Sri Lanka
3 Chapter Investment Environment
-
-
1 Chapter Coming Soon
2 Chapter Basic knowledge
2.1 Basic knowledge of Sri Lanka
3 Chapter Investment Environment
3.2 Investment regulation, incentives
4 Chapter Establishment
4.1 Characteristics of business base
4.3 Company liquidation and withdrawal
5 Chapter Company Law
5.2 Shareholders (shareholders meeting)
6 Chapter Accounting
6.1 Accounting system of Sri Lanka
6.2 Disclosure system of Sri Lanka
7 Chapter Tax
7.2 Individual Issues in Sri Lanka Domestic Tax Law
8 Chapter Labor
8.3 Social security system and social insurance law
8.4 Points to keep in mind while having Japanese people in Japan
-
-
-
Investment environment
■Current status of business environment 2015The World Bank and the International Finance Corporation (IFC) have jointly announced the current state of business environment 2 0 16 in 2004. From this questionnaire you can see the assessment of the world to Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka ranked 107th in the country with the overall ranking of 189 and the region, ranking from 113th in the 2001 edition. On the other hand, Japan was ranked 34th.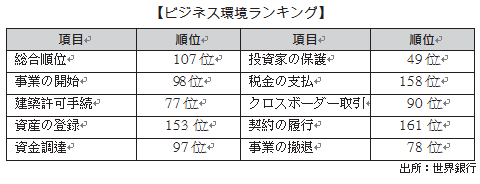 In the ranking of the 2016 edition, Sri Lanka had a particularly advantageous position over the overall ranking as "start of business" "construction permission proceeding" "fund procurement" "investor protection" "cross-border transaction" "business withdrawal" It will be 6 points.■Exchange rateAccording to the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, the exchange rate has stabilized from the latter half of 90 rupees per US dollar until the first half of 100 rupees per US dollar until November 2011, but the exchange rate rapidly depreciated from 2012, As of October 2015 it is about 1 US dollar = 140 LKR.
In the ranking of the 2016 edition, Sri Lanka had a particularly advantageous position over the overall ranking as "start of business" "construction permission proceeding" "fund procurement" "investor protection" "cross-border transaction" "business withdrawal" It will be 6 points.■Exchange rateAccording to the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, the exchange rate has stabilized from the latter half of 90 rupees per US dollar until the first half of 100 rupees per US dollar until November 2011, but the exchange rate rapidly depreciated from 2012, As of October 2015 it is about 1 US dollar = 140 LKR.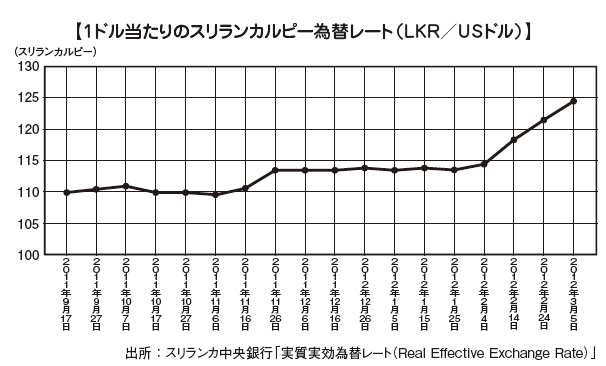 ■ Direct finance (stock) marketThe Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE: Colombo Stock Exchange) was founded in 1985 and has 293 listed companies (as of September 2014). The Colombo Stock Exchange has two main indexes.(1) ASPI (All Share Price Index) calculated from all listed stocks(2) MPI (Milanka Price Index) composed of representative 25 issues
■ Direct finance (stock) marketThe Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE: Colombo Stock Exchange) was founded in 1985 and has 293 listed companies (as of September 2014). The Colombo Stock Exchange has two main indexes.(1) ASPI (All Share Price Index) calculated from all listed stocks(2) MPI (Milanka Price Index) composed of representative 25 issues
ASPI is called TOPIX in Japan, MPI falls under the Nikkei average. ASPI started at 1,000 points in 1985 when the Colombo Stock Exchange was established, 7,055.84 points (as of November 23, 2001) and about seven times in 30 years.Since the end of the civil war since May 2009, the Sri Lanka market has gained worldwide attention, and the trading value has also expanded. On October 4, 2010, due to the large trading of Hatton National Bank, etc., the market capitalization doubled from 488.8 billion Sri Lanka rupee as of the end of 2008 to 1.921 billion Sri Lanka rupee at the end of 2009, further 2014 It is 3,660 billion Sri Lanka Rupee in September. The price earnings ratio (PER: Price Earnings Ratio) has also increased sharply, reaching 5.4 times in 2008 and 1.66 times in 2009, exceeding 26 times in 2014. Companies in Sri Lanka are analyzed that the assets contained are calculated by 16 years ago figures, and therefore there is still room for upside price in terms of price at PER.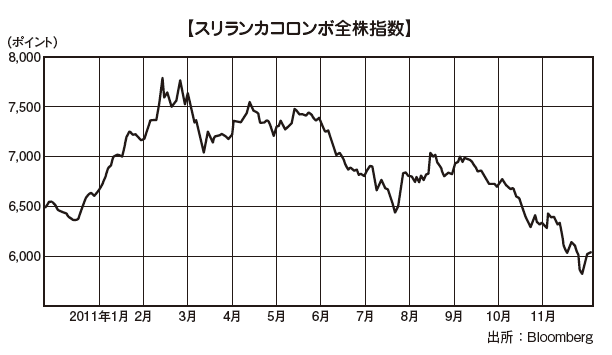 ■ FDI (FDI)Recent inward direct investment (base approved by Article 17 BOI Act) is US $ 915 million (2013) and foreign direct investment is US $ 605 million.
■ FDI (FDI)Recent inward direct investment (base approved by Article 17 BOI Act) is US $ 915 million (2013) and foreign direct investment is US $ 605 million.
Japan's Sri Lankan direct investment is US $ 38 million in 2013, 5.2% lower than the previous year's US $ 26 million, 13 th place by country / region. Fishery processing for ocean fishery / export, fruit cultivation can be mentioned as fields. Investment in Sri Lanka shows a steadily increasing trend as the declining trend of direct investment becomes remarkable worldwide due to the financial crisis.
With the conclusion of the civil war, in addition to investment demand mainly in the northern and eastern regions, investor confidence in security has also recovered rapidly in the background.There are many points that Sri Lanka must deal with in order for Japan to invest in Sri Lanka. In order to solve various problems "joint government-private forum" was held in August 2009, Japan asked Sri Lanka side to improve both soft and hard side. BOI plans to invest in the following important sectors so that it can make a concrete contribution to improve the business environment of Sri Lanka.
· Development and modernization of the tourism sector· Education and vocational skill developmentHigh-quality infrastructure (roads, communications, power stations, etc.)· Investment in agriculture[Foreign investment receipts by country]Looking at the country by country, India is a continuing investment host country, Hong Kong is ranked first in 2013, it is US $ 259 million, accounting for 19.4% of the total. The share of investment from Japan is not large, 1.9% of the total.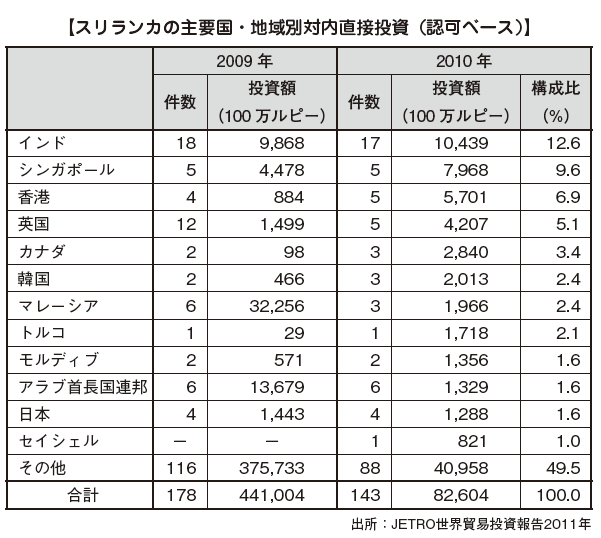 [Amount of Foreign Investment Accepted by Industry]By industry, the service industry accounted for 85.5% of the total investment at 70.642 billion rupees, making it the largest acceptance area. Major projects in the field include hotels and restaurants, information technology / software development, power generation, trading companies, agricultural projects and others.However, when comparing 2009 and 2010, the total amount will decrease more than 80%. In the manufacturing industry, the metal processing, machinery and transportation machinery sectors decreased by more than 99%, to 1.9% from the previous year, which was over 50% of the total foreign investment. It is presumed that this factor greatly affected the authorization-based investment amount from the report that the investment approval acceptance was virtually suspended by reviewing the investment incentive measures of BOI.The only increase is paper and paper products, which is recorded on a monetary basis by more than 12 times compared to 2009 and 2010.
[Amount of Foreign Investment Accepted by Industry]By industry, the service industry accounted for 85.5% of the total investment at 70.642 billion rupees, making it the largest acceptance area. Major projects in the field include hotels and restaurants, information technology / software development, power generation, trading companies, agricultural projects and others.However, when comparing 2009 and 2010, the total amount will decrease more than 80%. In the manufacturing industry, the metal processing, machinery and transportation machinery sectors decreased by more than 99%, to 1.9% from the previous year, which was over 50% of the total foreign investment. It is presumed that this factor greatly affected the authorization-based investment amount from the report that the investment approval acceptance was virtually suspended by reviewing the investment incentive measures of BOI.The only increase is paper and paper products, which is recorded on a monetary basis by more than 12 times compared to 2009 and 2010.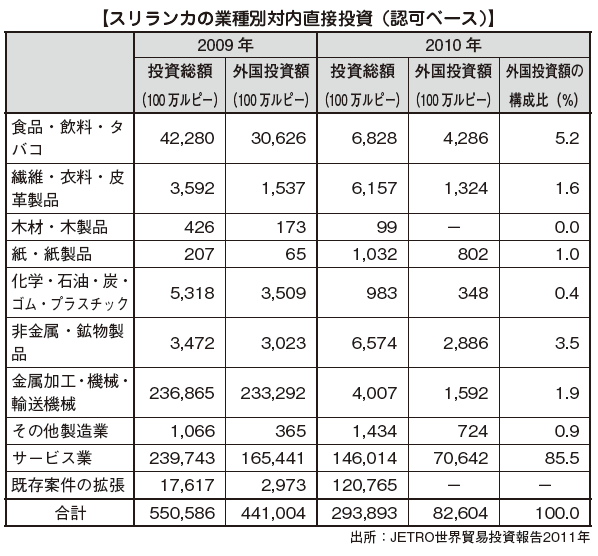 ■ State of Japanese companies entering the marketAs of 2001, the number of enterprises in Japan was 56, but to 2014 it has increased to about 118 companies (members of the Sri Lankan Japanese Commerce Association and JETRO exclusive research).Manufacturers aimed at exporting products to Japan and its neighboring countries accounted for the majority, and FDK, YKK, Mitsui Mining, Noritake, New Japan Airlines, Onomichi Shipbuilding, NTT Communications, ITOCHU Corporation, Mitsui & Co., Sumitomo Corporation, Marubeni etc. Leading companies are making progress in Sri Lanka.
■ State of Japanese companies entering the marketAs of 2001, the number of enterprises in Japan was 56, but to 2014 it has increased to about 118 companies (members of the Sri Lankan Japanese Commerce Association and JETRO exclusive research).Manufacturers aimed at exporting products to Japan and its neighboring countries accounted for the majority, and FDK, YKK, Mitsui Mining, Noritake, New Japan Airlines, Onomichi Shipbuilding, NTT Communications, ITOCHU Corporation, Mitsui & Co., Sumitomo Corporation, Marubeni etc. Leading companies are making progress in Sri Lanka. -
Investment merits and issues
■ Investment BenefitsSri Lanka is an attractive country for investing in the following three areas.· Development of infrastructure of communication, electricity and traffic· Geopolitical advantage· Prosperity of tourism industry
■ Infrastructure development[Telecommunications infrastructure]In recent years, telecommunications is the most successful field of maintenance planning. Deregulation in 1996 and partial privatization of Sri Lanka Telecom (SLT: Sri Lanka Telecom) in 1997 accelerated growth in the telecommunications field. The fixed line telephone network nearly doubled from 1997 to 2001, and a telephone network of 708,200 lines was installed. The number of users tripled from 1999 to 2001 due to intense competition, and the number of users was 667,662. The penetration rate of the telephone in 2005 reached 6.3 per 100 people including the mobile circuit.In 2009, we launched 3G (3G mobile communication system) service ahead of neighboring countries. International service providers such as Telecom Malaysia, Bharti Airtel in India, Hutchison Whampoa in Hong Kong, Maxis Telecom, etc. provide services. Moreover, large capacity submarine fiber optic cables SEA - ME - WEIII and SEAME - WEIV are passing right next to Sri Lanka, and it is expected to expand further.
[Power infrastructure]In Sri Lanka, as of 2014, 10% of electricity is covered by renewable energy, 22% by coal-fired power generation, 33% by oil-fired power generation and 34% by hydroelectric power generation.To respond to the rapidly increasing demand for power, three coal-fired power stations were established from 2011 to 2014 under the aid of the EXIM Bank of China in cooperation.The Government has set a goal to reduce the amount of electricity generated by renewable energy to 20% by 2020 and the capacity of electric power supply facilities to 2,200 MW in 2025.
[Transport infrastructure]Today, transportation in Sri Lanka depends mostly on roads, and it is said that both passengers and cargo account for 80% of the total transportation volume. Approximately 30% of the total population is concentrated in the Greater Colombo Region where the capital is located (Gampaha District, Colombo District, Colombo District, Kalutara District), and in the Large Colombo Sphere it is overloaded with roads and comprehensive Chronic traffic congestion has become remarkable since traffic management is not done, and the average hourly speed of the car at the peak time in commuting at the time of 2005 was 10 km / h, and even during the day, average travel time is only 30 km / h The government has made improvements to existing roads, development of new roads and expressways, development of rural roads and concrete pavement in order to cope with frequent occurrence of traffic accidents etc. due to an increase in traffic volume Improvements not only in urban areas but also in national road networks have given high priority to the construction of rural roads in particular.
With the "Gama Neguma" program (rural development program) that promotes government-led rural road development and concrete paving, which began in 2009, local governments and research institutes are mainly engaged and maintenance is still underway. In 2014, the Asian Development Bank made loan assistance of US $ 800 million to implement this plan in six provinces of Sri Lanka, Southern Province, Sabara Gamuwa, Central Province, North Central Province, North West Province and Kalutara District.
Railroads are an important means to reduce traffic congestion around Colombo while satisfying commuting demand. As of March 2010, Sri Lanka's railway network is 1,447 km in length, 172 stations, 10 routes, spreading radially around Colombo.
By improving railway and airport, infrastructure development project is being promoted to encourage shifts from the deviation of road use to the use of public transportation, and to activate citizen's activities and economic activities. If this situation improves, it is expected that logistics and flow of people will be smooth, improvement of the quality of people's lives, rectification of regional disparity, and economic growth of the whole country.
Port service is developed in Sri Lanka, Colombo Port is rated as Port of South Asia No. 1.
The Port of Colombo has taken on the role of a relay base in South Asia, taking advantage of geographically favorable conditions located between the Bengal Bay and the Arabian Sea. It is also the most strategic trade area between the Middle East and the Far East as well as Asia. It is a strategically important position to become a gateway to Asia that is showing the highest economic growth rate in the world, and Middle Eastern countries such as Dubai.
The Free Trade Agreement (FTA: Free Trade Agreement) signed between Sri Lanka and India, and Pakistan has also expanded the possibility of using Sri Lanka. It is active as a trade hub for 9th to Yokohama, 8 to 3 days to major Indian ports, 3 days to Singapore and 5 days to Middle East Dubai / Bahrain 5th. In addition to Colombo Airport, Mattara Rajapakusa International Airport has been built in the southern part of Sri Lanka and improvement is being promoted as Sri Lanka's second international airport.
Geopolitical advantageRegarding the geopolitical superiority, it is said that the distance to India which is a member of BRICs is only 30 km away from the nearest place. Since long ago Sri Lanka and India are deeply interacting, India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement(ISFTA: Indo Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement) is connected. As a result, the customs duties of many items do not apply to trade with India.It is also located at the midpoint connecting Africa, the Middle East and Asia, and it also shows that it is a very important country as a logistics hub. From now on, we can fully demonstrate this geopolitical advantage, and we expect great growth as next Asia.
■ Prosperity of Tourism IndustryRegarding the prosperity of the tourism industry, there are 8 World Heritage sites (6 cultural heritage sites and 2 natural heritage sites), so there is a possibility to bring in many travelers from all over the world.Furthermore, on the southwestern coast of Sri Lanka there is a brown beach called golden beach, and further down the south, the world's leading resort hotels line up. At present, the annual number of visitors to Sri Lanka will exceed 1 million in 2012, the end of the civil war and the robust economy will be primed and further growth is expected in the future. Especially from India, which has over 300 million middle classes, we can expect many visitors in the future.
Investment IssuesInvestment in Sri Lanka the following three problems are related to the environment.
(1) Government's opaque policy management
As improvement measures, improvement of supply of industrial water in the export processing zone (EPZ: Export Processing Zone) managed by BOI and improvement of efficiency of customs clearance system can be mentioned.
(2) Unstable political and social conditions
Although the civil war continued and it came to an end, it still has the impression that the social situation is unstable, and furthermore the uncertain legal system is also one factor that can not be invested.
(3) Inadequate development of infrastructure
Transportation by railway is also used in Japan in view of the environment, railway transport is common. Meanwhile, in Sri Lanka the railway is a minor presence, not only the transport sector, but even passenger transport is not expanded.
As mentioned in the above investment merits, the infrastructure side has been gradually improved. Although it can be mentioned as an investment task now, completing maintenance will lead to economic growth in Sri Lanka.
-
-
-
Investment regulation and incentives
■Investment regulationBecause various notifications have been issued, it is difficult to systematically organize investment restrictions in Sri Lanka for reasons such as differences in responses by officials in charge of authorities.■ Prohibited Industry / Regulated IndustryRegulation of foreign capital of Sri Lanka is established by the Investment Bureau (BOI). Depending on the degree of investment regulation, it can be roughly divided into three categories.
[Industry in which entry of foreign capital is prohibited]For the following businesses, investment by foreign capital companies is prohibited.
· Money lending business· Pawn shop business· Retail trade with capital less than US $ 1 million· Coastal fishery
[Industry requiring automatic approval or conditional approval by Government of Sri Lanka]When conducting the following businesses, if the foreign capital ratio is 40% or less, you can do business with automatic approval. However, if the foreign capital ratio exceeds 40%, you will have to go through the BOI review and obtain project approval for each investment case.· Production of export goods subject to quota restriction established internationally by export from Sri Lanka· Tea · Rubber · Coconut · Cocoa · Rice · Sugar · Spice cultivation and primary processing· Mine extraction and primary processing of irreproducible natural resources· Forestry using wood from Sri Lanka· Fishery (ocean fishery)· The media· Education industry· Freight transportation·Travel agency· Shipping agency business
[Industry requiring prior approval by related government agencies]When conducting the following projects, you must obtain prior approval of the relevant government agency (in certain cases, BOI).· Air transportation business· Coastal shipping industry· Industry projects listed in the second schedule of Law No. 46 of 1990, Industry Promotion Law: industries producing weapons, ammunition, explosives, military vehicles, military equipment, military aircraft, and other military hardware. Poison, narcotics, alcohol, dangerous drugs, hazardous poisons, hazardous substances, industries producing carcinogenic substances. Industry that creates money, coins, securities certificate documents.· Large-Scale Jewelry · Mechanized Mining Industry· Tornado's torso business■ Regulations concerning landForeigners and foreign companies will prohibit the purchase of land, so in the case of entering Sri Lanka, land will be leased. Applicable target is land purchased after January 1, 2013.
So far, foreign companies were able to purchase land in Sri Lanka when paying asset transfer tax of 100% of the purchased asset value, but it was enacted in 2015 (Law No. 8 of 2004, Fiscal Law and the same revision) Under the New Land Law, land purchasing is forbidden when foreign companies and foreign capital hold shares of more than 50%.
For condominiums, it is not applicable to the 4th floor or above (the 1st to 3rd floors are prohibited to be occupied by foreign companies / foreign capital). In the future, in addition to the current stamp duty and value added tax, lease tax on the lease of the land portion is imposed.■ Branch regulationsIt is possible to set up a branch office to do activities similar to the head office without setting up a local corporation. In the case of a branch office, the content of regulation differs partly due to a different notice from the case of establishing a local corporation.
[Prohibited industries]Businesses and trading activities that overseas branches should not do· Money lending · pawn shop business· Retailing with capital less than 2 million US dollars· Coastal fishery· Brown, rubber tree, coconut, and rice cultivation and primary processing· Mining and primary processing of nonrenewable domestic resources· Freight transportation· Shipping agency business· Mining of gems by machine· Lottery business· Security services including security consulting for individuals and private companies
[From the exchange control agency] Industry requiring prior approval]Production of goods whose export of Sri Lankan is subject to internationally defined quota restrictions· Cultivation and primary processing of plants as raw materials for sugar, cocoa, spices· Timber related business using wood from Sri Lanka· Ocean fishery· The media· Education industry· Travel agency overseas· Regional air transportation industry· Coastal shipping industry· All business related to manufacturing or production of the following items· Weapons, ammunition, explosives, military vehicles, military equipment, military aircraft, and other military equipment· Poisons, anesthetics, alcohol, powerful drugs, toxic substances, hazardous substances, and carcinogenic substances· Currency, coins, or securities
■ Regulations concerning capital[When Not Obtaining BOI Approval]Local company ➡ Retail / wholesale business (BOI opinion, but no regulation in ROC opinion) over US $ 100,000, logistics industry up to 40% foreign capital for cargo shipping / shipping agency, others (aviation / coastal transportation) Within the permitted range of.[When acquiring BOI certification]BOI Act 1 6 Authorization ➡ Retailer · Wholesale business (BOI opinion) is over US $ 100,000, logistics industry is up to 40% foreign capital for cargo shipping / shipping agency, and other permitted range.BOI Act 1 7 Certification ➡ No regulation (Exception: Part of domestic production enterprises has exceptional treatment).
[Overseas branch]In the retail / wholesale business (BOI opinion, capital over 200,000 dollars in ROC opinion) over 2 million US dollars, logistics industry banned foreign capital for cargo shipping / shipping agency. Within other permitted range■ Exchange control regulation[Trade Transaction]Regarding the import transaction of goods there is no particular regulation. Importers can purchase necessary foreign currencies from commercial banks at the time of delivery of import permission letters, import letters of credit issuance request, shipping documents of bill payment terms, or shipping documents under acceptance conditions.Exporters can freely make export transactions without being subject to regulation of foreign exchange control. For the export fee, you can choose either to deposit to a rupee-denominated account that is opened in a commercial bank in Sri Lanka or to a foreign currency account, or to reserve it in a commercial bank outside the country.
[Non-trade transaction]As a general policy, for transactions that fall under the category of international balance of payment transactions, you can remit money abroad freely by submitting the remittance purpose.For example, remittance of salaries of employees employed in Sri Lanka companies, dividends to shareholders, etc. are applicable.[Capital transaction]If you directly liquidated the investment capital, you can remit to your home country. It is also permitted to remit the deposit balance to your home country when the expatriate leaves Sri Lanka.On the other hand, if a resident of Sri Lanka invests abroad, it will be accepted only if it promotes the export of Sri Lanka and brings about benefits such as technology transfer and transfer of expertise.[Borrowing]Borrowing from a foreign countryCompanies that have concluded an agreement with BOI in accordance with Article 17 of the BOI Act,You can borrow money from foreign countries without regulation of management, but in that case you must repay it from foreign currency revenue. In exchange of rupees for foreign currency, central bank approval is required.For other companies, short-term borrowing from foreign countries is regulated. Mid- to long-term borrowing is permitted depending on borrowing conditions such as interest rate. When borrowing funds from a foreign country, you must obtain approval from the central bank.
Borrowing in JapanCommercial banks in Sri Lanka are permitted to lend foreign currency to exporters that are expected to acquire foreign currency sufficiently. In this case, principal and interest payment must be made in foreign currency.
[Regulations concerning branch offices]FinancingIn the case of a branch, the method of financing is restricted as follows.· You have to invest at least US $ 200,000 through rupee-denominated special account called "Inward Investment Account" (IIA) at Sri Lankan commercial bank· The remittance certificate must be submitted to the company registration office (Registrarof Companies) within 30 days from the registration date
Remittance to home countryIn case of remittance from overseas branch to home country, the following documents are required.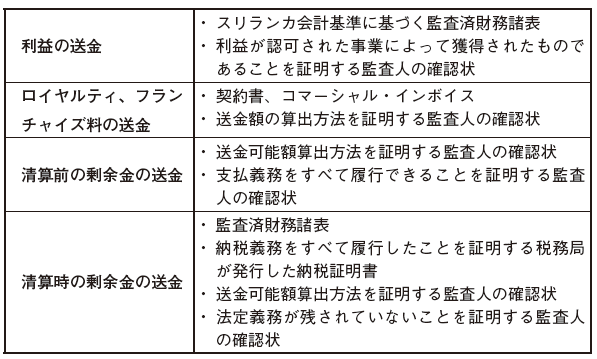
[Bringing in / carrying out by cash]If you bring over 15,000 US dollars into Sri Lanka you have to declare at customs. However, if you intend to bring over US $ 5,000 or more when you leave Japan, you will need to file a customs declaration even if you bring in less than US $ 15,000.If you bring foreign currency of US $ 10,000 to overseas, customs declaration is unnecessary and you must file a declaration when bringing over 5,000 US dollars with banknotes.
■ Investment incentivesIn order to attract foreign investment, BOI gives incentive measures centering on the reduction and exemption of taxes, which is a great advantage for enterprises in charge. However, there are some ambiguous points in operation, such as which laws are in force, which laws apply. Here, we are posting content on tax exemption of income tax which is currently announced by BOI. In addition to this, we exclude customs duties etc. are allowed by industry. In the case of actually proceeding, it is necessary to check the presence or absence of preferential treatment and contents beforehand.The criteria for providing incentives for BOI are set as follows.
· There are public merits in Sri Lanka· Contributing to acquisition of foreign currency· Increase employment· Provide technology
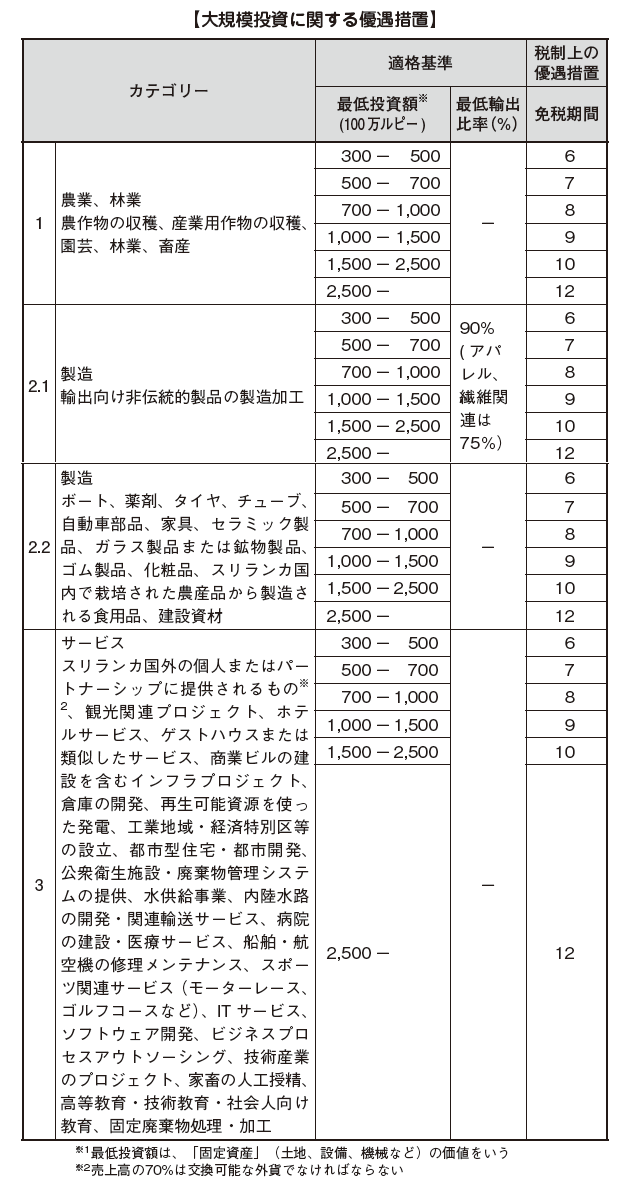
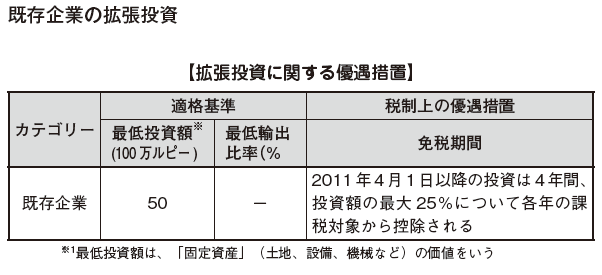
[Incentive measures under Article 17 of the BOI Act and 17 A of the Internal Revenue Code]According to the 2012 budget plan, the contents of incentives will be systematically developed. Depending on the size of the investment, it distinguishes preferential content, and it became a mechanism that can obtain greater merit as large investment is made.
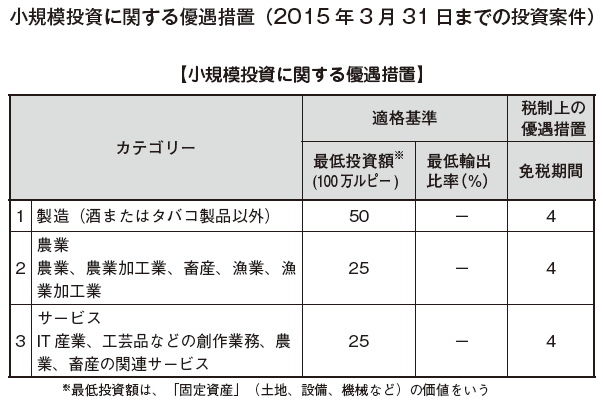
In addition to the above, tariffs on imports of raw materials of capital goods and export-type projects are exempted.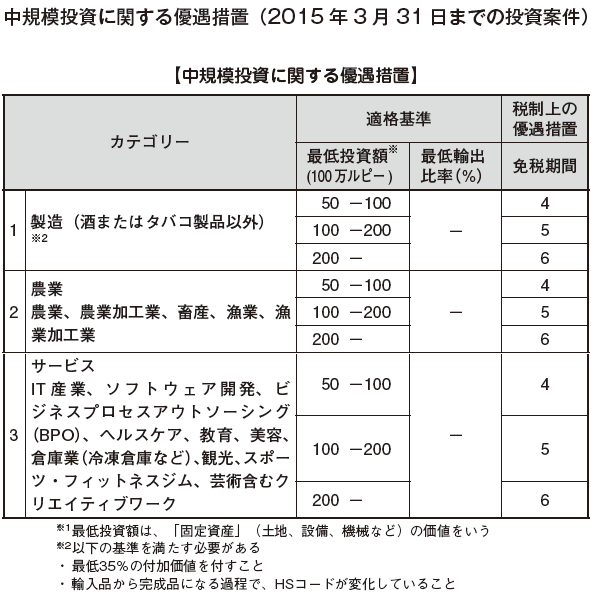
In addition to the above, tariffs on imports of raw materials of capital goods and export-type projects are exempted.
In addition to the above, tariffs on imports of raw materials of capital goods and export-type projects are exempted.
Import substitution industrial investmentIn order to nurture alternative industries of import, incentives for taxation will be given to industries that fall under the following.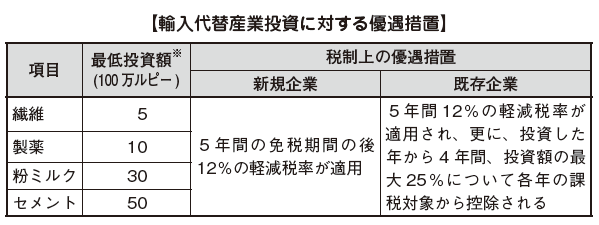
Common incentivesIn the case of receiving preferential treatment under Article 17 of the BOI Act, in order to reduce the costs incurred on imported goods such as machinery and equipment related to the project, the VAT, tariff, PAL (Port and Airport Development Tax) Will be exempted during project implementation period if approved by BOI.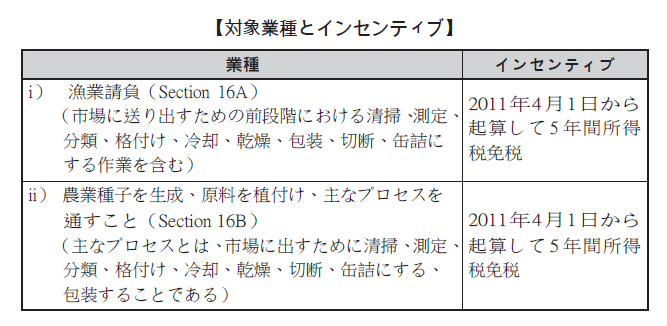
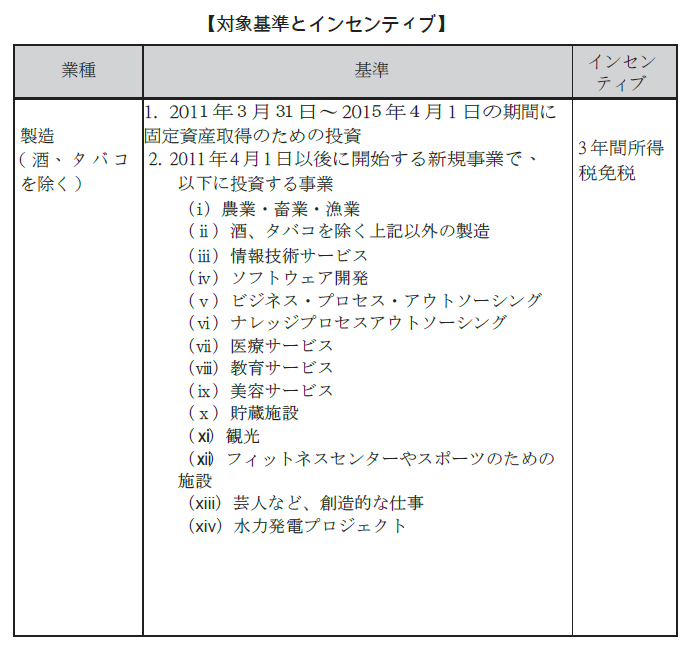
■ Industrial park informationThere are 10 export processing zones (EPZ: Export Processing Zone) and two industrial parks (IP: Industrial Park) in Sri Lanka, mainly in the area near Colombo.The most popular enterprises are Katunayaka EPZ, which is located about 30 km north of Colombo Port, with more than 80 companies operating.In addition to the infrastructure being maintained, the EPZ is given tax incentives, which brings significant benefits to enterprises.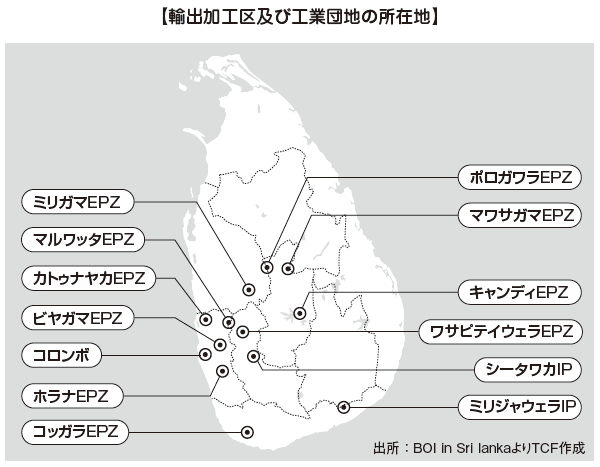
-
-
-
Websites
[1] JETRO
[2] http://www.ide.go.jp/Japanese/Research/Region/Asia/Srilanka/index.html
[3] 外務省
[4] コロンボ証券取引所
[5] スリランカ各国情勢
[7] スリランカ株式投資情報
[8] MSN天気予報
[9] ジェトロ世界貿易投資報告2011年版Departmentof Election
[10] World Bank Search
-
Babiliography
[1] ARCレポート2006スリランカ
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya