Sri Lanka
2 Chapter Basic knowledge
-
-
1 Chapter Coming Soon
2 Chapter Basic knowledge
2.1 Basic knowledge of Sri Lanka
3 Chapter Investment Environment
3.2 Investment regulation, incentives
4 Chapter Establishment
4.1 Characteristics of business base
4.3 Company liquidation and withdrawal
5 Chapter Company Law
5.2 Shareholders (shareholders meeting)
6 Chapter Accounting
6.1 Accounting system of Sri Lanka
6.2 Disclosure system of Sri Lanka
7 Chapter Tax
7.2 Individual Issues in Sri Lanka Domestic Tax Law
8 Chapter Labor
8.3 Social security system and social insurance law
8.4 Points to keep in mind while having Japanese people in Japan
-
-
-
Basic knowledge of Sri Lanka
■ Formal Country ➡ Sri Lanka Democratic Socialist RepublicEnglish name: Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri LankaSinhala language name: ශ්රීලංකාප්රජාතාන්ත්රිකසමාජවාදීජනරජයTamil language name: இலங்கைசனநாயகசோஷலிசககுடியரசுThe country name of Sri Lanka is Sinhala, "Sri = shining" and "Lanka = Island", meaning "a shining island." In Kanji, it is written as "Tin Lan".
■National flagSri Lanka was once called Ceylon. Ceylon is a Sanskrit word meaning "the island of the lion" and its remnant appears in the national flag. The national flag was first established in 1948 as a self-governing body within the Commonwealth of the United Kingdom, which has been revised several times and is in its present form.
The sword represents the authority of the king, the yellow shows the protection of Buddhism, and the green and orange bands mean the Muslim Moorish and the Hindus Tamil who are minorities. These two colors are used even in the flag of India, and it is regarded as a symbol of ethnic harmony. Furthermore, four Buddhist leaves of Buddhist have been added, and since 1978 it became the current national flag.
■ Area · Country land ➡ 65,610 ㎢ (about 0.17 times of Japan)Sri Lanka is located in the southeast of India, surrounded by Indian Ocean, Manly Bay, Bengal Bay and Pork Bay, separated from India by the Pork Strait. The land area is 65,610 ㎢, about 0.17 times the size of Japan, about 0.8 times that of Hokkaido. The Indian Peninsula connects with the Adams Bridge which is followed by the sands and shoals, and between the northwest and the Indian Peninsula coral reefs are developed on a large continental shelf.
■ Capital ➡ Sri Jaya Waldana Pula KotteEnglish name: Sri Jayewardenepura KotteAlthough the capital city is Sri Jaya Waldana Pula Kotte, the de facto capital is Colombo.■ Year ➡ Buddhist calendarAdding 544 years to the Christian calendar is Buddhist calendar. The Buddhist calendar used in Sri Lanka is supposed to be the first year of the era of Buddha in 544 BC which is the year when Buddha went through. Because in Thailand, they use 543 BC as the first year of Buddhist era, Sri Lanka and Thailand have the same Buddhist calendar but will also result in one-year difference.
Buddhist calendar 2560 = year 2016 = Heisei 28
■Climate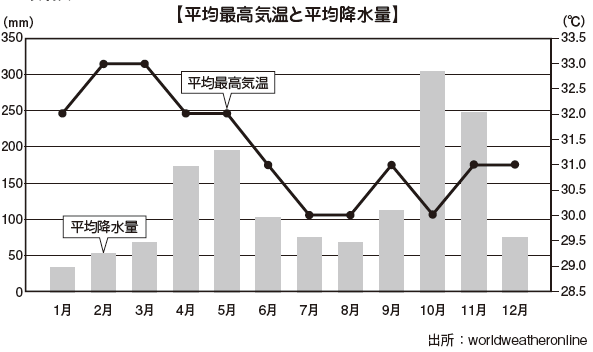
The climate of Sri Lanka is greatly affected by the Northeast monsoon and the Southwest monsoon.The Northeast monsoon brings rain in the entire island in the November to March era, especially rain in the mountains and the northeastern bank region. The southwest monsoon creates two climates, dry and rainy, across the mountain ranges (Piduruthalagala) running from the middle to the south in the period of May to September. On the northeastern slopes of the mountains, only a small amount less than 508 mm will rain, the weather will dry for a long time, while heavy rains will be brought to the southwest slope of the mountain range and the flat area in the southwestern part of the island.
Thus, the annual rainfall concentrates in the southwestern part, and the northern part, the eastern part, and the southeast part are less than 1,905 mm.
A zone with a rainfall of more than 1,905 mm is called a wetland area, which occupies a quarter of the area of the island, 60 to 70% of the population, almost all of the cultivated areas of black tea, rubber and coconut, 40% of the area belongs to this area. On the other hand, the area of less than 1,905 mm is called a dry zone, but rice cultivation and slash-and-burn agriculture are operated in the jungle highland here.
The temperature continues for the maximum temperature throughout the year, over 30 ℃. Humidity exceeds 75% on average, and it feels hot above the temperature.
■ Time difference ➡ - 3.5 hours (UTC: + 5: 30)There is a time difference of 3.5 hours with Japan. Daylight saving time is not introduced.
■ Population ➡ 20.67 million (2014)More than 70% of the people are Sinhalese, followed by Tamil Sri Lanka and Moore.
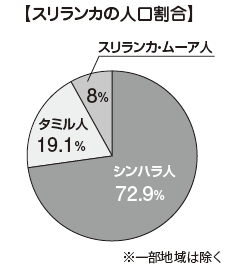 ■ Language ➡ Sinhala TamilThe official languages are Sinhala and Tamil. In terms of population proportion, Sinhala is 74% and Tamil is 18%. English is said to be a link language connecting Sinhalese and Tamils (Link Language), about 10% of the population can speak, English is also used within the government.
■ Language ➡ Sinhala TamilThe official languages are Sinhala and Tamil. In terms of population proportion, Sinhala is 74% and Tamil is 18%. English is said to be a link language connecting Sinhalese and Tamils (Link Language), about 10% of the population can speak, English is also used within the government.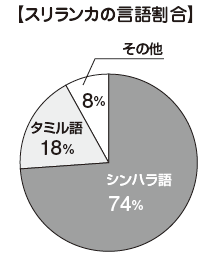
■ Currency ➡ Sri Lanka Rupee (LKR)In Sri Lanka Rupee (LKR), the auxiliary unit is Sri Lanka cents. There are 10 kinds of banknotes of 2,000, 1,000, 500, 200, 100, 50, 20, 10, 5, 2 rupees, but 5 rupees and 2 rupee bills are hardly circulated.Types of coins are 10, 5, 2, 1 rupee, 50, 25, 10, 5, 2, 1 cents, and less than 50 cents are hardly distributed. The exchange rate is 1 LKR = 0.84 yen as of December 2015.
■ReligionBuddhism (70%), Hinduism (10%), Christianity (11.3%), Muslim (8.5%).
■ Main history of Sri Lanka.png) ■ Political system ➡ Republic
■ Political system ➡ RepublicHead of state: President Maithripala Sirisena
In January 2015, President Maithripala Sirisena took over as former president Rajapaksa and became the new president. Although the former administration had received great support from China, Mr. Sirisena is expected to depart from dependence on China and it is thought that diplomacy will increase access to neighboring country India.[Administrative Organization]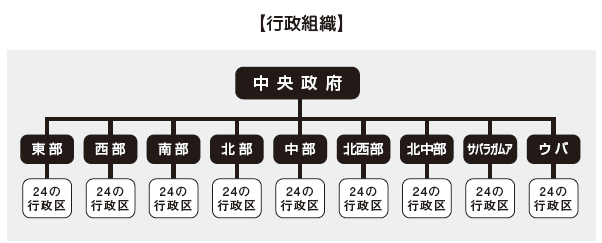
There are approximately 100 ministries and agencies within the central government, including major ministries and agencies 24. In addition, the region is divided into nine provinces of eastern, western, south, north, central part, northwestern part, north central part, Sabaragamua, Uba, and there are 24 administrative districts (districts) in each state. In the prefecture there are categories of the city (Municipal Council), the county (Urban Council), the district (Pradeshi Sabhawa), and they are responsible for regional administration in each region.
[Diet]
In a unicameral system, the capacity is 225 and the term of office is 6 years. 196 people out of the capacity are decided by the proportional representation system of 22 blocks and the remaining 29 people allocate seats by the voting rate of each party in 22 blocks as a whole.
In the general election held in August 2015, the Unified National Party (UNP) led by President Sirisena ruled over the victory and formed a coalition with the Sri Lanka Liberals (SLFP).Since President Sirisena has stated the expulsion of corruption and the promotion of diplomatic relations with Japan, Europe and the United States, expectations are placed on future relations between the two countries. At the same time, the former president of Rajapakusa who will promote the undergraduate route will also be elected, and the possibility of strengthening the friction between the ruling and opposition parties will require attention in the future.■ Education system
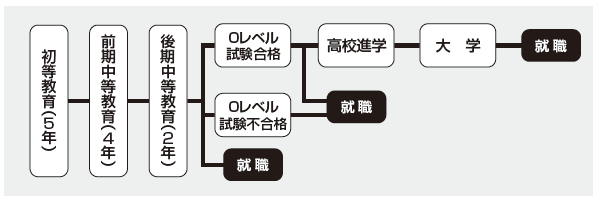
The education system is 5, 4, 2, 2 system. After 5 years of primary education, and 4 years of first half of secondary education, there is2 years of second half of secondary education. This second-term secondary education is the preparation period for nationally unified examination O (O) level examination. O level test is equivalent to junior high school graduation and high school entrance examination in Japan. Only those who pass the O level can go on to high school, and for the two years of high school, it is preparatory period to go on to university.
Among the students who entered elementary school, 70% of students going to the O level are among O grades, 36% of the students going to high school. The entrance to the university is quite a challenge, and the passing rate is about 10% of the examinees. In addition,
there is a gratuity education system from kindergarten to university, the citizen's literacy rate boasts 92%. Even though India's literacy rate in neighboring countries is in the 60% range, we can see that in Sri Lanka primary education is spreading throughout the country.
Also, most students are getting popular with practical lessons such as foreign languages and accounting because they get jobs after secondary school or high school graduation. As a result, it is also characterized by the number of qualified acquirers of Certified Public Accountant (CIMA), an international professional qualification, second largest after the UK.
On the other hand, there are also present conditions that the number of IT related fields is overwhelmingly small. The cause is that in Sri Lanka there are only 15 university facilities (as of September 2014), and the university entrance rate is only about 18%. This figure is very low compared with the average 30 to 40% of developed countries.
As you can see, in Sri Lanka, although the literacy rate is high, it is understood that sufficient professional education has not been done. This also has a tremendous influence on working, which is why we can not escape from the situation of low skill and low wage.
■ Politics · Economics
At the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Summit held on April 29, 2010, President Rajapaksa met with former Prime Minister Manmohan Singh in India. Both the leaders
discussed the ethnic problems of the Tamil community in Sri Lanka, and agreed to advance efforts towards solution. Prime Minister Shinzin blessed the victory of President Rajapaksa 's election and expressed expectations for expanding the exchanges of government officials including mutual visits by the two leaders.
Although Sri Lanka is blessed with abundant potential in terms of both human resources and geographical conditions, it has not been able to achieve rapid economic growth by the civil war. However, after the end of the civil war, due to its economic growth potential and promising investment destination, it became known as a wonder of Asia. Also in the parliamentary election in August 2015, the ruling party Unified National Party (UNP) of the new Syrizina president will become the first party, further expanding corruption bureaucracy and Japan-Sri Lanka relationship is expected. In addition, because President Rajapaksa, a former parent of the Chinese school, has also won a seat, friction among political parties is expected within the parliament.
The research company Economist Intelligence Unit ranks Sri Lanka 10th in the top 10 fastest growing countries in the world in 2014.
■ Relationship between Japan and Sri Lanka
Since the establishment of diplomatic relations in 1952, good relations have continued, mainly between trade and economic and technical cooperation between Japan and Sri Lanka. When the former Soviet Union proposed to divide Japan at the San Francisco Peace Conference in 1951, Mr. Jaya Waldana of Sri Lanka, who was a Ceylon country at the time, quoted the words of Buddhism and appealed the spirit of forgiveness. Thanks to that speech, it is said that Japan was able to be independent without being split. As represented by this episode, the relationship between Japan and Sri Lanka has been good for a long time.
Based on this history, Japan has provided various support to Sri Lanka. Since the ceasefire agreement in 2002, from the perspective of contributing to the "contribution to peace consolidation", Mr. Yasuo Akashi General of the UN Secretary-General for the UN is appointed "Government representative of peace-building and reconstruction and restoration in Sri Lanka" and regularly appointed Sri Lanka We have been dispatching to the people concerned, and have been working on related people. In addition, in March 2003, peace negotiations with the LTTE were held in Hakone, and in June of the same year, "Tokyo Conference on Reconstruction and Development in Sri Lanka" was held to actively support the peace process in Sri Lanka.
Furthermore, at the "Tokyo Conference on Reconstruction and Development in Sri Lanka", the 4 Co-Chairmen countries (Japan, the US, Norway and the EU) regularly meet to monitor the situation of the Sri Lankan peace process. After the end of the civil war in May 2009, through opportunities of Sri Lanka's VIP coming and going, they will urge the Sri Lankan government to make efforts to achieve a national reconciliation in order to achieve a permanent peace and sustainable development and also support the government as well.
On cultural aspect, the Sri Lankan Cultural Heritage Exhibition was held at the Tokyo National Museum from September to November 2008, co-sponsored by the museum, the Yomiuri Shimbun and the Sri Lankan government. In this exhibition, more than 150 cultural heritages centered on Buddhism were exhibited, and during the period Emperor Hiroshi Emperor 's Emperor' s Emperor 's Emperor' s Emperor and Empress was there, and about 80,000 visited. In addition, the Sigilly Rockford attached museum, which is the world cultural asset boasted by Sri Lanka, opened with the full support of Japan, and Prime Minister Fukuda participated in this opening tape cutting. Buddhist relatives also provide economic assistance to orphanages, child facilities and temples to cultural exchanges.
Prime Minister Shinzo Abe visited Colombo in September 2014 and met with President Rajapaksa. Japanese Prime Minister visited Sri Lanka for the first time in 24 years and emphasized President Rajapaksa, who had taken New Policies at the time, strengthening relations with Japan and economic importance. At the talks, agreement was reached on a cooperative structure in maritime security and agreed that the two countries will strengthen ties at international negotiation places and build closer relations than ever before.
In August 2015, the new president of Silisena took office and has changed diplomatic routes from past diplomacy to omnidirectional diplomacy. In October 2015, Prime Minister Wikla Masinha visited Japan and met with Prime Minister Shinzo Abe. It is expected that the relationship between the two countries will build more and more.[Number of Japanese residents]
1002 people (as of 2013, Survey of Japanese Embassy in Sri Lanka)
■ Politics of Sri Lanka[Internal affairs]Sri Lanka is a democratic country that employs the presidential system, and since its independence in 1988, the two major parties, the Unified National Party (UNP) and the Sri Lanka Liberal Party (SLFP), are in charge of regime alternately.At the Sri Lankan presidential election in January 2005, the opposition Party's new President Siri Sena took office with 51.28% of the votes cast, defeated President Rajapaksa who was in the presidential position since 2005, We are planning to promote diplomacy that takes into consideration the balance between Japan, India, and China from the underlying routes.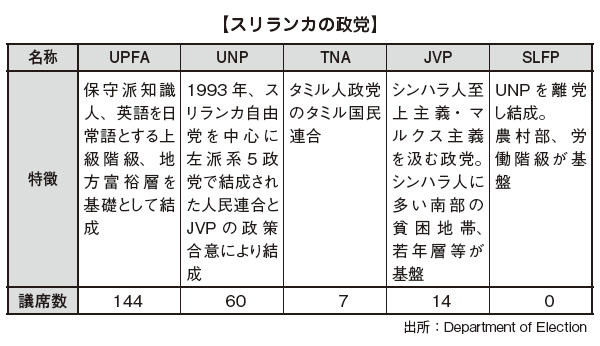
[Ethnic Issues]After independence in Sri Lanka, the Sinhalese preferential policy was taken by the government centered on majority Sinhalese. In 1948, the deprivation of the citizenship of 900,000 people, which is 70% of the Tamil people, triggered the Sinhala-Tamil ethnic problem.Minority Tamils living mainly in the northern and eastern parts of Sri Lanka seek their own rights expansion, but never realized. The trigger of the civil war is that the Tamil youth who said the North and the East region to be their own home land began an armed struggle for independence and separation. Tamil youth formed an extremist faction such as LTTE, and fought an armed struggle, and since the year 1983 battle with the government forces intensified, and it developed into a full-scale civil war.In February 2002, a ceasefire agreement was signed between the government and the LTTE through the intermediary of the Norwegian government. Thereafter, six peace talks and two direct consultations were held, but there was no progress in peace between the government and the LTTE, and the situation continued to always violate the ceasefire agreement.At the end of July 2006 the ceasefire agreement was eventually broken and the battle intensified. In January 2008, the Sri Lankan government decided to withdraw from an ineffective ceasefire agreement in light of the frequent occurrence of military conflicts and terrorist incidents, and officially lost the ceasefire agreement.In January 2009, the government forces dropped all major LTTE bases in the north, and the remaining forces of the LTTE were driven to the northern coastal area in March. LTTE had carried over 200,000 internally displaced people (IDP: Internally Displaced Persons) as "human shields". However, the government announced that she had rescued all of the IDP by May, killed the Pravascaran LTTE leader and dissolved the LTTE. Former president Rajapaksa declared the end of battle in the National Assembly and declared in future that it will proceed with resettlement of many IDPs and national reconciliation.
■ReligionReligion is about 70% of Buddhist (Buddhist divination) about the whole population, mostly Sinhalese. Tamil people, mainly Hinduism, 10%, Christians and Muslims follow.Sri Lanka is a Buddhist country, but the caste system is seen in both Sinhalese and Tamil as well as neighboring India.In the case of Sinhalese, land cultivators called Goigama, the closest one to the king during the Candy Kingdom, had authority is the highest caste. The goyama is still influential in political and administrative aspects, accounting for about half of the Sinhalese.On the other hand, in the case of the Tamils, the top caste is called Vellalar, which is also a land cultivator, accounting for about half of Tamils.In Sri Lanka caste there are various kinds, such as fisherman caste Karava, car basketball castor Batogama, drum beating caster Berava, beggar caste Rodi , It is closely related to occupation.
-
-
-
Economy of Sri Lanka
■Economic structureThe nominal GDP of Sri Lanka, a South Asian island country with a population of approximately 250,000 people, is US $ 67.2 billion (2001: World Bank), Pakistan of the neighboring country (232.7 billion US It is a much smaller size compared with the Bangladesh (US $ 161.7 billion).However, GDP per capita is 3,280 US dollars, which shows that it exceeds Pakistan (1,274 US dollars) and Bangladesh (1,033 US dollars) both countries. Despite tiredness in civil war for decades, the per capita national income has nearly doubled between 2001 and 2010.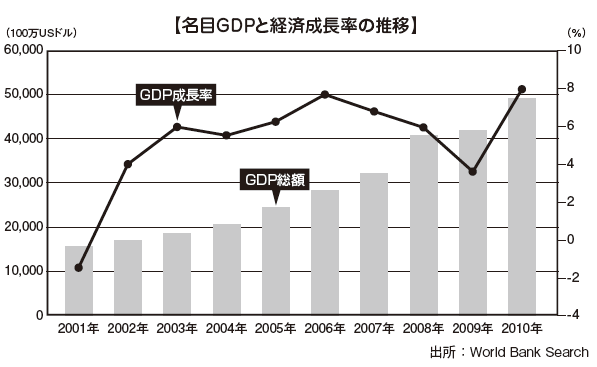
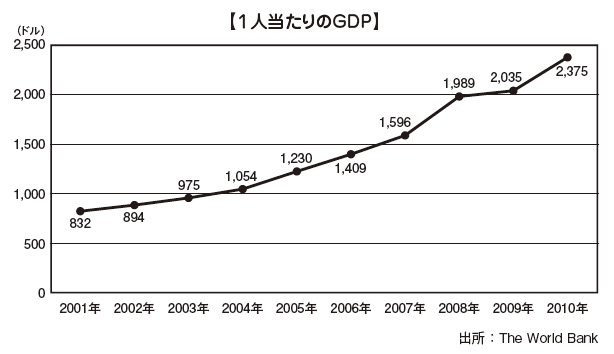 In addition, the following will be the nominal GDP (1 million US dollars) and the economic growth rate after 2011, which will be assumed values in 2015.
In addition, the following will be the nominal GDP (1 million US dollars) and the economic growth rate after 2011, which will be assumed values in 2015.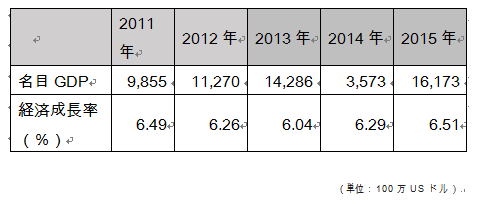 And the following is the nominal GDP per capita (US dollar), and here is also the assumed figure for 2015.
And the following is the nominal GDP per capita (US dollar), and here is also the assumed figure for 2015.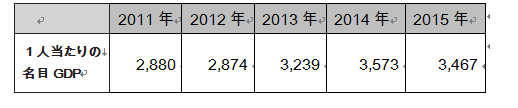
[Current account]The civil war lasting 25 years ended in 2009, and next year in 2010 the economic activity became active due to the recovery of the world economy and reconstruction demand, public investment and consumption expanded, real GDP growth rate exceeding the previous year was achieved, Trade value also recovered to the 2008 level. The government is trying to reduce the burden of public bonds while keeping expenditure on investment to maintain high economic growth and keep the fiscal deficit to a sustainable level.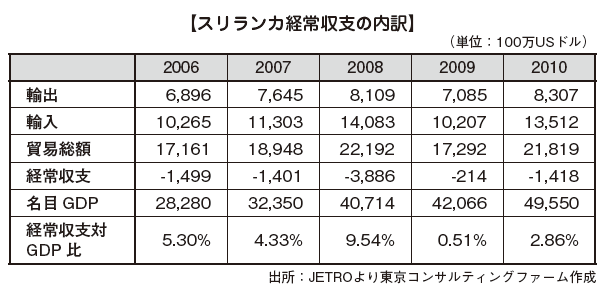 Below are the figures after 2011. The total trade volume is changed to trade balance and the current account balance vs. GDP ratio is changed to real GDP growth rate
Below are the figures after 2011. The total trade volume is changed to trade balance and the current account balance vs. GDP ratio is changed to real GDP growth rate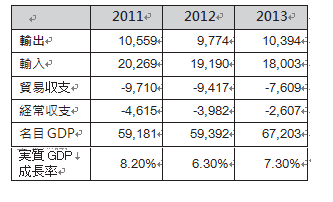
[Foreign exchange reserve]Sri Lanka 's reserve foreign currency respondents are on an upward trend, especially after the end of the civil war.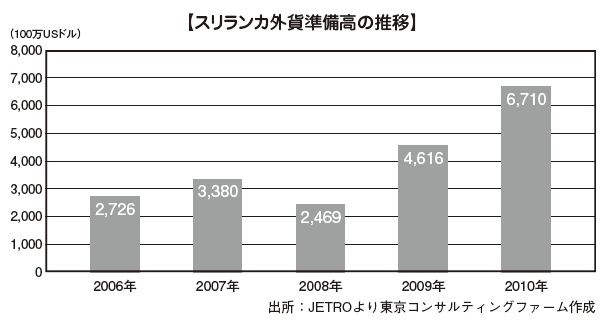 The following will be foreign exchange reserves after 2011.
The following will be foreign exchange reserves after 2011.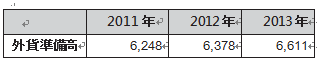
[Inflation rate]After experiencing historical inflation in 2008, it is regaining calm.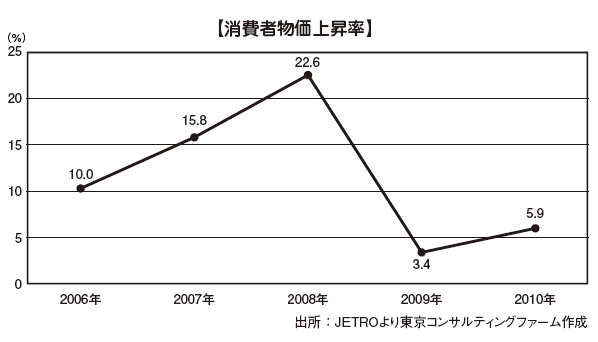 Below is the inflation rate after 2011. It has been on a downward trend since 2012.
Below is the inflation rate after 2011. It has been on a downward trend since 2012.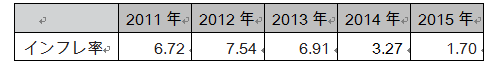
Even though Sri Lanka is located at a favorable point of access to Asia and the Middle East, the civil war between government forces and anti-government extremist groups over 20 years did not lead to rapid economic growth.
Sri Lanka has adopted socialism, but as colonial economic structure changed in the 1970s, it was forced to switch. In 1977, when UNP came to power, it was the first in South Asia to switch to a policy that emphasized economic growth based on liberalization and opening up to the outside. In the same year, the Jaya Waldana administration introduced market free liberation economic policy. At the same time, it adopted the export-led industrialization policy and promoted the opening of the economy to the outside world based on liberalization and privatization.
However, after about 20 years from the latter half of the 1970s to 2000 until the opening economy, the Sri Lankan economy was unable to demonstrate its full potential through various internal and external factors. As external factors, trade was greatly influenced by economic fluctuations and market trends in major exporting countries. The internal factors include the fact that it was influenced by the weather in the case of agricultural crops, the deterioration of security due to intensified civil war, the decline in foreign capital, and the serious deficit caused by expansion of military expenses. At the moment the civil war has ended, it can be said that the Sri Lankan economy can finally make a leap forward.
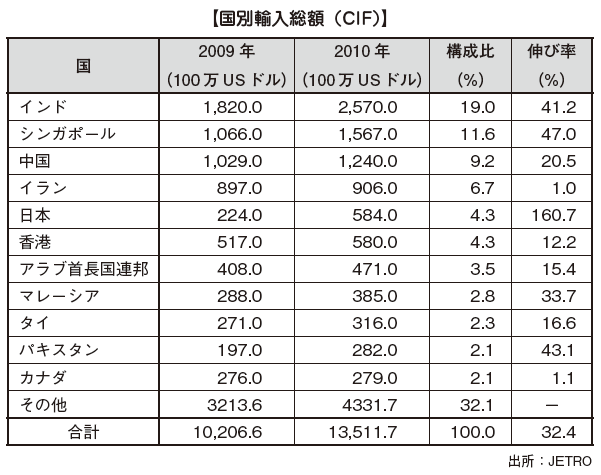
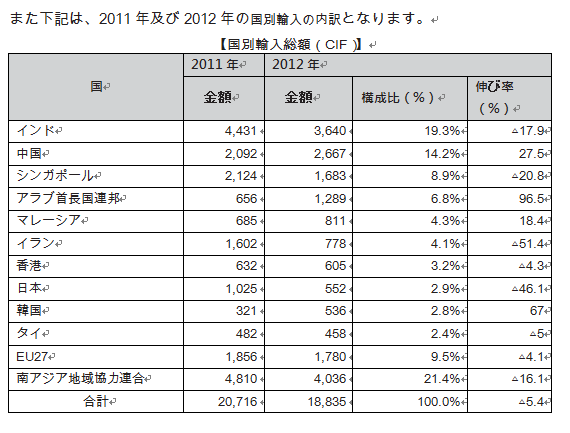
■ Amount of tradeIn Sri Lanka trade, the structure of imports exceeding exports has been established and the trade deficit tends to increase. However, this trade deficit has been offset by service trade surplus and remittances from overseas migrant workers. As for trade trends in Sri Lanka, it can be seen that trade value decreases both imports and exports as a result of the global recession.
[Export]Export items include "agricultural products" consisting of traditional export items such as black tea, rubber, coconut and palm products, textiles and clothing items, machinery and equipment, rubber products, diamonds, jewelry, etc. " Products ", jewelry(Raw ore) mainly "mining products" is classified as three. The most influential of these is "industrial products". This ratio in fiscal 2014 accounts for 74.6% of the total. "Agricultural products" account for 24.8%, and the remaining "mining products" account for 0.5%.By product, textiles, clothing items and tea are the main items, accounting for about 42.2% of export items as a whole, and the reliance on these 2 items is getting bigger.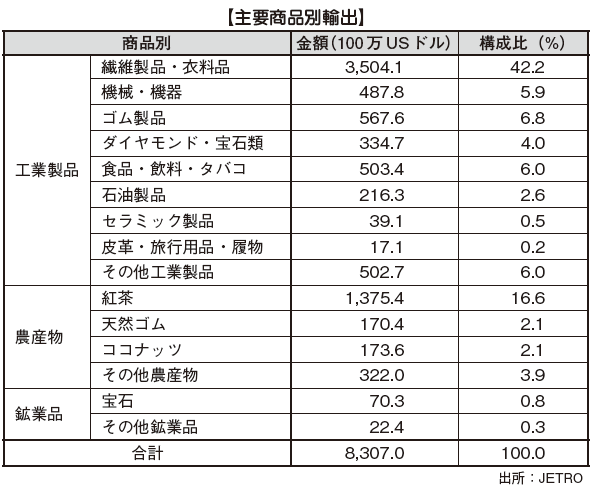 [Import]"Consumer goods" composed of foods such as rice, wheat, sugar and general consumer goods, "intermediate goods" mainly composed of industrial raw materials such as fuels containing oil, fertilizer, textile clothing, and chemicals, "Capital goods" such as machinery, equipment, transportation equipment etc. can be categorized. Of these, "intermediate goods" are the most frequently imported, accounting for 58.6% of the total book in FY 2014. By item, the largest imported item is petroleum, accounting for 2.4% of the total imports. Because it is used for raw materials for textiles and clothing, imports of petroleum tend to increase as export volume increases.
[Import]"Consumer goods" composed of foods such as rice, wheat, sugar and general consumer goods, "intermediate goods" mainly composed of industrial raw materials such as fuels containing oil, fertilizer, textile clothing, and chemicals, "Capital goods" such as machinery, equipment, transportation equipment etc. can be categorized. Of these, "intermediate goods" are the most frequently imported, accounting for 58.6% of the total book in FY 2014. By item, the largest imported item is petroleum, accounting for 2.4% of the total imports. Because it is used for raw materials for textiles and clothing, imports of petroleum tend to increase as export volume increases.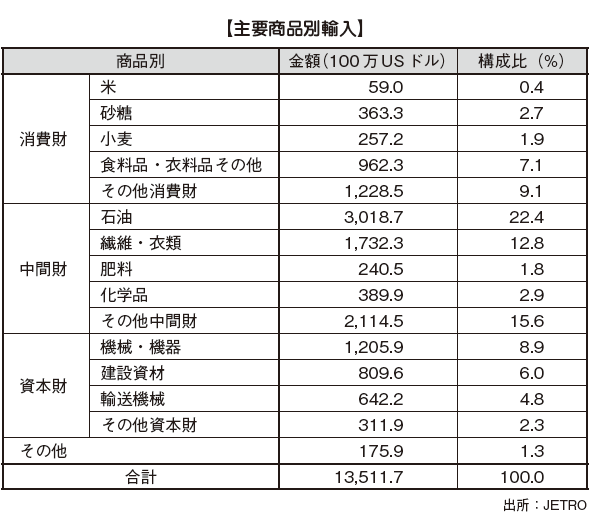
■ Trade with JapanThe amount of trade in 2013 is about 87.76 billion yen (Japan Treasury Trade Statistics), and Japan is an important trading partner for Sri Lanka.Looking at the amount, imports from Japan are US $ 668 million, accounting for 4.3% of the total. Japan is the 56th largest importer country, with automobiles, general machinery, chemical raw materials, textiles and electrical machinery as main import items.On the other hand, exports to Japan are US $ 224 million, which is 2.0% of the total. Japan is the 119th export partner, and the main items are black tea, marine products (tuna, shrimp), textile products.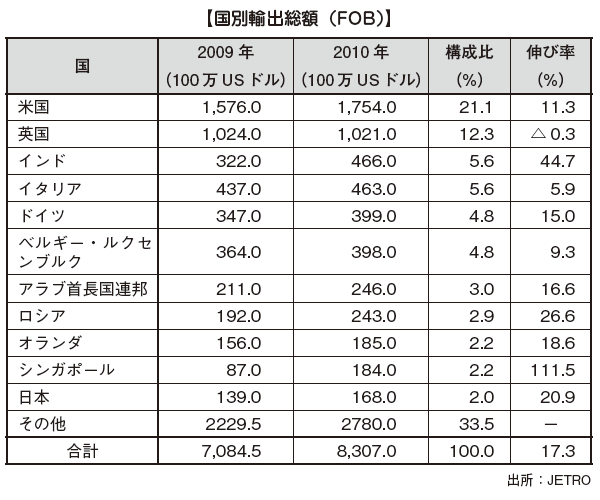
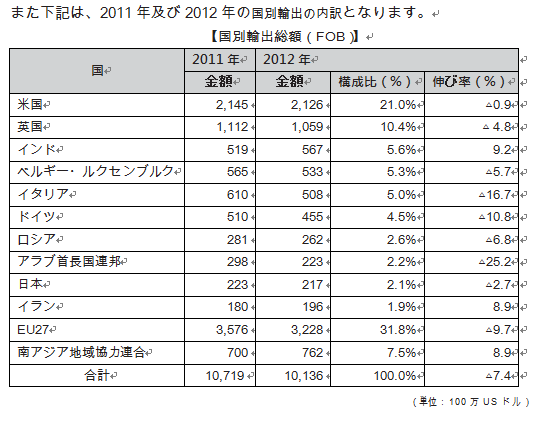
 ■Industry structureIn recent years, the importance of agriculture is somewhat retreating on the industrial structure. In the annual report issued by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, the share of agriculture in GDP was 2 0.1% as of 2010, but it decreased to 10.09% as of 2014. On the other hand, the service industry is 57.60% and the industry is 32.31%, the ratio is increasing.However, by individual industry, the share of agriculture is the size that follows the largest field of commerce in the service industry, and agriculture remains important as it is still. Moreover, about one-third of the working population is farmers, and agriculture is the most important department in terms of employment. As agricultural products that support the lives of the people, rice, tea, rubber, coconut and spices can be mentioned.There is also a structural problem that the productivity does not rise because of small business by small farmers in the management aspect of agriculture. It is due to the fact that the policy of modernization is delayed, but storage and transportation of agricultural crops are still close to primitive situations, and it is said that about 40% of agricultural crops are lost after harvest. Efforts to expand private investment towards agriculture are not fruit, too, while inconsistent prices and commercial policies are taken, excessive market intervention by the government is also a problem.Regarding the manufacturing industry, the share of GDP tends to expand over the long term so far, it is one of the fastest growing industries. In 2001, exports of manufacturing industry were suppressed by sluggish external demand, but exports of manufactured goods tend to be increasing every year.Although Sri Lanka is unlikely to develop the heavy chemical industry from the vulnerability of its economic base, light industry has the advantage of overflowing with dynamism and strong resilience. Clothing, which is a light industry, is the largest industry in the manufacturing industry. In addition, foods, beverages, chemical products, and rubber products are also positioned as important areas of the manufacturing industry.Sri Lankan's exports depend heavily on two items, tea in agricultural products and clothing items in manufacturing industry. It is said that it is possible to build a stronger export industry by diversifying export items for both agricultural products and manufacturing industries as a future measure.Especially in clothing items, competition in the international market is intensifying, as the "international textile trade agreement" which decided the import frame of each clothing item in 2005 came to an end. Unfortunately we are not yet able to secure competitiveness in this market as it is currently, it will be one of the future tasks.While the importance of primary industries in Sri Lanka is gradually declining, the proportion of secondary industry and service industry is increasing. The ratio of service industries to GDP accounts for 50% of the total and the service industry is expanding. Especially rapidly developing is telecommunications. Also, the tourism industry is also prosperous and tourism income is also an important source of foreign currency acquisition. The New York Times ranked Sri Lanka as "one of the best places to visit in 2 010" in the touristic ranking of the world. As evidence, Sri Lanka has 6 cultural heritage sites, 2 natural heritage sites, and 7th place in Asia.
■Industry structureIn recent years, the importance of agriculture is somewhat retreating on the industrial structure. In the annual report issued by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, the share of agriculture in GDP was 2 0.1% as of 2010, but it decreased to 10.09% as of 2014. On the other hand, the service industry is 57.60% and the industry is 32.31%, the ratio is increasing.However, by individual industry, the share of agriculture is the size that follows the largest field of commerce in the service industry, and agriculture remains important as it is still. Moreover, about one-third of the working population is farmers, and agriculture is the most important department in terms of employment. As agricultural products that support the lives of the people, rice, tea, rubber, coconut and spices can be mentioned.There is also a structural problem that the productivity does not rise because of small business by small farmers in the management aspect of agriculture. It is due to the fact that the policy of modernization is delayed, but storage and transportation of agricultural crops are still close to primitive situations, and it is said that about 40% of agricultural crops are lost after harvest. Efforts to expand private investment towards agriculture are not fruit, too, while inconsistent prices and commercial policies are taken, excessive market intervention by the government is also a problem.Regarding the manufacturing industry, the share of GDP tends to expand over the long term so far, it is one of the fastest growing industries. In 2001, exports of manufacturing industry were suppressed by sluggish external demand, but exports of manufactured goods tend to be increasing every year.Although Sri Lanka is unlikely to develop the heavy chemical industry from the vulnerability of its economic base, light industry has the advantage of overflowing with dynamism and strong resilience. Clothing, which is a light industry, is the largest industry in the manufacturing industry. In addition, foods, beverages, chemical products, and rubber products are also positioned as important areas of the manufacturing industry.Sri Lankan's exports depend heavily on two items, tea in agricultural products and clothing items in manufacturing industry. It is said that it is possible to build a stronger export industry by diversifying export items for both agricultural products and manufacturing industries as a future measure.Especially in clothing items, competition in the international market is intensifying, as the "international textile trade agreement" which decided the import frame of each clothing item in 2005 came to an end. Unfortunately we are not yet able to secure competitiveness in this market as it is currently, it will be one of the future tasks.While the importance of primary industries in Sri Lanka is gradually declining, the proportion of secondary industry and service industry is increasing. The ratio of service industries to GDP accounts for 50% of the total and the service industry is expanding. Especially rapidly developing is telecommunications. Also, the tourism industry is also prosperous and tourism income is also an important source of foreign currency acquisition. The New York Times ranked Sri Lanka as "one of the best places to visit in 2 010" in the touristic ranking of the world. As evidence, Sri Lanka has 6 cultural heritage sites, 2 natural heritage sites, and 7th place in Asia.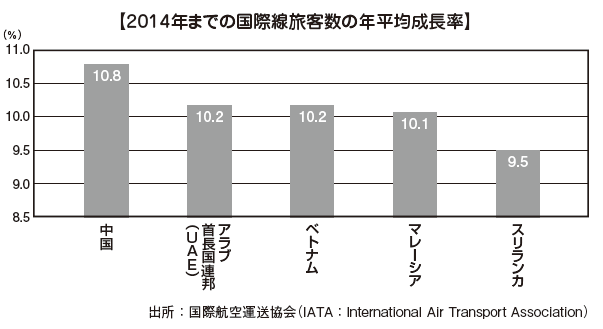
The number of people visiting Sri Lanka from abroad has increased due to active campaigns such as the end of the civil war and investment in the tourism sector.
However, due to the civil war, tourism revenues are sluggishly steeper than at peak hours, and the ratio of GDP is low. From now on that the civil war has come to an end, taking the policy of extending tourism income will be the key to economic development.
Although infrastructure development is indispensable for sightseeing, electricity, gas, water supply etc. are not enough in addition to the transportation sector. The Sri Lanka Investment Authority (BOI: Board of Investment) has a department specializing in the promotion of investment in this infrastructure sector, but it is currently not going well.
Regarding the road network, the construction of the expressway connecting Colombo and the airport has already been started, and the construction of a ring road over the highway connecting Colombo and Candy, which is planned to be undertaken under Japan's assistance, along with Colombo outer rim.
However, in any case, it is not in a financial state that can be invested, and it is expected that it will take time to solve traffic congestion, as the rapid increase of cars and insufficient maintenance of railway transportation.■ The future of the Sri Lankan economyThe driving force for economic growth is the private sector, centered on manufacturing and service industries. Especially in the textile and clothing industries in the manufacturing industry, sub-sectors such as telecommunications, transportation and finance are expected to play a role as the driving force for economic growth in the service industry.Regarding prices, it seems that overall inflation is greatly influenced by soaring oil prices. In fiscal 2006, the salary of civil servants was raised, and the pressure to raise prices further increased.Tsunami related reconstruction projects have already been constructed, and a lot of construction finished in 2008 with the financing of aid funds. With this, it can be said that the reconstruction from the damage caused by the Sumatra Great Earthquake and the Indian Ocean Tsunami has finished.In future it is expected that a project aiming for development from recovery will be done. As part of the project, direct investment is being attracted. In the northern and eastern regions, which are the later regions in Sri Lanka, the poverty rate of Sri Lanka as a whole is higher than 22%, and we have formulated a program called "300 Factories". Consumers have been the drivers of economic growth so far, but "300 Factories" is a program to realize economic growth with leadership of investment. Therefore, in addition to public investment, we will focus more on expanding private investment.Regarding the industry, there are various problems such as intensifying competition in the clothing industry, low productivity of agriculture, inadequate infrastructure, and certification of black tea. Furthermore, in addition to risk factors related to conflict, there are problems such as increasing commercial borrowing from foreign countries, excessive public debt, expanding budget deficit. In order to solve these problems, merely setting measures for the government of Sri Lanka has insufficient aspects, and measures on a global scale are required.
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya