurance. If it is planned to arrive within one year, they shall be a resident in Japan, so they shall join the National Pension.
However, if they are planning to move over a year, they shall be a non-resident of Japan, so in principle they do not need to join the National Pension. Those who wish to join the Japanese pension system can do voluntary procedures for the national pension (Article 5 of the National Pension Law Supplement). The voluntary participation requirement of the national pension is as follows.
· It must be over 20 years old and under 65 years old with Japanese nationality
· It is possible to pay insurance premiums in Japan (It is also possible for payment by substitution by relatives etc)
The merit of voluntary joining is that you can receive basic disability funds if you get into a fault condition due to an accident.
■ Points to keep in mind when using the Japanese health insurance system abroad
Even if you receive medical practices abroad while they are in overseas, if they are qualified as an insured person in Japan's health insurance, they can apply for "overseas medical expenses" to their health insurance association etc. However, they need to pay attention to the following points when applying.
· In order to apply for "medical expenses", the full amount of overseas medical expenses will be fully redeemed by the principal and applied to the Japanese health insurance union etc
· The amount calculated by deducting the self-payment amount from the amount calculated on the basis of the treatment expenses when medical treatment of the same injury in the domestic medical institution (when the amount paid abroad actually is less)
In addition, the foreign currency conversion rate on the day when payment is decided is used as the conversion rate for currency conversion in payment calculation.
The following documents are necessary for health insurance overseas medical expenses application, and if the submitted documents are written in languages other than Japanese, a Japanese translation that clearly states and imprints the translator's name and address You must attach it.
· Medical treatment expenses application form
· Certificate of medical treatment contents
· Receipt statement
· Receipt (Original)
[Continuation of health insurance system in Japan]
If the employment relationship with a company in Japan does not continue, the insurance qualification of health insurance will be lost. However, you can join the health insurance system in Japan by using the health insurance optional continuous insured system or by joining the National Health Insurance (Health Insurance Law Article 37).
In addition, the voluntary continued insured system of health insurance can acquire qualification for up to two years retroactively to the date of qualification loss. However, since the voluntary continued insured system of health insurance needs to be done within 20 days after the loss of the qualification and the National Health Insurance must be completed within 14 days after the loss of the qualification, urgent response is required.
[Health insurance Optional continued insured's insurance premium]
The amount obtained by multiplying any of the following lower rates by the insurance premium rate is the insurance premium of the health insurance optional continuing insured. However, unlike in office, you will be responsible for insurance fees paid by the establishment.
· Standard remuneration monthly fee at retirement
· Average amount of standard remuneration monthly fee determined for each insured person who subscribed
[National Health Insurance Premium]
Depending on the income of the insured person, it is the amount calculated according to the provision of the municipality.
■ Special subscription to workers' accident insurance
Workers' accident insurance is excluded from workers who go to overseas offices because workers who work at business establishments in Japan are eligible for insurance benefits.
For employees who go to overseas, it is possible to receive insurance benefits for workers 'compensation insurance by using the overseas dispatcher special enrollment system (Article 33 of the Workers' Compensation Insurance Act). However, it is in the case of transferring to a special enrollment system of workers' accident insurance, and it is not applied in the case of transfer to a transfer.
The insurance premium of the special subscriber is the amount obtained by multiplying the insurance premium calculation basic value by the insurance premium rate, which is at least 5,108 yen per year, maximum 36,650 yen a year, the special participants are as follows.
· Workers who are dispatched from projects (excluding fixed term projects) to be held in Japan and engaged in overseas projects
· Employers who are dispatched from projects (excluding fixed term projects) to be conducted in Japan and who engage in SMEs * who always use a certain number or less of overseas workers * and who are not workers other than
* The size of SMEs
Financial industry · insurance industry · real estate industry · retail business: 50 or less
Wholesale / service industry: 100 or less
Other than above business type: 300 or less
· International Cooperation Organization, etc. Persons who are dispatched from organizations conducting technical cooperation to developing regions (excluding fixed term projects) and engaged in businesses undertaken in developing countries
■ Overseas travel accident insurance
[Handling at the Time of Appointment as a Representative]
When transferring overseas, it is desirable to consider subscribing to overseas travel accident insurance in addition to joining public insurance. Overseas travel accident insurance can receive medical treatment without cash when treatment is done at a hospital where insurance company has a contract. Also, unlike public insurance, actual expenses of medical expenses actually paid by limiting the contracted insurance amount will be paid. Since new procedures for overseas travel accident insurance can not be made after leaving Japan, it is necessary to complete the enrollment procedure before departure.
[Handling at the time of returning from an expatriate]
If an expatriate is to return, it will be subject to the year-end adjustment of that year. The target salary is the salary paid since the day you became a resident (the day you returned). In addition, when income other than salary is more than a certain amount, you need to make a final tax return in addition to the year-end adjustment.
-
Salary Design and Calculation Example of Expatriate
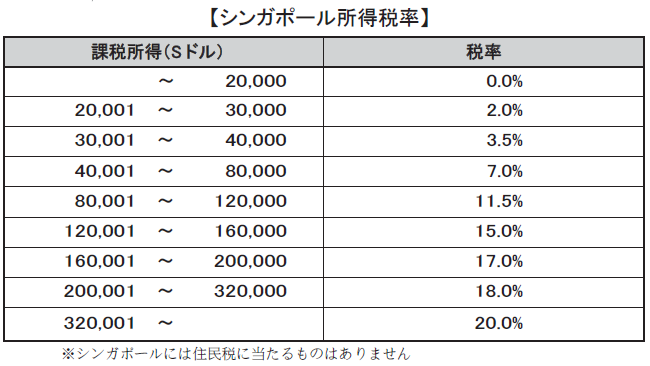
■The problem of salary inequality between Japan and SingaporeSince payroll method and applied tax rate differ between Japan and Singapore when paying salaries to Singaporean expatriates, payment amount is not the same as in Japan, but considering the setting of salary amount and form of payment in advance is needed.Basically, paying salaries similar to those in Japan raises the amount of salary earned in Singapore.[Comparison of tax rates between Japan and Singapore]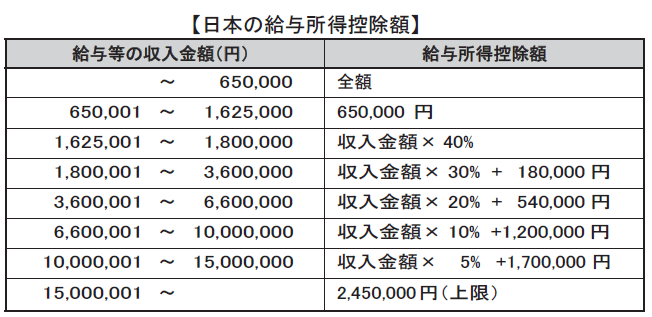
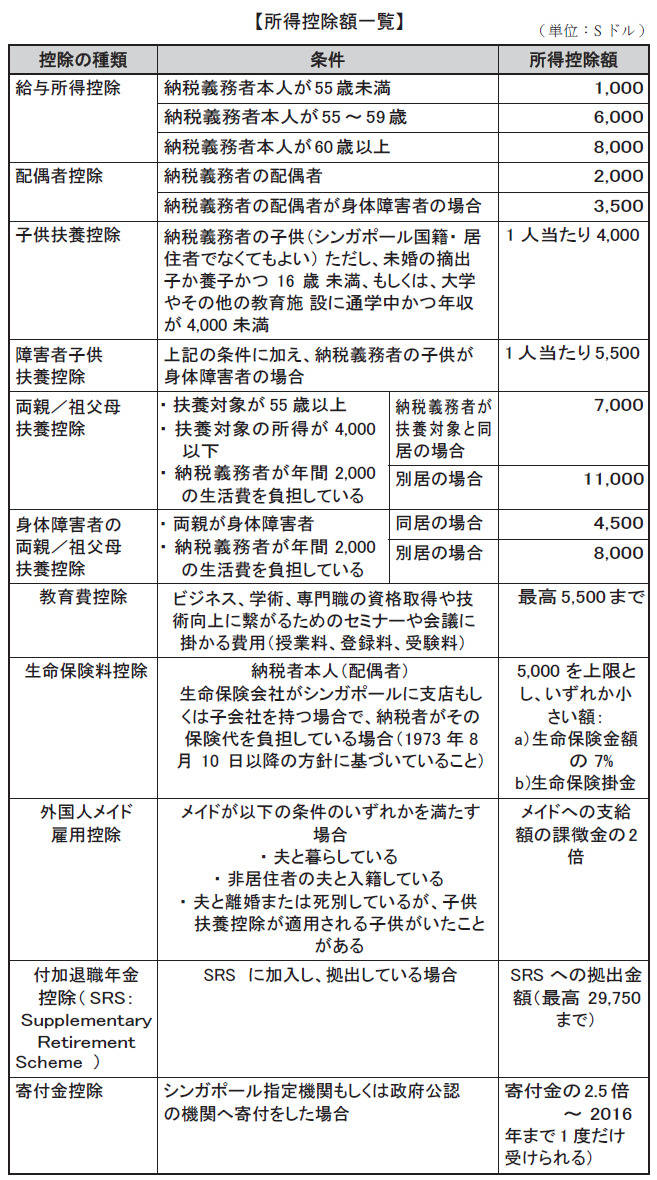 [Example of income tax calculation in Japan and Singapore]Precondition40-year-old man, annual income in Japan 6.48 million yen, unmarried, planned 3 years1 yen = conversion to 0.01 S dollar (rate as of September 2013)※ Actually, other deductions need to be taken into account, but here we do not consider it because it is a simple calculation
[Example of income tax calculation in Japan and Singapore]Precondition40-year-old man, annual income in Japan 6.48 million yen, unmarried, planned 3 years1 yen = conversion to 0.01 S dollar (rate as of September 2013)※ Actually, other deductions need to be taken into account, but here we do not consider it because it is a simple calculation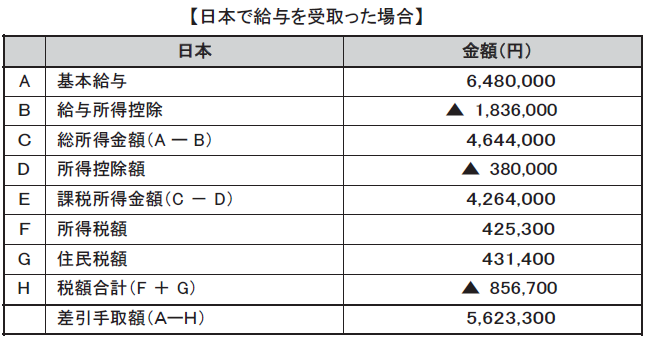
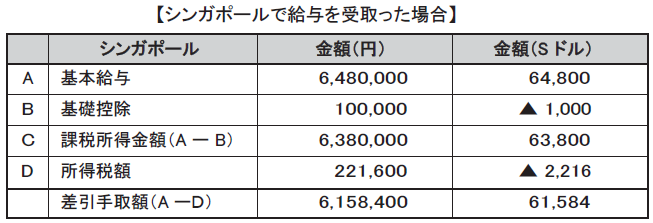 As mentioned above, in the case of receiving salary in Japan, the proceeds amount is 5,623,300 yen, and in the case of receiving salary in Singapore, the takeover amount is 6,158,800 yen, so in the case of receiving salary in Singapore The takeover amount will be 535,100 yen more. In this way, if the proceeds are not reduced, it is not necessary to calculate gross-up compensation for salary compensation.However, if it is the case that you are also assigning a place of employment to a country other than Singapore, in order to prevent the employee's takeover amount from becoming a big difference depending on the place of assignment, There are also cases in which salary is set again in some cases.
As mentioned above, in the case of receiving salary in Japan, the proceeds amount is 5,623,300 yen, and in the case of receiving salary in Singapore, the takeover amount is 6,158,800 yen, so in the case of receiving salary in Singapore The takeover amount will be 535,100 yen more. In this way, if the proceeds are not reduced, it is not necessary to calculate gross-up compensation for salary compensation.However, if it is the case that you are also assigning a place of employment to a country other than Singapore, in order to prevent the employee's takeover amount from becoming a big difference depending on the place of assignment, There are also cases in which salary is set again in some cases.
-
-
-
Websites
[2] Department of Statistics Singapore
[3] 世界保健機構(WHO)
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya