Pakistan
6 Chapter Tax
-
-
1 Chapter Basic knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.2 Investment regulation and incentives
3 Chapter Establishment
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.3 Company liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter Corporate Law
4.4 REGULATORY BODY/BODIES AND AFFILIATED INSTITUTIONS
5 Chapter Accounting
5.1 Accounting system in Pakistan
5.2 Disclosure system of Pakistan
6 Chapter Tax
6.2 Individual Issues in Pakistan Domestic Tax Law
7 Chapter Labor
7.4 Points to keep in mind while having Japanese people in Japan
-
-
-
Tax overview
■ Pakistan's Tax LawIn Pakistan, the 1979 Income Tax Ordinance (Income Tax Ordinance, 1979) has been adopted as the law for the law of tax law for a long time, but the Income Tax Ordinance 2001 (Income Tax Ordinance, 2001) is currently applied.Under this law, both corporate income tax and personal income tax are stipulated as "income taxes", and the income tax rules in 2002 (Income Tax Rules, 2002) and the Federal Tax Revenue Bureau, which specifies enforcement regulations and actual declaration procedures, etc. in tax practice It is supposed to be taxed in accordance with the announcement (SROs) announced irregularly from.Tax regulations and tax rates are also revised every year and will be announced by the Finance Act / Ordinances.In Pakistan, the Federal Bureau of Federal Revenue (FBR) is regarded as the highest authority on enforcement of the tax law and tax collection.In this chapter, we will explain the overall picture of tax system in Pakistan and individual tax items.
Pakistan's tax systemThe main tax items in Pakistan are as shown in the table below.The tax system is largely divided into "national tax" and "local tax", among which it is further divided into "direct tax" and "indirect tax".
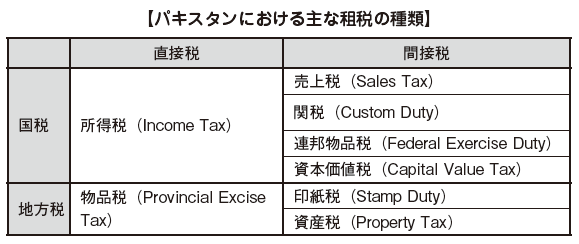
[National tax and local tax]National taxThe national tax is basically the tax collected by the federal government. However, there are also some national taxes collected by local governments like the Uzhel tax (agricultural crop tax).
Local taxThe local tax is largely divided into "state tax" and "municipal tax" and is basically collected by local governments. However, some local taxes such as automobile taxes are collected by the federal government.
[Direct tax and indirect tax]Direct taxDirect tax is the tax that taxpayers who pay tax and those who actually pay taxes are the same. In Pakistan income tax (individuals and corporations) etc. falls under this.
Indirect taxIndirect tax refers to different taxes between those paying taxes and those actually borne by them. In Pakistan, value added tax etc. fall under.
-
-
-
personal income tax
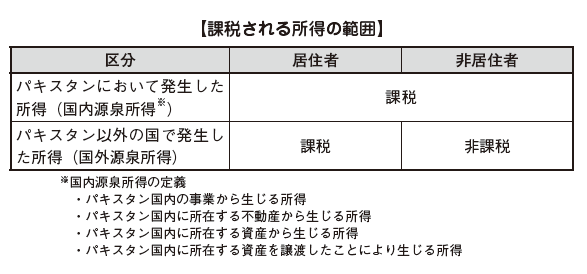
Taxable yearThe taxable year in Pakistan is from July 1 to June 30 of the following year.■ Determination of HabitabilityWhen calculating the personal income tax amount in Pakistan, it is first necessary to judge whether the target person is "resident" or "non-resident". Due to the difference in this category, the range of income to be taxed will differ.Residents' definition in Pakistan is considered to fall under any of the following requirements.· Total number of days stayed in Pakistan during the tax year is 183 days or more· Public officials engaged in government and local administration are dispatched outside the country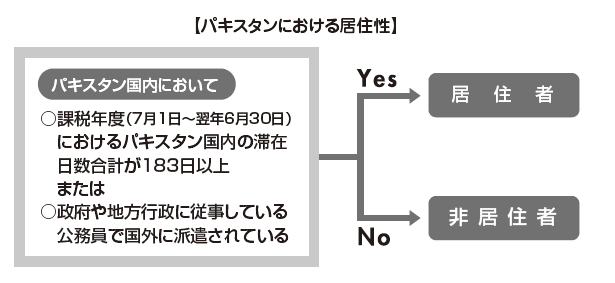 In addition, those who do not fall under the requirements of the resident above are considered nonresidents.The range of income taxed by the classification of resident, nonresident is as follows.
In addition, those who do not fall under the requirements of the resident above are considered nonresidents.The range of income taxed by the classification of resident, nonresident is as follows.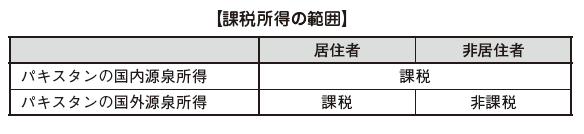 Domestic source income in Pakistan is as follows.
Domestic source income in Pakistan is as follows.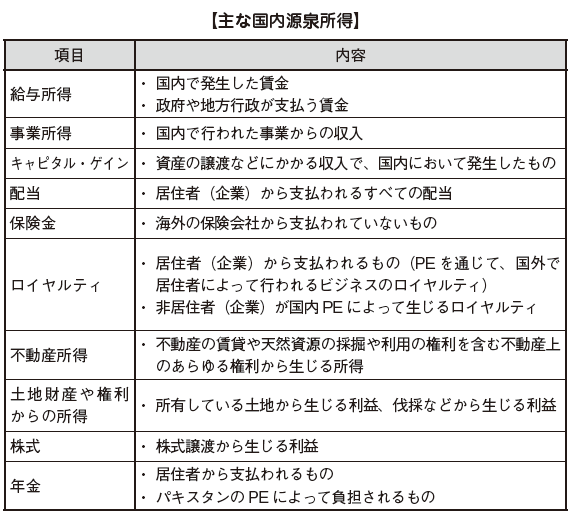 Basically, income which is said to have occurred in Pakistan domestically becomes domestic source income, and income receiving place is irrelevant. In the case of residents, even if they are paid outside of Pakistan, they will be domestic source income as long as they receive salaries from employers in Pakistan.In other words, if you become a "resident" in Pakistan, not only income in Pakistan but also income generated in other countries will be taxed.In the case of non-residents only income generated in Pakistan is taxed in Pakistan.However, in Pakistan we define residents as those who stay in Pakistan for 183 days or more, whereas in Japan's income tax law, they have residence in the country or reside individuals who have continued to stay for more than one year Because it is defined as a person, in certain cases, both in Japan and Pakistan are qualified as resident and income tax is doubly taxed.If it is necessary to travel frequently to Pakistan's subsidiaries etc. for assistance in launching a manufacturing subsidiary etc. or if you need to travel frequently for work and the total staying days reaches 6 months as a result, the case falling under this double taxation There are not many.In this case, the country of residence will be decided based on the Pakistan tax treaty.■ Calculation of gross income tax amount in Pakistan[Income category]According to the 2001 Income Tax Ordinance (Income Tax Ordinance, 2001), income is divided into the following categories, and income calculation method is stipulated for each category (called Heads of Income).·Employment income· Real estate income· Business income· Capital · gain (Including asset derived income, asset transfer)· Other income[Expenses that can be deducted from income]In calculating the income amount, the amount that can be deducted from the income amount is stipulated as follows for each income.
Basically, income which is said to have occurred in Pakistan domestically becomes domestic source income, and income receiving place is irrelevant. In the case of residents, even if they are paid outside of Pakistan, they will be domestic source income as long as they receive salaries from employers in Pakistan.In other words, if you become a "resident" in Pakistan, not only income in Pakistan but also income generated in other countries will be taxed.In the case of non-residents only income generated in Pakistan is taxed in Pakistan.However, in Pakistan we define residents as those who stay in Pakistan for 183 days or more, whereas in Japan's income tax law, they have residence in the country or reside individuals who have continued to stay for more than one year Because it is defined as a person, in certain cases, both in Japan and Pakistan are qualified as resident and income tax is doubly taxed.If it is necessary to travel frequently to Pakistan's subsidiaries etc. for assistance in launching a manufacturing subsidiary etc. or if you need to travel frequently for work and the total staying days reaches 6 months as a result, the case falling under this double taxation There are not many.In this case, the country of residence will be decided based on the Pakistan tax treaty.■ Calculation of gross income tax amount in Pakistan[Income category]According to the 2001 Income Tax Ordinance (Income Tax Ordinance, 2001), income is divided into the following categories, and income calculation method is stipulated for each category (called Heads of Income).·Employment income· Real estate income· Business income· Capital · gain (Including asset derived income, asset transfer)· Other income[Expenses that can be deducted from income]In calculating the income amount, the amount that can be deducted from the income amount is stipulated as follows for each income.
 Employment incomeFor salary income calculation, there is no expenses that can be deducted and salary income is salary income.Real estate incomeThe following expenses can be deducted for the calculation of real estate income.· Provision for repair (amount up to 1/5 of rent)· Insurance premiums on real estate, interest on borrowings, taxes· Other fixed expensesBusiness incomeFor income and expenses, individuals are permitted to continue to apply either "Cash Basis" or "Accrual Basis". In principle, those used for business can be deducted for calculation of business income. However, regarding the following items, there is a separate provision for the amount of deduction, so it is necessary to process accordingly.· Depreciation· Intangible property· R & D expenses· Training fee· Credit loss· Borrowing InterestReserve fundCapital gainIf loss (capital loss) occurs, it can be deducted from taxable income. However, we can not deduct from taxable income about losses due to assignment of sculpture, art, jewelry, antiques, posters, books etc.[Calculation of Income Tax Amount]Tax rate applied for personal income tax differs between salary income taxpayer * and other taxpayers.* Persons with a ratio of taxable wage income to taxable income exceeding 50%For salary income taxpayers, we calculate the amount of income tax based on the following tax rate table. For example, if the salary of the expatriate is 5,000,000 rupees, 5,000,000 x 20% = 1,000,000 rupees will be the income tax.
Employment incomeFor salary income calculation, there is no expenses that can be deducted and salary income is salary income.Real estate incomeThe following expenses can be deducted for the calculation of real estate income.· Provision for repair (amount up to 1/5 of rent)· Insurance premiums on real estate, interest on borrowings, taxes· Other fixed expensesBusiness incomeFor income and expenses, individuals are permitted to continue to apply either "Cash Basis" or "Accrual Basis". In principle, those used for business can be deducted for calculation of business income. However, regarding the following items, there is a separate provision for the amount of deduction, so it is necessary to process accordingly.· Depreciation· Intangible property· R & D expenses· Training fee· Credit loss· Borrowing InterestReserve fundCapital gainIf loss (capital loss) occurs, it can be deducted from taxable income. However, we can not deduct from taxable income about losses due to assignment of sculpture, art, jewelry, antiques, posters, books etc.[Calculation of Income Tax Amount]Tax rate applied for personal income tax differs between salary income taxpayer * and other taxpayers.* Persons with a ratio of taxable wage income to taxable income exceeding 50%For salary income taxpayers, we calculate the amount of income tax based on the following tax rate table. For example, if the salary of the expatriate is 5,000,000 rupees, 5,000,000 x 20% = 1,000,000 rupees will be the income tax.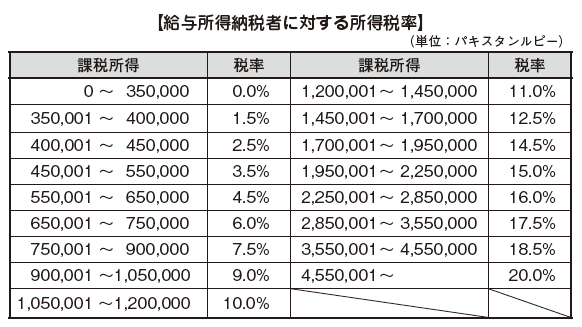 On the other hand, a person other than the salary income taxpayer calculates the income tax amount at the following tax rate.
On the other hand, a person other than the salary income taxpayer calculates the income tax amount at the following tax rate.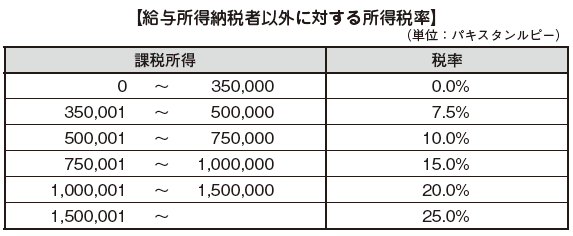 ■ Declaration / Payment ProcedureThe taxable year of Pakistan is from July 1 to June 30 of the following year, taxpayers must submit a declaration by September 30.However, as an exception there is no need to submit a declaration if the employer only has salary income and the employer has submitted a withholding slip. This is the same system that Japanese salaried workers settle for excess / deficiency tax at year - end adjustment without filing a final return.However, any person whose salary income exceeds 500,000 Pakistan Rupee must file a statement with the asset attached to the tax return even if the employer has submitted the above withholding slip. . Even if it is not salary income, those who have gross income over 500,000 Pakistan rupees in the last fiscal year or the current fiscal year must submit their property reports and their details.Also, in Pakistan there is a quarterly planned tax payment system that prepays the tax payment quarterly.The planned tax payment amount is the amount of tax calculated by the income tax regulation in the latest year divided by four.
■ Declaration / Payment ProcedureThe taxable year of Pakistan is from July 1 to June 30 of the following year, taxpayers must submit a declaration by September 30.However, as an exception there is no need to submit a declaration if the employer only has salary income and the employer has submitted a withholding slip. This is the same system that Japanese salaried workers settle for excess / deficiency tax at year - end adjustment without filing a final return.However, any person whose salary income exceeds 500,000 Pakistan Rupee must file a statement with the asset attached to the tax return even if the employer has submitted the above withholding slip. . Even if it is not salary income, those who have gross income over 500,000 Pakistan rupees in the last fiscal year or the current fiscal year must submit their property reports and their details.Also, in Pakistan there is a quarterly planned tax payment system that prepays the tax payment quarterly.The planned tax payment amount is the amount of tax calculated by the income tax regulation in the latest year divided by four.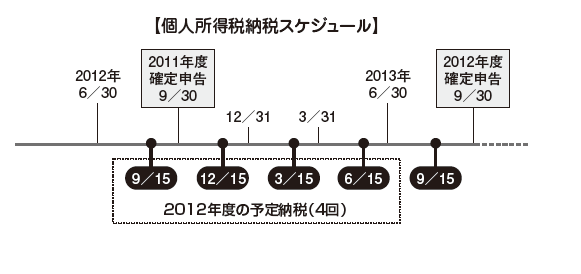
-
Corporate income taxes
The corporate income tax is tax imposed on income obtained regardless of domestic corporation or foreign corporation in Pakistan. It is a tax item that always participates in the case of establishing a business / activity base in Pakistan.
There are two ways of taxing corporate income tax in Pakistan, NTR (Normal Tax Regime) and FTR (Final Tax Regime).NTR is taxed on annual taxable income. FTR is a constant income, a different tax rate depending on the nature of the incomeThe taxation on such income will be terminated by this. In other words, taxable income of FTR is not taxed at corporate tax rate, but it is handled in the same way as separation taxation of income tax in Japan, where taxation is terminated by taxation with a fixed tax rate.
■ TaxpayerRegarding corporate income tax, whether that corporation is a "resident enterprise"Depending on whether it falls under "non-resident enterprise", the range of income subject to taxation will differ.
Definition of resident company· Corporations founded under the laws of Pakistan· Corporations whose management is all done in Pakistan· State Government, or Regional Bureau
If it does not apply to any of these, the corporation will be a non-resident enterprise under Pakistan's corporate income tax law. In the case of a non-resident enterprise, only income with source in Pakistan is subject to taxation. Conversely, the corporation which falls under any of the above requirements is treated as a resident enterprise and all income obtained by the corporation, so-called "global income" is subject to taxation.
■ Calculation of taxable income[Classification of Income]In Pakistan, income amounts are classified into "business income", "capital / gain", "other income" according to their contents, and the method of calculating income amounts is stipulated for each item.In addition, business income of residents and non-resident companies with permanent establishment (PE: Permanent Establishment) are taxed on the net amount deducting expenses etc from income, but non-permanent establishment For business income of a resident enterprise, so-called "estimated taxation" is carried out, which taxes uniformly without deducting expenses etc. from income.
[Calculation of business income]The calculation of business income is calculated by applying the principle of accounting treatment adopted by the corporation on an ongoing basis.In the case of a corporation, it is necessary to calculate the income amount by continuously applying "accrual principle".Flow of rough income calculation, the enterprise first calculates business income based on accounting treatment generally accepted as fair and reasonable. Next, from the calculated amount of business income, the income subject to FTR is deducted, the balance is multiplied by the tax rate, and the income tax amount is calculated.
[Amount of Deduction]In principle, expenses to be borne by corporations for the purpose of carrying out projects can be treated as deductible for the calculation of business income.On the other hand, the following items can not be processed as deductible.
· Punishment charges and excess taxes· Of salaries, brokerage commissions, rental fees, payment amounts of commissions that have not been withheld at the time of payment· If you do not pay for account items that exceed 50,000 Pakistan Rupees through the prescribed bank routes (Specified Banking Channels)
In addition, individual provisions concerning deductive inclusion are stipulated for the following items.
Credit lossIn order to include the credit loss amount as a deductible, the following requirements must be satisfied.
· Due to the calculation of business income, this amount has been deducted· The corresponding bad credit amount is truncated from the claim amount· There is a legitimate reason for being uncollectible
Depreciation costIncome Tax Ordinance It is possible to include it in the amount of deductible amount only for the depreciation limit calculated by the basic rate of depreciation according to the type of asset described in Schedule 3 of the Income Tax Ordinance. The depreciation rates of the main assets are as follows.

■ First year amortization (Initial Allowance)In the first year of tax payment, it is permitted to deduct the acquisition price of depreciable assets to be used for business execution in Pakistan. The timing of inclusion of deduction will be the later point in time of the use of the asset or its operation.However, the following assets are not allowed to be amortized in the first year.
· Vehicles other than for business use· Furniture (including fittings etc.)· Factory and machinery
Also, for depreciable assets not included in the first-year amortization described above, the acquisition of the acquired amount is permitted as a first year allowance. It includes factories, machinery, and other accessories, but there are restrictions that it must be a specific area determined by the government. The government separately needs to set specific areas.
[Intangible assets]Intangible assets are permitted to be deducted from amortization. Examples of intangible assets are software, patent rights, design and model information, copyright and so on.As a condition of deductibility, some or all intangible assets must be related to business income.Also, intangible assets are usually treated as having a useful life of more than 10 years. For intangible assets that have started to be used in the middle of the tax year, we calculate the deductible amount separately according to the number of days of use.
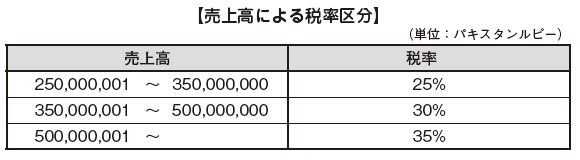
■ Tax calculationThe corporate income tax rate has been adopted by the uniform taxation system, and now it is 35%. As an exception, a small tax rate of 20% will apply to small companies that meet all of the requirements below.
· What has been established since June 30, 2005· Capital is not more than 25 million Pakistan Rupee· Annual turnover is less than 250 million Pakistan Rupee· The number of employees is 250 or less
Also, for Modaraba (other than dividends income taxed by FTR and other income), a 25% tax rate applies.
Even if sales exceed the 250 million Pakistan Rupee, we can gradually apply the reduced tax rate until sales reaches Pakistan Rupee of 500 million.
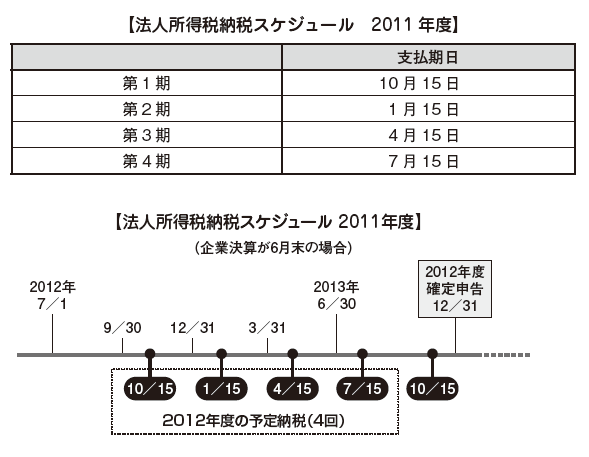
■ Declaration / Payment MethodA company that has selected a normal taxable year (July 1 - June 30 of the following year) must submit a tax return by December 31.In addition to tax returns, taxpayers themselves must estimate and pay the prepayment tax based on the Income Tax Law. If the estimated tax payment schedule exceeds the tax amount calculated from the following formula, the taxpayer is required to submit an estimate to the commissioner, adjust if any amount already paid, You have to pay.Estimated tax payment quarterly estimates are calculated by the following method.
(A * B / C) - D
A: Sales in the target quarterB: Estimated tax amount for last fiscal yearC: Sales of last fiscal yearD: Tax amount deducted out of paid tax amount
■ If the gross income at the previous declaration exceeds 500 thousand Pakistan Rupee or if the gross income for this fiscal year exceeds 500 thousand Pakistan Rupee, attach the property statement (Wealth Statement) and its details to the declaration There is no doubt. -
Minimum Tax Basedon Turnover
In Pakistan, the lowest alternative taxation system is adopted as a system to complement income tax. The minimum alternative tax system is a mechanism to pay additional difference when the calculated minimum substitute tax amount exceeds the tax amount to be normally paid.It is subject to the minimum alternative tax if the following requirements are satisfied.
· A corporation that fulfills certain conditions (eg in case of red letters)· Individuals who posted sales of more than 50 million rupees· Association of Persons who posted sales of 50 million rupees or more
If these taxpayers have zero taxes to pay in a given year or if the amount of tax to be paid is less than 0.5% of sales, it is necessary to pay tax on the difference.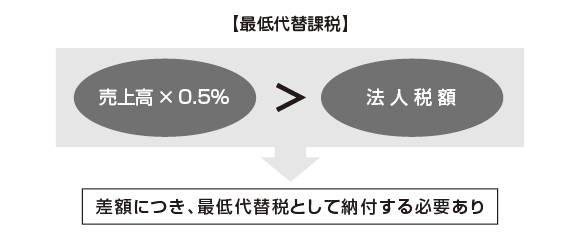
In addition, in the case of a corporation in which the amount of income before depreciation and other certain amount of money is deducted is in the red, there is no application of the lowest alternative taxation system. However, this is not the case if it is judged that after the deduction of depreciation and amortization expenses is in the red or if it is judged that the accounts have become in the red due to the change in accounting treatment.In the case of paying the minimum alternative tax, the payment amount can be deducted from the amount of tax that will be generated in the future by carrying forward the tax amount only during the 3 taxable years. -
Sales tax (SalesTax)
Sales tax is stipulated in the 1990 Sales Tax Act (Sales Tax Act, 1990) and is tax collected at the time of provision and import of goods and services, and the value added tax (VAT) in other countries Tax) has become the same system.
■ TaxpayerThose who provide taxable products and fall under the following conditions must register sales tax obligations.
· Manufacturers whose taxable sales over the last 12 months are above the 5 million Pakistan Rupee. Or an annual utility fee for the last 12 monthsManufacturers (electricity, gas, telephone) payments outperform 700,000 Pakistan Rupee· Retailers with sales in excess of 5 million Pakistan Rupees in the past 12 months· Importer· Wholesalers
As described above, it is not necessary to charge sales tax for the provision of goods and services that do not fall under anyone who needs to register sales tax obligation.If you provide taxable goods or services without registering, you will be punished according to the law despite the need to register sales tax obligation for sales tax.
Taxable itemsSales tax is generally taxed on imported products, those produced in Pakistan in principle. For those produced domestically, those imported are taxed at the import stage in the sales stage.However, the following items are excluded from the taxation of sales tax.
· Computer softwareKakin· Feeding poultry·medicine· Unprocessed agricultural products etc.· Other items stipulated in Appendix 6 of the 1990 Sales Tax Law
In addition, items may be updated under notification of SROs issued from FBR. You can check these information on the FBR website.
■ Tax rateAs a rule, the current tax rate of sales tax is 16%. However, the tax rate for export transactions of products is set at 0%. As an exception, according to the Statutory Regulation Ordinance (SRO) 537 (I) issued in 2008, 18.5% or 21% will be taxed for items listed in SRO 644 (I) .
■ Calculation of payment tax amountThe tax payment amount of sales tax is the sum of the sales tax (provisional sales tax) received in the taxing period minus the sales tax (provisional sales tax) paid.However, if the provisional sales tax exceeds 90% of the provisional sale tax, the excess portion can not be deducted from the temporary election sale tax, and it can be deferred in the next taxable period. If you can not deduct even in the next taxable period, you can request a refund.In cases where the company is mainly engaged in export business or handling mainly products with 0% taxation, the provisional sales tax will often exceed the provisional sales tax. In this case, the excess amount will be refunded within 45 days by making a refund request.
■ Declaration methodThe sales tax taxpayer is required to submit a sales tax return by the 15th day of the following month for the tax amount of the previous month. In addition, in this case, until the 15th day of the following month the payment must be declared on the electronic, the declaration using FBR's E-portal (electronic filing) will be submitted until the 18th of the following month It is necessary to do. -
State Goods Tax (Federal Excise Duty)
State excise tax is taxed on the basis of the 2005 State Goods Tax Law (Federal Excise Act, 2005). The state excise tax is usually taxed based on the value or selling price of the goods, but certain items such as tobacco will be taxed by the metered system (the tax amount is determined according to the criteria such as quantity) I will.
Taxable itemsTaxes on state goods tax are subject to certain imported goods, products manufactured in Pakistan, or services offered in Pakistan (services provided outside Pakistan but services provided in Pakistan Including tax) will be taxed.Taxable products include edible oil, tobacco, cement, fuel oil, transportation vehicles, etc.Taxable services include advertisements, air services, domestic air cargo, transportation agencies, private communication services, insurance, financial services, franchise services, services provided by builders and developers.
■ Tax rateAs a rule, the tax rate of state goods tax is 15%, but it will be collected at different tax rates depending on the target goods and services. In addition, the 0% tax rate applies for the export of goods and certain goods prescribed by the law.Please note that these tax rates may change depending on notification by FBR. -
Special Excise Tax (Special Excise Duty)
Special item tax is taxed on goods manufactured in Pakistan, or imported items in Pakistan and will be collected separately from the above state goods tax. In addition, this special excise tax is not taxed at the wholesale, logistics, and retail phases, and tax is imposed on manufacturers, importers and others.Partially, the following items are exempt from special excise tax.· Agricultural products·Cooking oil·Natural gas· LP gas·fertilizer· Sales tax 0% Taxable goods· Products for export· Import duty-free productsRegarding the applicable tax rate, it was previously a fixed rate of 1%, but it was raised to 2.5% by the notification SROs 261 (I) / 2011 issued by FBR on March 19, 2011. -
Tariff
Regarding tariffs, the Customs Act of 1969 (The Customs Act, 1969) is the basis law, and the FBR has the authority to collect taxes. In Pakistan, tariffs account for the majority of government revenues and also play a role in protecting domestic industries.■ Tariff RateTariff rates are listed in Attachments 1 and 2 of the Customs Act of 1969 and can be checked at any time on the FBR website.Appended Table 1 stipulates the fixed tax rate applicable to imported goods and Export Table 2 in Exhibit 2. The revision of the tariff rate is made every year, according to the provisions of the fiscal law at the time of budgeting. Also, various laws of reduction and exemption are taken depending on other laws and individual notifications, and in case they fall under these, the reduced tax rate stipulated by each will be applied.Tax rates are generally high for luxury goods and non-daily necessities, and the plant material and equipment required for industry are set at a lower tax rate than for general consumer goods.Furthermore, for the purpose of protecting and revitalizing the domestic industry, the import rate of automobiles (finished products) is applied at a high tax rate, and as of January 2009 the tax rate varies according to the cylinder capacity (Cylinder Capacity), 800 to 1,000 CC is 55%, 1,000 to 1,500 CC is 60%, 1,500 to 1,800 CC is 75%, 1,800 CCThose exceeding 150% high tax rate.■ Adjustment tariff (Regulatory Duty)For specific items, adjustable tariffs will be applied, in addition to the basic tax rate, up to 100% of the tax base.Additional tariff (Additional Customs Dutyon Imported Goods)For certain items, additional tariffs will be applied, up to 35% of the tax base, in addition to the basic tax rate.■ Special tariff (Special Customs Dutyon Imported Goods)For specific import items competing with Pakistan domestic industry, additional tariffs are applied in addition to the basic tax rate, but special tariffs (Special Customs Duties) may be imposed on importing goods. Taxable items are limited to items that are subject to excise duties when they are goods produced in Pakistan. Tax rates are applied that do not exceed the rate of excise tax.Please note that this special tariff part is not included in the amount of consideration that is the basis for calculation of sales tax.Preferential tariffFor trade with SAPTA member countries (India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Maldives, Bhutan), mutual tariff reduction is applied. Other free trade agreements are as follows.· Pakistan · Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement (agreed in June 2005)· Pakistan · China Free Trade Agreement (agreed in November 2006)· Pakistan · Malaysia Free Trade Agreement (agreed in November 2007) -
Withholding tax system
The withholding collection system is a system that collects the tax to be paid by the recipient when paying the consideration at the time of payment and pays it to the country instead.The main income and tax rates subject to withholding tax in Pakistan are listed in the table below. Also, since tax treaties have been concluded between Japan and Pakistan, it is possible to apply the tax treaty tax rate for the items stipulated in the Convention.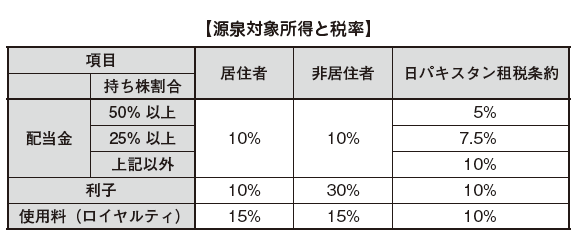
-
Japan-Pakistan tax treaty
I outlined the outline of the tax treaty in the introduction, but here we will look at the details of some tax exemptions concluded between Japan and Pakistan.
■ Definition of PE (Article 2 of the Pakistan Tax Treaty)In Article 2 of the Japan - Pakistan DTA, the definition of permanent establishment (PE: Permanent Establishment) is stipulated, and the place where companies such as business management offices, branches, custody warehouses etc are conducting is PE It has been.In addition, it does not include storage facilities temporarily used in Pakistan, and only the fact that it operates in Pakistan through an agent such as an intermediary, a wholesaler or the like having an independent position from a Japanese company does not indicate PE Is stated in the tax treaty.
■ Special Affiliated Companies (Article 4 of the Pakistan Tax Treaty)In the Pakistan tax treaty, there is a provision on transfer pricing taxation.As a content, if a company or the same person of one Contracting Party is directly or indirectly participating in the business management, control or capital of another Contracting Party, the terms of the transaction are When it is different from the terms and conditions, if it is assumed that there is no such condition, taxation will be imposed on one of the Contracting Parties concerning the profit which the enterprise etc of one Contracting Party would originally obtain, and in summary it is " If you do business between affiliates, you must follow the terms of the third party transaction ".
■ Taxation on royalties (royalty etc.) (Article 7 of the Pakistan tax treaty)In Japan and Pakistan there are cases where royalties are collected as consideration for providing know-how etc. For this royalty, the tax treaty states "to tax in that Contracting StateIt can be done ". In other words, if royalties are paid from Pakistan to Japan due to technical provision from Japan, withholding tax will be imposed on payment.For transactions between affiliated companies, tax rates under the tax treaty will not apply to parts beyond third-party prices, and will be taxed at the normal tax rate.
■ Personnel service income for short-term residents (Article 10 of the Pakistan Tax Treaty)Under the Japan - Pakistan DTA, it is stated that salary income is taxed only in countries where actual work is being carried out. In other words, if you do not work as a salary source, you will not be taxed in the country for salary income and will be taxed in the actual work place.When traveling from Japan to Pakistan, if the following requirements are satisfied, Pakistan side will not be taxed on remuneration or salary paid (short-term stay duty exemption).
· If the number of days stayed in the tax year does not exceed 183 days and the service is carried out for Pakistani corporations· It is a stay of 90 days or less in the tax year, the service is related to the execution of duties of free occupation and the fee received for that service is 750,000 yen or equivalent amount of Pakistan Rupee When not exceeding
As an exception, income acquired by personal activities conducted by actors, musicians, other entertainers and athletes in Pakistan will not be subject to short-term stay duty exemption and will be taxed on the Pakistan side.
■ Elimination of double taxation (Article 14 of the Pakistan tax treaty)The same clause describes the method of double taxation exclusion between bilateral countries in Pakistan and Japan. Each allows the deduction from the amount of tax to be paid in each country to the extent of the tax amount calculated based on the tax laws of each country.Also, if tax reduction or exemption is made on Pakistan side by Japanese companies regarding payment, royalties, and interest received from Pakistan, the amount of tax reduced was also considered as the amount of tax paid in Pakistan, You can make a foreign tax credit with.
■ Bilateral consultations on double taxation (Article 17 of the Japan Pakistan DTA)In accordance with the tax laws of either Japan or Pakistan, if you receive a tax that does not comply with the provisions of this tax treaty, you can file an appeal against an authorized authority in your country of residence.In this case, the competent authorities of both countries will keep in touch with each other and hold mutual consultation with each other to eliminate taxation that does not conform to the provision of this tax treaty.If this provision is not stipulated in the tax treaty, or for countries where tax treaties have not been concluded with Pakistan, tax will be imposed based on the tax law stipulated in their respective countries.
-
-
-
References
Huzaima Bukhari & Dr. IkramulHaq “Law & Practice of Income Tax”Huzaima Bukhari & Dr. IkramulHaq “Tax Laws of Pakistan”Huzaima Bukhari & Dr. IkramulHaq “Practical Handbook of Income Tax”
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya