Singapore
9 Chapter Tax
-
-
1 Chapter Importance of Management by Regional Headquarters
1.1 Importance of Asian market
1.2 Regional management of the Asian market
1.3 Comparison of countries as headquarters
2 Chapter Regional Headquarters System and Utilization Examples
3 Chapter How to Utilize Regional Headquarters
3.1 Method of Consolidating Profit by Dividend and Making it as Reinvestment Base
3.2 Utilization as a Finance Company (Loan Function)
3.3 Example of Utilization of Efficiency by Consolidating Settlement Functions
3.4 Example of Reviewing Supply Chain Functions and Risks
4 Chapter How to Make Regional Headquarters
4.1 How to Set Up a Regional Headquarters
4.2 Singapore as a Business Base
4.3 Corporate Law in Singapore
5 Chapter Overseas Relocation of Head Office Functions
5.1 Head office relocation to low tax rate country
6 Chapter M&A
6.1 Trends in M & A in Singapore
6.2 Points to keep in mind when doing M & A
6.3 Laws and regulations concerning M & A
6.7 Investment regulatory environment of Singapore
7 Chapter Accounting
7.1 Accounting System in Singapore
7.2 Accounting Standard in Singapore
7.3 Disclosure System in Singapore
7.4 Accounting Audit in Singapore
8 Chapter Tax Risk of Regional Headquarters
8.1 Tax · Haven Countermeasure Tax System
8.2 Foreign Subsidiary Dividend Income Non-inclusion System
8.5 Taxation of Country of Residence and Double Taxation by Source Taxation
8.6 Tenuous Capital Tax System
9 Chapter Tax
9.2 Personal income tax in Singapore
9.3 Corporate income tax in Singapore
9.6 Singapore withholding system
9.7 International tax in Singapore
10 Chapter Labor
10.1 Work environment in Singapore
10.3 Social Security System in Singapore
10.4 Points to keep in bringing Japanese to Singapore
11 Chapter Q&A
-
-
-
Overview
Singapore has no Local Tax or Citizens tax, it is only National Tax. The types of taxes are as follows.
· Corporate income taxes
· Personal income tax
· Goods and services tax
· Property tax
· Stamp duties
· Customs duties (import tax, excise tax)
· Foreign labor tax, technical development tax
· Automobile related tax (registration tax, additional registration tax, road tax)
Regarding the corporate income tax and the personal income tax, it is stipulated in the Income Tax Law. It is detailed in the provisions of such as enforcement orders, enforcement regulations, basic instructions, individual notifications, and tax special measures law are not provided in Japan. In many cases, tax administration has been executed based on judicial precedents and customs. However, since 1993 the tax authorities have announced the interpretation, practice, and clarifying to reduce the ambiguity of tax administration interpretation.
-
-
-
Overview
When calculating personal income tax in Singapore, the range of income taxed depends on whether the target taxpayer is a resident or a nonresident. Therefore, when calculating income tax, it is necessary to judge the comfort of housing first.
■ Definition of Habitability / Non-Habitation
Judgment of habitability is based on the address of Singapore, none of which is based on nationality, domicile nor birthplace.
In Singapore, the calendar year (from 1st January to 31st December of the year) is the taxable year and when the number of days of stay in Singapore within the calendar year is 183 days or more therefore It is classified as a resident. If not, it will be considered a non-resident. In addition, among non-residents, if the number of days stayed is more than 60 days, they are quasi-residents and tax-separated.
The range of income to be taxed is classified as follows according to the classification of habitability.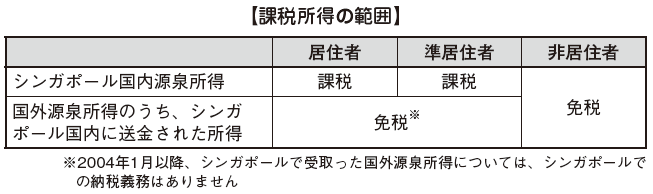
■ Definition of Domestic Source Income
Domestic source income is define as follows. They will not ask for the place of receipt of income.
· Income from domestic business establishment or business in Singapore
· Income arising from assets located in Singapore
In addition, a tax resident refers to a person who falls under any of the following items.
· Permanent resident
· Person who is staying in Singapore for 183 days or more on a calendar year basis
· Those staying or working in Singapore actually for the third consecutive year even if the number of stay in Singapore for the first and third years is 183 days or less
For example, if he arrived in November 2009 and returned to Japan in March 2011, even if the number of stay days in both 2009 and 2011 was less than 183 days, not only in 2010 but also in 2009 and 2011, the target period will be considered to the resident.
On the other hand, if it is more than 61 days and less than 183 days, it will be subject to income in Singapore as a quasi-resident and a large rate of either 15% or the residence tax rate will be taxed. In the case of directors, the tax rate is 20%. In addition, quasi-residents are not eligible for tax deduction.
Application forms use Form M (income tax return for non-residents). If the number of days stayed in each year is 60 days or less, it is considered a nonresident.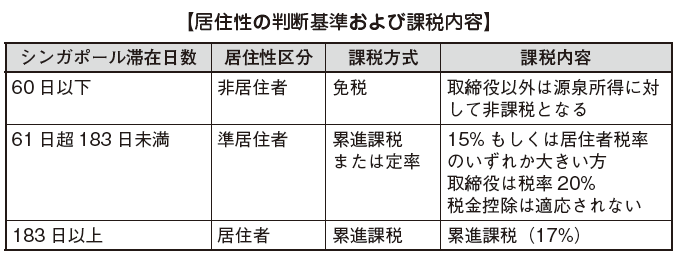
■Tax duration
The taxable period of the personal income tax is the calendar year of January 1 to December 31.
■ Calculation of income tax amount
The income tax calculation in Singapore are stated below.
Taxable income = gross income - income deduction
Income tax to pay = taxable income x income tax rate - tax deduction
[Income Amount]
First of all, it is necessary to divide all income in the taxable year into taxable income and tax-free income. The taxable incomes are as follows.
· Salary · Bonuses income
· Allowance for transportation expenses
· In-kind benefits (rent, furniture, airline tickets, tuition fees of dependent families, membership fees, cars, payment by employers, etc.)
· Real estate income
· Interest · dividend income
· Special remuneration (including down payment and retirement allowance)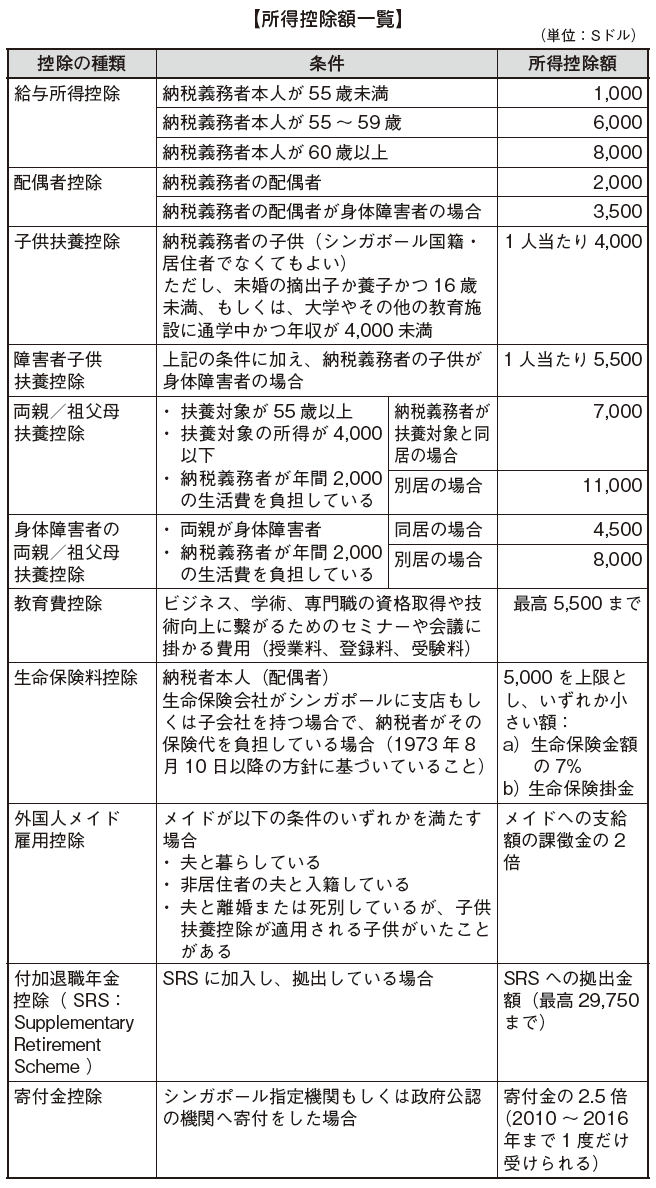
When calculating the total income amount as for the above income, there is certain amount can be deducted for the amount spent and it will obtained that income.
Deduct various income deductions from income amount and calculate taxable income amount. Only Singapore residents can receive an income deduction. As for an income deduction, see the types listed in the table.
■ Notes on non-resident employers
[Issuance of certificate by guarantor]
If the taxpayer is not a Singaporean national, they must issue a certificate of the estimated payment amount from the Singapore corporation or bank and submit it to the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (Singapore IR) every fiscal year.
[Submitting Form IR 21 (payroll statement from employer)]
At least one month before retirement or departure from Singapore, the employer must submit a Form IR 2 1 (payroll statement from employer) and pay the tax before the employer departs.
[Special Measures of Regional Expatriates]
In the case where the activities of the regional headquarters based in Singapore as an expatriate work for each country, it is possible to apply for taxation on an income generated in Singapore in proportion to the number of days stayed in Singapore. However, all of the following conditions must be satisfied.
· Employed by non-resident employers
· Be based in Singapore for regional convenience
· Being out of Singapore for work purposes
· The salary to be paid is not transferred to the permanent facility account in Singapore
Application method
When applying, they will submit the previous year of the following documents by April 15 of the following year.
· Regional Expatriate Application Form
· Employment contracts or job schedules for which foreign letter's letterhead (representative or corporate name and address) has been printed and the representative has signed it
· Local travel schedule table
Regular business trip schedule does not need to apply every year unless the employer changes.
Taxable income
The taxable income will be the greater of:
① Income received in Singapore
② Total number of days stayed in Singapore ÷ 365 days × salary income
In kind benefits
All tax benefits to be paid in Singapore will be taxed.
[Calculation of Income Tax Amount]
The income tax amount is calculated by multiplying the taxable income amount calculated above by the next progressive tax rate.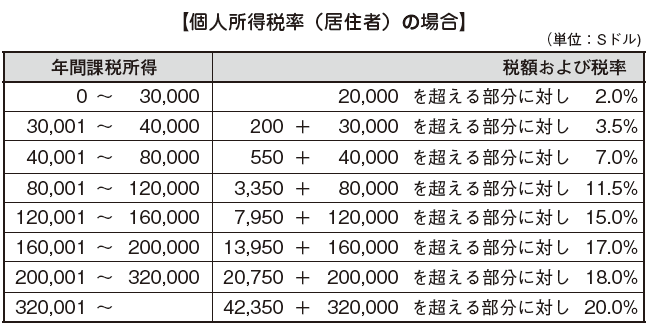
.png)
■ Declaration / Payment Procedure
[Imitation Taxation System]
In Singapore, an imposition taxation system has been adopted, tax authorities will assess and decide the tax amount based on the tax returns filed by taxpayers. It is a time-consuming system to conduct a tax examination as necessary and then to charge the final tax amount on it.
With the voluntary declaration method adopted in Japan and the levy taxation method adopted in Singapore, there are no substantial difference between the point that the taxpayer prepares the declaration form and the procedure to submit to the tax authorities. However, the method of voluntary declaration is a taxpayer and the taxation method is different from tax authorities to finalize the final tax amount.
[Declaration method]
There are two types of personal income tax declarations in Singapore: one that fills in the prescribed form directly and the other is electronic filing e-Filing.
Since IRAS encourages electronic filing, recently, the tax returns itself are not sent to taxpayers, and only passwords for electronic filing etc. are sent.
[Payment Schedule]
The taxable period of personal income tax in Singapore is January 1st to December 31st and Form B1 (for resident) will be sent from the tax authorities by the end of February the following year of the taxable year. Employers also create a Form IR8A (payroll statement from employers) and deliver it to the employees. The taxpayer must require to declare to the local tax office by April 15 (April 18 in case of filing on e-Filing). When the declaration is accepted without any problem, a notice of determination of charge is issued by around June to September.
As it will be sent, taxpayers must pay the tax one month after the date stated on the charge decision notice.
Also, if an expatriate returns to Japan in the middle of the year, it is necessary to file an income tax to the tax authorities before the employment in Singapore is over. As a guide, it must be done one month before returning home.
[Payment method]
Partial payment is allowed and it is possible to divide up to 12 times by using GIRO (automatic bank withdrawal), which can automatically withdraw from the bank account..png)
-
-
-
Overview
In Singapore, the place of residence is determined according to an administrative dominance.
A company established in accordance with the Company Law in Singapore is treated as a resident corporation even for foreign capital such as Japan. However, regardless of whether it was established based on the Corporate Law of Singapore, if a general meeting of shareholders and board of directors are held in countries other than Singapore and the operation & management of business execution are being conducted, the Singapore tax law Above, it becomes a non-resident corporation.
In Singapore's tax system, residents are given preferential treatment and non-residents are not subject to the tax exemption for the new company, tax exemption for foreign source income, and reduction or withholding tax etc. are all based on the double tax avoidance treaty. Residents' judgment is made in each taxable year.
■Taxable year
In Singapore, the tax year for corporate income tax is in the principle of standard for the fiscal year. -
Calculation of taxable income
Taxable income in the revenue law is generally calculated by deducting all deductions from all gross profits related to businesses that were operated in one accounting period (usually the business year). The business year is assumed to be 12 months in principle.
In addition, gains and losses are calculated based on the accrual principle. All gains and losses incurred during the business year are included in the transfer, and deductible expenses are included in the calculation of the income amount regardless of whether or not payment is made.
■ Taxable gains
Singapore's corporate income tax is calculated by territorial system. In other words, income from Singapore source or Singapore foreign source income will be subject to taxation in Singapore. Personal income tax is also calculated by territoriality.
· Gains and benefits earned from the business
· Dividend, interest, and rent
· Royalty Profit earned from other assets
· Gains and benefits other than those mentioned above with the nature of income
However, the following profit is exceptionally subject to tax exemption.
· Gain on sale of fixed assets
· Foreign Exchange Margin by Capital Transaction
■Deduction calculation
In Singapore, in calculating taxable income, taxable income is calculated by adding or subtracting adjustment items from accounting profit like Japan. However, whereas in Japan there are provisions that allow deductibility as a requirement for deductibility accounting like depreciation and amortization. The Singapore income tax law does not prescribe the independent accounting treatment of the tax law, and the proper opinion of the certified public accountant and also the accounting treatment of the financial statements with the attached items were considered to be appropriate under the tax law as well.
Moreover, from the draft budget for 2013, they will be able to receive a cash grant of up to 15,000 dollars in the total for the three years from 2013 to 2015, so that the deduction of traditional productivity and innovation PIC: Productivity and Innovation Credit). The target areas are as follows.
· Acquisition or lease of PIC approved automation equipment
· Empowering employees' training capacity
· Registration of intellectual property rights
· Acquisition of Intellectual Property Rights, Design
· Research and development activities
· Invest in design project
With small businesses in mind, they will refund cash of up to 60 thousand dollars for PIC target investment of 100 thousand dollars annually in the 2011 to 2012 tax year, and 100 thousand dollars annually for 2013 to 2015 tax years that has been established a mechanism.
[Calculation of Depreciation Expenses]
In Singapore, depreciation expense is calculated accounting as symbolized by capital gains tax exemption but tax deduction is not allowed for tax purposes. This is because it is not allowed to include deduction of expenditure related to capital items in principle. As a general rule, accounting depreciation expenses are added to taxable income in full and the tax depreciation expenses are calculated again and subtracted from taxable income.
Method of depreciation
Since the method of depreciation is not stipulated in the Internal Revenue Code, basically follow the tax depreciation method. If you do not do the first year's amortization at the time of acquisition, you cannot write off from the following fiscal year. Also, if you do not do depreciation on the way, it is not permitted to include deductible sums in the past when amortizing again.
Depreciation rate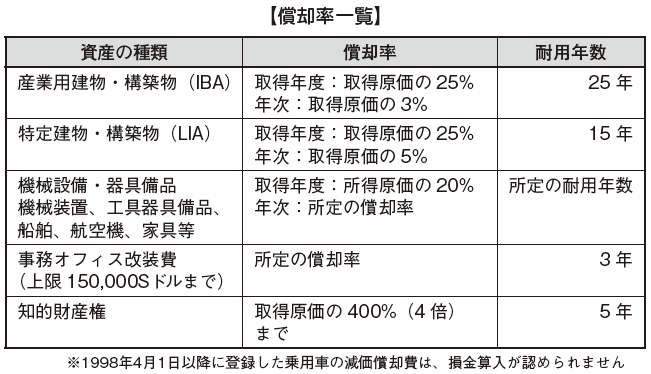 Acquisition year lump-sum depreciationAssets that fall under the following conditions are allowed to be amortized in bulk during the acquisition year.
Acquisition year lump-sum depreciationAssets that fall under the following conditions are allowed to be amortized in bulk during the acquisition year.
Acceleration depreciation
Assets are classified as newly purchased machinery and equipment. They are permitted to be fully amortized using the straight-line method with a useful life of 3 years, and this is called Acceleration Amortization.
Earnings’ expenses before opening
Relevant expenses are incurred during the first income year can be included in deductible expenses. Also, from the 2012 tax year, in addition to the year in which the first income occurred, expenses that occurred in the previous fiscal year can also be included in deductible expenses.
R & D expenses
Research content that falls under R & D expenses means that the results of scientific or technical R & D that can lead to productivity and product quality improvement can be included in deductible expenses. This does not apply to data collection and questionnaire surveys that are regularly conducted, echo surveys and market research of sales advertisements, or software development that is not intended for sale. Mainly, it is the criteria whether there is innovative creativity that does not exist in a new product development or in Singapore.
Automobile related expenses
In general, the expenses of rental cars used in Singapore are not allowed to include deductions even if they are intended for business purposes. However, for rent-a-car expenses outside the country, deduction is allowed if it is for business purposes. In addition, depreciation expenses of passenger cars required by the company for business are permitted.
Entertainment expenses
In Singapore, there is no clear provision for classifying necessary expenses, all expenses necessary for business activities are allowed to be deducted. However, private expenses such as private dining expenses accompanying the family are considered non-deductible.
Provision of allowance for doubtful accounts
Regarding provision allowances, in principle, they are not included in the amount of deductible expenses. However, the provision for doubtful accounts is the amount that can confirm the certainty of defaults is included in the amount of deductible expenses. Therefore, preparation of appropriate evidence based on the following points is indispensable for inclusion of deductible.
· Name and address of obligor
· Date on which the claim occurred, its nature
· Amount of money that cannot be collected
· Reserve processing, reasons for bad debt treatment
· Processes taken during collection
Donation
Deduction is only allowed for donations made to specific organizations recognized by the Government and Charity Committee and performing only philanthropic activities.
Start-up cost
Since opening fees are not expenses for earning income, it is not generally permitted to include deductions. However, as policy preferential treatment, the inclusion of deduction for opening fee incurred in the same tax year as the year in which sales were recorded is permitted. -
Types and classification of taxable income
■ Taxable Income
Taxpayer of corporate income tax in Singapore is supposed to be operated in Singapore within a corporation / association established in Singapore and a corporation / association established by foreign law, and these are called genus land ownership, Singapore domestic income and overseas income, which becomes an income in Singapore is subject to taxation.
Taxable income in Singapore are as follows.
· Income incurred in Singapore
· Income received in Singapore out of foreign source income
■ Foreign source income
Of the foreign source income, the income received in Singapore is regarded as source income earned in Singapore and subject to taxation. However, of foreign source income that is remitted to Singapore, income for which dividends and branch income and service income are taxed for income tax of 15% or more in that country in foreign countries is taxed in Singapore not.
Also, even if you are not engaged in Singapore domestic business, foreign companies are subject to taxation in Singapore if they conduct business at permanent facilities and are subject to withholding tax provisions.
■ Types of taxable income
Since Singapore's income tax law is targeted at corporations and individuals, there is no clear provision for corporate taxation standards. Therefore, in Japan's income tax law, the income is prescribed for each type, and these methods are combined to form taxable income. The income is as follows.
· Business income
· Income arising from employment
· Investment income (dividends, interest or discounts)
· Pension
· Asset income (income arising from assets such as rent, usage fee etc.)
· Gain or profit with other income characteristics -
Corporate income tax rate
A tax rate of 17% is applied from 2010 taxable year.
■ Income Tax Reduction
Singapore's corporate income tax rate of 17% has been applied, but Partial Tax Exemption has been adopted as before, and 75% of the taxable income up to the 10,000 S dollar is 75%, 10,000 About 2 90,000 S dollars, 50% is tax free.
In addition, a tax incentive system is introduced to newly established companies from the 2005 taxable year. Three years from the establishment, 100% of the normal taxable income of 100,000 S dollars in the first year and 50% of the 200 thousand dollars in the next fiscal year will be tax exempted. From the 2010 tax year, limited liability guarantee companies will be included in the tax exemption measures applied to the new company.
Furthermore, it was announced that a new tax reduction will be applied to all corporations from the 2013 tax year to the 2015 tax year in the 2013 budget draft issued by the Singapore Ministry of Finance. The tax reduction amount is 30% of the corporate income tax amount and the upper limit is 30 thousand dollars for each year. This tax reduction is also effective for corporations that have already applied the reduced tax rates.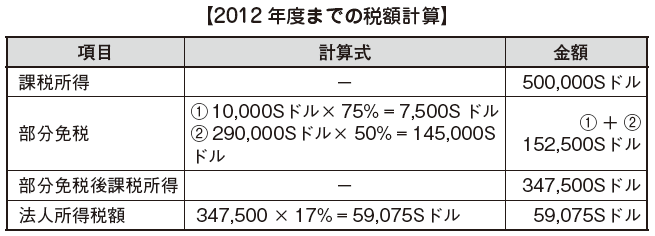

■ Tax calculation
Assuming taxable income to be 500,000 S as a result of the tax reduction measures, the effective tax rate up to 2001 was about 1.8%, but from the fiscal year 2001 it is about 8.3%, which is even lower It becomes a tax rate.
■ Preferred tax system for regional headquarters
A preferential tax system will be applied to companies that meet certain conditions and active in Singapore as regional headquarters. If you were recognized as a Regional Headquarters, the tax rate is 15% or less, and if they are approved as the International Headquarters, the tax rate is 10% or less.
-
Declaration and Payment Procedures
■ Tax return
The planned tax payment is made after the closing date by submitting Estimated Chargeable Income (ECI) and Estimated tax payment to IRAS. After that, they will finalize the corporate income tax amount by submitting the corporate income tax return form (Form C) and pay the difference with the planned tax payment amount.
[Tax payment]
All companies must file an ECI and estimated tax payment amount for the relevant business year to IRAS within three months from the last day of the business year.
After the submission of ECI, a notice of assessment (NOA) will be send from IRAS in several months. Because NOA will be send from authorities as forecast based on revenue from taxable period, if there is a difference from income tax amount determined later, it will be the flow of adjustment.
In addition, if the annual profit is less than S $ 10,000, declaration of ECI is unnecessary.
Declaration deadline
Every year, a Form C will be send from IRAS in April. 1 They have to submit the Form C after attaching audited settlement statement and an income tax statement (Tax Computation) by January 30. In addition, if the Form C was not send by April 30, it must be downloaded from the tax authority's website or asked to send tax returns to tax authorities.
[Tax on corporate income tax]
A few months after submitting Form C, NOA should be send. Payment or refund of the difference between the planned tax payment amount and the corporate income tax amount are made, and in the case of payment, the difference must be paid within 30 days from the issue date of NOA..png)
[Partial payment]
With the approval of the tax authorities, payment of corporate income tax can be paid in bulk or up to 10 times. The number of permitted split payments depends on the timing of ECI submission. Because they are promoting e-Filing, dividing payment by e-Filing is allowed more times than written of declaration. However, if ECI is submitted after 3 months from the fiscal year, split payment will not be accepted.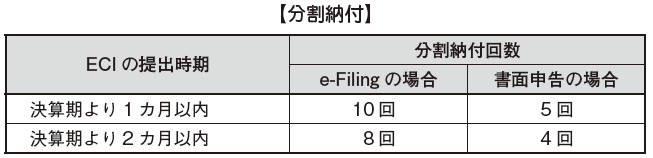
■ Penal Provisions
Contents of penalties differs between cases where it is determined by the Internal Revenue Service that the declaration content is not appropriate and cases where it is judged to be avoidance of tax due to willful or gross negligence. Declaration contents and penalties are as follows.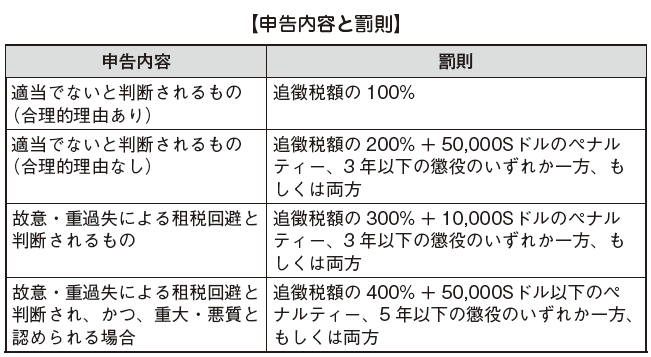
[Delay]
The payment deadline is within 30 days from the issue date of NOA if they do not use the split tax payment system. If they do not pay by the payment deadline, a delayed tax equivalent to 5% of the tax amount to be paid is charged. If the delay continues after 30 days, a dunning letter will be issued, and if you are delinquent after 60 days from the stated date, the 1% delinquent tax will be added every month. However, the total overdue tax will not exceed 12%. If delinquency continues, IRAS is permitted to take legal measures.
-
-
-
Overview
Goods Service Tax (GST) is an indirect tax imposed on goods and services traded in Singapore. Indirect tax is different from the direct tax that real tax burdens and taxpayers become together and the substantial tax burden holder and the taxpayer refer to different taxes. Since GST is similar in tax collection method to consumption tax in Japan, it is interpreted as being equivalent to Japanese consumption tax. In addition, the GST tax rate has been raised to 7% from July 1, 2007.
■ Taxpayer
In any one of the past years, taxpayers are obliged to pay taxes on businesses that have sold more than 1 million S dollars, and the business entities need to register as a taxable business on IRAS.
■Tax exempt object
Tax exemptions in Singapore are mainly for the purchase and sale of property for living, loans and financial services. Also, among the travel and advertising agencies, tax rates of 0% are applied for those that are recognized as international services *. Furthermore, since 1 October 2012, investment-grade gold, silver and platinum are excluded from taxation from imported goods currently subject to taxation.
* Examples of international services includes the services directly related to products located outside Singapore at the time the service is offered
-
Calculation of payment tax amount
■ Offering goods or services
The provision of goods or services are "the business operator provided goods or services in some form due to business conduct."
In recognition of the provision of goods or services, the following requirements must be taken into consideration.
[place]
Targeted transaction
· In case of providing goods or services including imports in Singapore
· In Singapore, a resident of Singapore provided goods or services
Transactions that will be tax exempt
· A person residing outside Singapore's country provides goods or services to a person residing in Singapore's country
Tax exemption transaction
· If a resident living in Singapore provides goods or services to a person residing outside Singapore, it is exempted as an international service
[season]
The provision of goods or services will be recognized at the earliest of the following:
· When the goods or service provider issues a GTS invoice (tax invoice)
· When the goods or service provider receives a consideration
[Taxable standard]
In principle, it is deal price, but in some cases fair market price is applied exceptionally.
■ Tax · Invoice system
Singapore's GST adopts a tax invoice method. If a taxing trader conducts a transaction where GST is taxed, it issues an invoice called tax invoice. With this as an evidence, the total GST amount listed can be included in the purchase tax deduction. In other words, GST must be recognized, invoiced and paid with backing by a tax invoice.
For tax invoices, they must always include Tax Invoice in the title, indicated the GST registration number, company registration number, and the GST amount. In the case of transactions denominated in foreign currencies, it is necessary to use the exchange rate permitted by the IRA, together with the foreign currency amount and Singapore dollar denominated price. In addition, if total payment is less than 1,000 S dollars, a simple statement is permitted.
■ Deduction method
The payment tax amount is obtained by subtracting the deductible input GST (GST related to purchase) from the received output GST (GST related to sales).
[a formula]
Payment Tax Amount = Output GST - Input GST
Tax duration
Tax durations are set every three months and it is necessary to file four declarations a year. -
Declaration and Payment Procedures
■Payment Procedures
Electronic filing became possible from January 2005. For new registrants after January 2007, electronic filing is obligatory.
With regard to refunds, within three months from the filing of the declaration, the authorities will transfer them to the designated bank account or a check will be sent.
■ Penal Provisions
[Declaration]
If the declaration is not made by the deadline, a penalty of 200 S dollars will be imposed for a monthly delay with a maximum of 10,000 S dollars.
[Payment]
If the specified payment deadline of GST has passed, a 5% overdue tax on the payment amount will be imposed. In addition, if payment is not made even after 60 days from the due date, a 2% delinquent tax will be added every month. However, the total tax rate for penalties is an upper limit of 55%.
-
-
-
Other taxes in Singapore
■ Property taxIn Property Tax in Singapore, the taxable object is real estate for residential use (building, house, land), the tax payment amount was the annual evaluation amount multiplied by 10%, but 2014 and 2015 From the taxable year, the payment tax amount is calculated by the newly introduced progressive tax rate.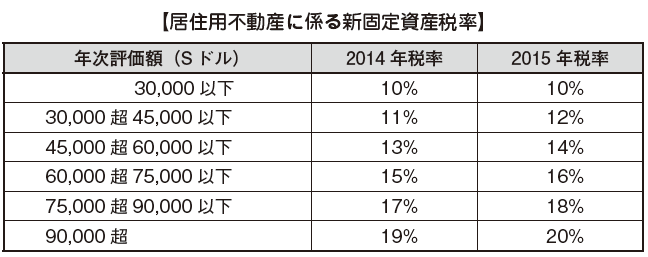
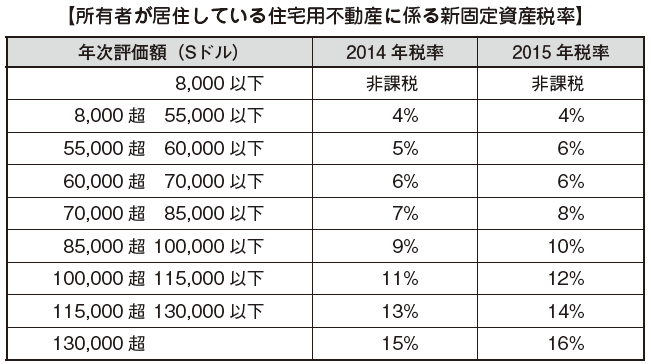 ■ stamp dutyStamp duty is a tax that is taxed on contracts created when trading real estate or stocks and is subject to taxation of Singapore corporate stocks and real estate in Singapore.[Contract pertaining to transfer of real estate]The stamp duty taxed on the contract for real estate transfer transaction is as follows.
■ stamp dutyStamp duty is a tax that is taxed on contracts created when trading real estate or stocks and is subject to taxation of Singapore corporate stocks and real estate in Singapore.[Contract pertaining to transfer of real estate]The stamp duty taxed on the contract for real estate transfer transaction is as follows.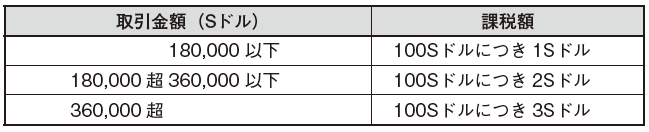
[Contract for lease / rental of land, buildings, other real estate]Stamp duty taxed on contracts related to leasing and renting of land, buildings and other real estate are as follows.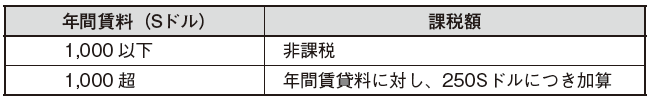
In addition, the tax amount added when the annual rent exceeds 1,000 S dollar depends on the lease term.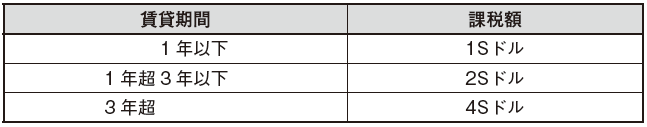 Taxes on real estate, stock mortgage securities and asset-backed securities are as follows.
Taxes on real estate, stock mortgage securities and asset-backed securities are as follows.
■ Import tax
Import duty (Import Duty) is divided into tariff and excise tax. There is no customs duty on export in Singapore.
Some taxes subject to customs duties includse alcoholic beverages, taxable items for excise duties include alcoholic beverages, tobacco, automobiles, and petroleum products.
[Major Exporter System]
The Major Exporter System (MES: Major Exporter Scheme) is a system to exempt taxes paid by Customs at the time of import. Originally, when imported by importers, they will pay the purchase tax at customs. However, when exporting such imported goods, tax is exempted, and the amount paid at the time of purchase will be refunded.
In other words, if you use MES, they do not need to pay the amount of tax they purchased at the time of import, so if they are importing on export assumption, they will not have to pay tax by applying for MES.
The advantage of MES is preferential treatment of cash flow. For heavy importers, the tax paid at import is heavy. MES is a system that exempts this from import at the time of import.
However, GST will be imposed when selling products that were tax-exempt at the time of importing in Japan. In order to acquire MES, it is necessary to apply for tax authorities.
■ Foreign Employment Tax
Foreign worker levy (Foreign Worker Levy) is to impose a certain tax on a person hiring foreign workers so that foreign workers do not increase unlimitedly. The target alien is the working permit owner, who is not a permanent resident of Singapore. For foreign employment taxes, taxes are determined according to the industry such as manufacturing, construction, and service industries.
■ Taxes and expenses on automobiles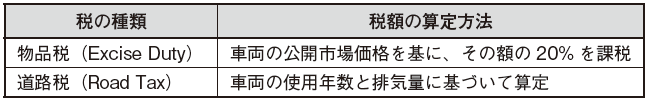 Registration fee (Registration Fee) and additional registration fee (Additional Registration Fee) are required for purchasing cost of the vehicle.■Skill Development TaxThe Skills Development Levy (SDL) is defined as the sum of the higher of 0.25% of the monthly salary (up to $ 4,500 S) or 2 S dollars, whichever is higher, for all employees, with a central pension It is the tax paid to the Fund.
Registration fee (Registration Fee) and additional registration fee (Additional Registration Fee) are required for purchasing cost of the vehicle.■Skill Development TaxThe Skills Development Levy (SDL) is defined as the sum of the higher of 0.25% of the monthly salary (up to $ 4,500 S) or 2 S dollars, whichever is higher, for all employees, with a central pension It is the tax paid to the Fund.
-
-
-
Overview
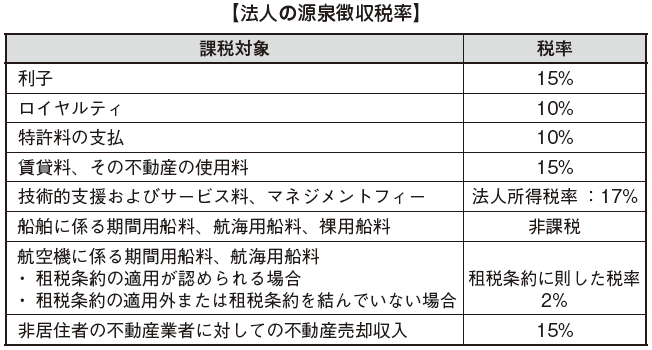
Singapore withholding tax is taxed on income paid to foreign corporations or individuals. Although it is not wide as the scope of taxation, it is necessary to pay attention because the tax rate is divided finely.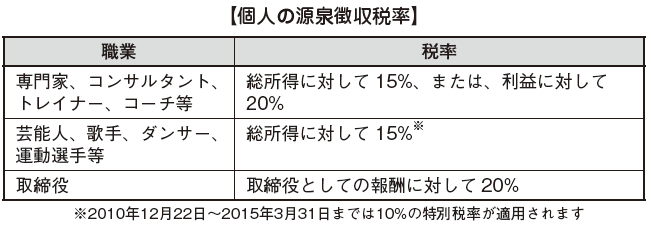
 ■ withholding tax on withdrawal of the additional retirement pension systemThe reserve fund of the Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS) is not a complete tax exemption, but the extent of taxation depends on the timing of refund.· Refund after receiving legal retirement age (current 62 years old): 50% of refund amount· Refund before the legal retirement age: 100% of the refund amount
■ withholding tax on withdrawal of the additional retirement pension systemThe reserve fund of the Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS) is not a complete tax exemption, but the extent of taxation depends on the timing of refund.· Refund after receiving legal retirement age (current 62 years old): 50% of refund amount· Refund before the legal retirement age: 100% of the refund amount[tax rate]
20% of the current non-resident tax rate will be imposed.
[Early withdrawal penalty]
If they receive a refund before the legal retirement age, they will be charged 5% of the withdrawal amount separately from the withholding tax. -
procedure
Submission of the declaration and payment of withholding tax are stipulated from the date of payment to the 15th day after the next month. Also, for the declaration form, use one of the following types of Form IR 37 A / B / C / D.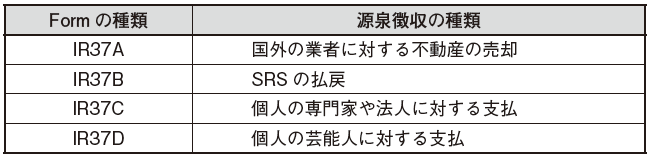 Also, if the following conditions are met, Form IR 37 can be filed twice a year on June 15 and December 15 in a batch.The payment date is the date of payment based on agreement or contract, but if there is no agreement or contract, it will be defined as the date stated on the invoice.· When tax exemption can be asserted in full by the tax treaty· You can claim a tax exemption due to royalty incentives■ Penal Provisions on Withholding CollectionIn case of delay or accrued payment concerning payment of withholding tax, the following penalty is imposed.· In cases where an additional tax of 5% is imposed➡The withholding tax has not been paid by the due date· In cases where an additional tax of up to 15% is imposed➡ If the withholding tax is not paid and the due date exceeds 30 days, an additional tax of 1% is added every month
Also, if the following conditions are met, Form IR 37 can be filed twice a year on June 15 and December 15 in a batch.The payment date is the date of payment based on agreement or contract, but if there is no agreement or contract, it will be defined as the date stated on the invoice.· When tax exemption can be asserted in full by the tax treaty· You can claim a tax exemption due to royalty incentives■ Penal Provisions on Withholding CollectionIn case of delay or accrued payment concerning payment of withholding tax, the following penalty is imposed.· In cases where an additional tax of 5% is imposed➡The withholding tax has not been paid by the due date· In cases where an additional tax of up to 15% is imposed➡ If the withholding tax is not paid and the due date exceeds 30 days, an additional tax of 1% is added every month
-
-
-
Tax treaty
■ Outline of tax treatyTax treaty is an agreement (treaty) between countries based on the composition to be concluded between countries for the purpose of avoiding double taxation and prevention of tax evasion. Since it is a promise between nations, it will be applied in preference to the domestic law prescribed by each country. In other words, even if it is "taxed" in domestic law, if it is said that it is "tax free" in the tax treaty, it can be treated as "tax exempt". The countries in which Singapore has a tax treaty are as follows.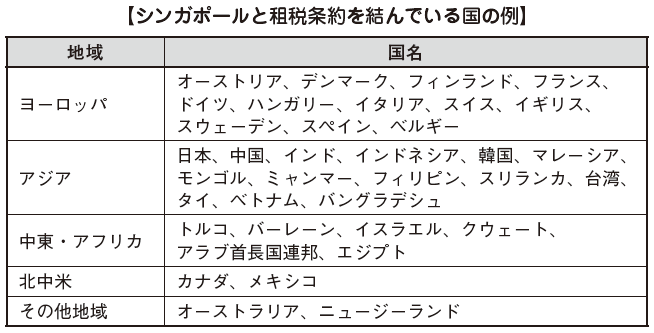 ■ Japan Singapore Tax Treaty (Japan-Japan Tax Convention)[Definition of PE (Japanese-Tax Convention Article 5)]In the Convention, permanent establishment (PE: Permanent Establishment) is defined, and the following are stipulated as PE.· Office managing business· Branch· Factory, workshop· Mines, petroleum or natural gas wells, quarry and other places to collect natural resources (excluding places used only for purchasing and storing assets)· In a supervisory activity related to construction work etc., if it exists for more than 6 months (construction PE)· In cases where the agent has the authority to conclude a contract on behalf of a Japanese company in Singapore and exercising this authority iteratively (referred to as agent PE)[Taxation on Dividends (Japan - Tax Convention Article 10)]Taxation on dividends will be imposed on dividends to be paid to a corporation that is a resident of one Contracting Party and a legal entity of another Contracting Party. In the following cases the tax rate will be determined.
■ Japan Singapore Tax Treaty (Japan-Japan Tax Convention)[Definition of PE (Japanese-Tax Convention Article 5)]In the Convention, permanent establishment (PE: Permanent Establishment) is defined, and the following are stipulated as PE.· Office managing business· Branch· Factory, workshop· Mines, petroleum or natural gas wells, quarry and other places to collect natural resources (excluding places used only for purchasing and storing assets)· In a supervisory activity related to construction work etc., if it exists for more than 6 months (construction PE)· In cases where the agent has the authority to conclude a contract on behalf of a Japanese company in Singapore and exercising this authority iteratively (referred to as agent PE)[Taxation on Dividends (Japan - Tax Convention Article 10)]Taxation on dividends will be imposed on dividends to be paid to a corporation that is a resident of one Contracting Party and a legal entity of another Contracting Party. In the following cases the tax rate will be determined.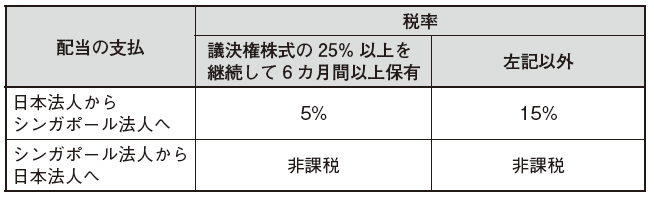 [Taxation on interest (Japan-Japan Tax Convention 11 Article)]Taxation on interest is imposed on the interest to be borne by one Contracting Party and paid to the resident of the other Contracting Party up to 10% of the interest amount. However, if the payee is a government or local public entity of the other Contracting Party, the interest will be tax exempt.[Tax on royalties (Japan-Star Tax Convention 12 Article)]For royalties, charges that do not exceed 10% tax will be imposed on royalty incurred by one Contracting Party and paid to residents of the other Contracting Party.
[Taxation on interest (Japan-Japan Tax Convention 11 Article)]Taxation on interest is imposed on the interest to be borne by one Contracting Party and paid to the resident of the other Contracting Party up to 10% of the interest amount. However, if the payee is a government or local public entity of the other Contracting Party, the interest will be tax exempt.[Tax on royalties (Japan-Star Tax Convention 12 Article)]For royalties, charges that do not exceed 10% tax will be imposed on royalty incurred by one Contracting Party and paid to residents of the other Contracting Party. -
Foreign tax credit
The Foreign Tax Credit (FTC) is a measure for adjusting double taxation of international income by deducting taxes paid outside of the country from overseas source income, from the taxes of the country of residence and this systems are defined as a method..png) ■ Foreign tax credit based on tax treatyAccording to the tax treaty, Singapore resident corporation can apply for a tax deduction of foreign tax (DTR: Double Taxation Relief) taxed on foreign source income generated in the signatory country and paid to the Contracting State.■ Unilateral tax deductionA resident corporation in Singapore is taxed on foreign source income generated in a country that has not concluded a tax treaty and can apply for deduction of foreign tax amount paid. This is called Unilateral Tax Credit (UTC).However, in order to apply for a one-time tax deduction, it is necessary to fulfill all three requirements below.· Be a resident of Singapore in taxable year· Foreign taxation has already been paid or planned to be paid abroad· The income is taxable in Singapore■ Pooling systemThe pooling system is a system that sums the taxes imposed on foreign taxes and can be deducted from the sum of Singapore taxes on all corresponding incomes. It was adopted from 2012 tax year, was introduced for the purpose of simplifying taxation and tax reduction on foreign source income. This system is one incentive for business activities with Singapore as a regional headquarters.In order to apply the pooling system, the following requirements must be satisfied.· The foreign source income is taxed in its source country· When the foreign source income is acquired in Singapore, the highest corporate income tax rate of the source country of the income is 15% or more· International source income is taxable in Singapore and qualified to apply foreign tax credit
■ Foreign tax credit based on tax treatyAccording to the tax treaty, Singapore resident corporation can apply for a tax deduction of foreign tax (DTR: Double Taxation Relief) taxed on foreign source income generated in the signatory country and paid to the Contracting State.■ Unilateral tax deductionA resident corporation in Singapore is taxed on foreign source income generated in a country that has not concluded a tax treaty and can apply for deduction of foreign tax amount paid. This is called Unilateral Tax Credit (UTC).However, in order to apply for a one-time tax deduction, it is necessary to fulfill all three requirements below.· Be a resident of Singapore in taxable year· Foreign taxation has already been paid or planned to be paid abroad· The income is taxable in Singapore■ Pooling systemThe pooling system is a system that sums the taxes imposed on foreign taxes and can be deducted from the sum of Singapore taxes on all corresponding incomes. It was adopted from 2012 tax year, was introduced for the purpose of simplifying taxation and tax reduction on foreign source income. This system is one incentive for business activities with Singapore as a regional headquarters.In order to apply the pooling system, the following requirements must be satisfied.· The foreign source income is taxed in its source country· When the foreign source income is acquired in Singapore, the highest corporate income tax rate of the source country of the income is 15% or more· International source income is taxable in Singapore and qualified to apply foreign tax credit[ Method of calculation]
The applicable amount of the foreign tax credit under the pooling system is the smaller of the total of foreign corporate income tax and the corporate income tax charged in Singapore against foreign source income.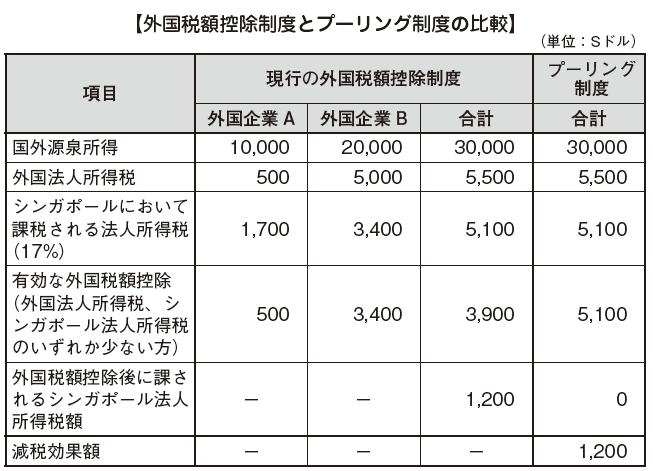
-
-
-
Websites
-
Babiliography
[1] 木村達也、江藤祐一郎、関口俊克『シンガポールの会計・税務・法務 Q&A〈第 2 版〉』税務経理協会、2012 年
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya