Pakistan
5 Chapter Accounting
-
-
1 Chapter Basic knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.2 Investment regulation and incentives
3 Chapter Establishment
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.3 Company liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter Corporate Law
4.4 REGULATORY BODY/BODIES AND AFFILIATED INSTITUTIONS
5 Chapter Accounting
5.1 Accounting system in Pakistan
5.2 Disclosure system of Pakistan
6 Chapter Tax
6.2 Individual Issues in Pakistan Domestic Tax Law
7 Chapter Labor
7.4 Points to keep in mind while having Japanese people in Japan
-
-
-
パキスタンの会計制度
■ Outline of accounting systemIn independence in 1947, Pakistan adopted the Indian Company Act of 1913 and the auditor certificate rules (Auditors Certificate Rules, 1932) established by the British government that colonized India. This is the establishment of Pakistan accounting. According to the company regulations of 1984 (Companies Ordinace, 1984) and the company regulations of 1985, the current Pakistan accounting system requires the preservation obligation of the accounting book, the shareholders' meeting, the reporting obligation of the annual report to the registration authority, the Pakistan accounting standard Fundamental rules such as compliance are prescribed, and other accounting processing will be carried out according to income tax regulations, stock exchange rules, etc. The Pakistan accounting standards created by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of Pakistan (Pakistan) currently apply mostly to IFRS and are internationally consistent.Accounting PeriodUnder the Companies Act of Pakistan, companies shall set a period of no more than 12 months as fiscal year (paragraph 2 of Article 233), unless special permission is obtained.In the taxable year for taxation, there are a normal tax year (normal tax year) and a special tax year (special tax year) (Income Tax Law Article 74). The normal taxable year must submit declarations by December 31, with a period of 1 year from July 1 to June 30 as the taxable period.If authorized by the authorities, you can set any 12 months as the taxable year (special taxable year). In this case, if the tax year ends from January 1 to June 30, we will file a declaration by 31 December. Companies that set tax years for other periods must submit declarations by September 30 of the following year after the tax year ends.Therefore, both the fiscal year and the taxable year can be set for each company, it is possible to set the same fiscal year as the parent company.[Accounting book]All companies must keep and keep account books. Accounting books are required to be put in registry offices (Registered Office) for at least 10 years.If you fail to comply with this provision, all directors are sentenced to imprisonment with work for not more than 6 months or a fine not exceeding 10,000 Pakistan rupees. However, in the case of a listed company, it is a fine of not more than 1 year imprisonment or a fine of not more than 50,000 Pakistan Rupees (over 20,000 Pakistan Rupees) in view of the magnitude of social influence.Registrar and SECP (Securities & Exchange Commissionin Pakistan) have the right to inspect accounting books at any time when it is deemed necessary. If there is any incompleteness in the creation and preservation of accounting books, you may be penalized. From the beginning of the establishment, it is necessary to establish internal control on bookkeeping and preservation of accounting books, or prepare to sign outsourcing contract to accounting office.[Currency / Language]Principles will be booking in Urdu, Pakistan Rupee construction, but you can also accept notation in English.■ Pakistan accounting standardPakistan's accounting standards are set, revised and eliminated by ICAP organized by a Chartered Accountant.Pakistan accounting standards have been established based on International Accounting Standards (IAS) over the past two decades. Today, as the International Financial Accounting Standards (IFRSs) emerge, the introduction work is ongoing.[Introduction of IFRS]International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have been established by a private specialized organization called the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and are applied in more than 100 countries worldwide.Even in Pakistan, its application has almost been completed, and IFRS 9 (Financial Instruments) is scheduled to be adopted from the fiscal year beginning January 1, 2013.
According to the company regulations of 1984 (Companies Ordinace, 1984) and the company regulations of 1985, the current Pakistan accounting system requires the preservation obligation of the accounting book, the shareholders' meeting, the reporting obligation of the annual report to the registration authority, the Pakistan accounting standard Fundamental rules such as compliance are prescribed, and other accounting processing will be carried out according to income tax regulations, stock exchange rules, etc. The Pakistan accounting standards created by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of Pakistan (Pakistan) currently apply mostly to IFRS and are internationally consistent.Accounting PeriodUnder the Companies Act of Pakistan, companies shall set a period of no more than 12 months as fiscal year (paragraph 2 of Article 233), unless special permission is obtained.In the taxable year for taxation, there are a normal tax year (normal tax year) and a special tax year (special tax year) (Income Tax Law Article 74). The normal taxable year must submit declarations by December 31, with a period of 1 year from July 1 to June 30 as the taxable period.If authorized by the authorities, you can set any 12 months as the taxable year (special taxable year). In this case, if the tax year ends from January 1 to June 30, we will file a declaration by 31 December. Companies that set tax years for other periods must submit declarations by September 30 of the following year after the tax year ends.Therefore, both the fiscal year and the taxable year can be set for each company, it is possible to set the same fiscal year as the parent company.[Accounting book]All companies must keep and keep account books. Accounting books are required to be put in registry offices (Registered Office) for at least 10 years.If you fail to comply with this provision, all directors are sentenced to imprisonment with work for not more than 6 months or a fine not exceeding 10,000 Pakistan rupees. However, in the case of a listed company, it is a fine of not more than 1 year imprisonment or a fine of not more than 50,000 Pakistan Rupees (over 20,000 Pakistan Rupees) in view of the magnitude of social influence.Registrar and SECP (Securities & Exchange Commissionin Pakistan) have the right to inspect accounting books at any time when it is deemed necessary. If there is any incompleteness in the creation and preservation of accounting books, you may be penalized. From the beginning of the establishment, it is necessary to establish internal control on bookkeeping and preservation of accounting books, or prepare to sign outsourcing contract to accounting office.[Currency / Language]Principles will be booking in Urdu, Pakistan Rupee construction, but you can also accept notation in English.■ Pakistan accounting standardPakistan's accounting standards are set, revised and eliminated by ICAP organized by a Chartered Accountant.Pakistan accounting standards have been established based on International Accounting Standards (IAS) over the past two decades. Today, as the International Financial Accounting Standards (IFRSs) emerge, the introduction work is ongoing.[Introduction of IFRS]International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have been established by a private specialized organization called the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and are applied in more than 100 countries worldwide.Even in Pakistan, its application has almost been completed, and IFRS 9 (Financial Instruments) is scheduled to be adopted from the fiscal year beginning January 1, 2013.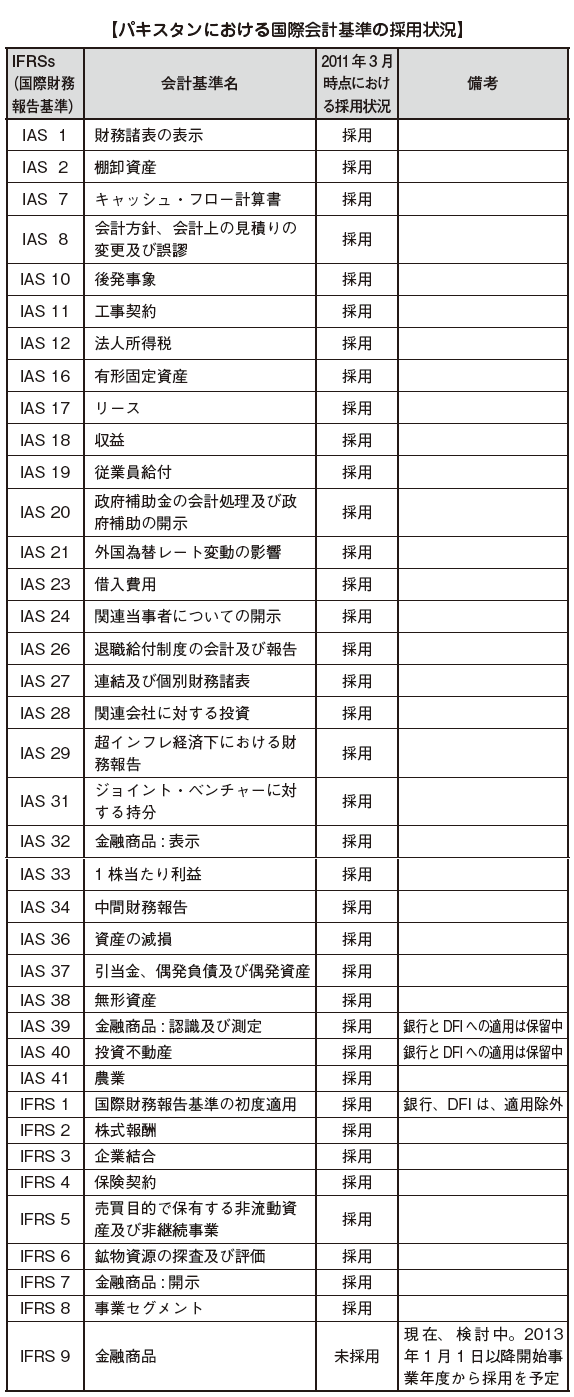 However, some standards are not applied to the banking industry and others. Regarding IAS 39 (financial instruments: recognition and measurement) and IAS 40 (investment property), at the request of state-owned banks of Pakistan, banks, development financial institutionsApplication to DFIs (Development Financial Institutions) has not been posted. Also, regarding IFRS 1 (first-time application), banks and DFI are excluded from application. In addition, the application period for IFRS 7 financial products (disclosure) and IFRS 8 business segments was also postponed.[Islamic Financial Accounting]Islamic finance is called Islamic finance. In Islamic sacred texts "Koran", income earnings are forbidden, and you can not accept "interest" such as loans. As a result, the financial industry has not developed quite well in the Islamic area, but in recent years bond technology has developed that can earn revenue in a form different from interest, and Pakistan also has a large amount of Islamic bonds to secure revenue Issuing.[Accounting Standard for SMEs]In Pakistan, for small and medium-sized enterprises, it is possible to carry out appropriate accounting even by a simple method, and rather than judging that the merit of reducing complications is larger, in addition to the above standards, SMEs (Accounting and Financial Reporting Standards for Medium - Sized Entities (MSEs) and Small - Sized Entities (SSEs)).Small and medium enterprises referred to here are companies that are distinguished between small and medium enterprises and satisfy the following requirements, respectively.Small business· The total amount of paid-in capital and surplus after dividends is less than 25 million Pakistan Rupee· Annual revenue (sales and other revenue) is less than Rs 200 millionMidsize company· It is not a listed company or a subsidiary of a listed company· Annual profit is less than 1 billion rupees· The number of employees is 750 or less· In addition, we do not own assets of outside people widely, we do not conduct public works etc.
However, some standards are not applied to the banking industry and others. Regarding IAS 39 (financial instruments: recognition and measurement) and IAS 40 (investment property), at the request of state-owned banks of Pakistan, banks, development financial institutionsApplication to DFIs (Development Financial Institutions) has not been posted. Also, regarding IFRS 1 (first-time application), banks and DFI are excluded from application. In addition, the application period for IFRS 7 financial products (disclosure) and IFRS 8 business segments was also postponed.[Islamic Financial Accounting]Islamic finance is called Islamic finance. In Islamic sacred texts "Koran", income earnings are forbidden, and you can not accept "interest" such as loans. As a result, the financial industry has not developed quite well in the Islamic area, but in recent years bond technology has developed that can earn revenue in a form different from interest, and Pakistan also has a large amount of Islamic bonds to secure revenue Issuing.[Accounting Standard for SMEs]In Pakistan, for small and medium-sized enterprises, it is possible to carry out appropriate accounting even by a simple method, and rather than judging that the merit of reducing complications is larger, in addition to the above standards, SMEs (Accounting and Financial Reporting Standards for Medium - Sized Entities (MSEs) and Small - Sized Entities (SSEs)).Small and medium enterprises referred to here are companies that are distinguished between small and medium enterprises and satisfy the following requirements, respectively.Small business· The total amount of paid-in capital and surplus after dividends is less than 25 million Pakistan Rupee· Annual revenue (sales and other revenue) is less than Rs 200 millionMidsize company· It is not a listed company or a subsidiary of a listed company· Annual profit is less than 1 billion rupees· The number of employees is 750 or less· In addition, we do not own assets of outside people widely, we do not conduct public works etc.
-
-
-
Disclosure system of Pakistan
Disclosure contents and schedule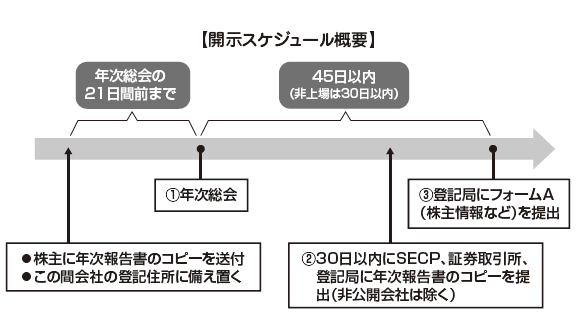 Disclosure ScheduleDisclosure of Annual ReportDirectors must submit an annual report to the annual general shareholders meeting (Article 233 (1)). The submission method must send copies of the annual report to shareholders at least 21 days before the annual general meeting.In addition, it is required to prepare a copy of the annual report in the registered address of the company (Article 233 (4)) so that shareholders and others can investigate for 21 days before the general meeting.In the case of a listed company, an obligation to submit a copy of the annual report to the SECP, the Stock Exchange, the Registration Authority will also be added (Article 233.5). Regarding the quarterly report, a copy of the quarterly report along with the company's business review of the directors will be sent quarterly to shareholders and the listed stock exchange, SECP, registration office within 30 days from the end of the quarterly period (Article 245).Furthermore, companies other than private companies must also submit a copy of the annual report to the company registration office within 30 days from the date of the annual shareholders' meeting (Article 242 (1) (3)).A fine of up to Rs. 5,000 will be imposed if not submitting the annual report etc to the prescribed place (Article 244).
Disclosure ScheduleDisclosure of Annual ReportDirectors must submit an annual report to the annual general shareholders meeting (Article 233 (1)). The submission method must send copies of the annual report to shareholders at least 21 days before the annual general meeting.In addition, it is required to prepare a copy of the annual report in the registered address of the company (Article 233 (4)) so that shareholders and others can investigate for 21 days before the general meeting.In the case of a listed company, an obligation to submit a copy of the annual report to the SECP, the Stock Exchange, the Registration Authority will also be added (Article 233.5). Regarding the quarterly report, a copy of the quarterly report along with the company's business review of the directors will be sent quarterly to shareholders and the listed stock exchange, SECP, registration office within 30 days from the end of the quarterly period (Article 245).Furthermore, companies other than private companies must also submit a copy of the annual report to the company registration office within 30 days from the date of the annual shareholders' meeting (Article 242 (1) (3)).A fine of up to Rs. 5,000 will be imposed if not submitting the annual report etc to the prescribed place (Article 244).
Disclosure of company information to Registration AuthorityRegardless of whether or not the annual general shareholders meeting is held, all corporations must submit form A describing shareholder information etc. once a year to the Registry Bureau (Article 156). Form A contains corporate information such as capital amount, shareholder list, company officer information.Listed company is within 45 days from the Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders (in the case of not holding regular shareholders meeting, the 31st December of that year), the unlisted company is an ordinary general meeting of shareholders (in the case of not holding the ordinary general meeting of shareholders, I will submit it to the Registration Authority within 30 days from January 31st.
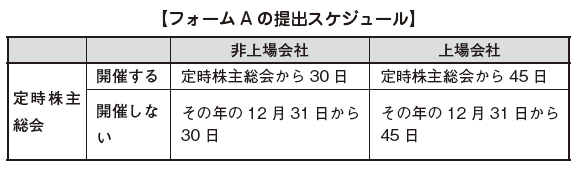
For a listed company, you can extend the deadline for submitting the report for a period of 15 days only if you obtain permission.If the report is delayed or not reported, the following fines will be imposed on the company and officers.
Listed company: In addition to 10 thousand rupees, a delay of 200 Rs per dayUnlisted company: In addition to 2,000 rupees, a delay of 50 rupees per day
[Disclosure details]Every company has an obligation to prepare an annual report (Annual Report) and submit it to the annual shareholders meeting (Article 233).The annual report required by the Company Ordinance consists of the balance sheet, income statement, notes table, audit report, and manager report (Directors Report) (Articles 233, 236). The balance sheet and profit and loss statement must be audited, and the executive report will describe the opinion on the situation of the company, the amount of dividends and the amount of retained earnings (Article 236 (1)).In the case of a listed company, in addition to the above, there are statutory of Changesin Equity, Cash Flow Statement, Compliance Statement on Code of Corporate Governance, compliance with the Corporate Governance Law You must create an audit report (Auditors' Report of Compliance of Code of Corporate Governance) (Article 234 (3)). The method of preparing financial statements will be prepared in accordance with Appendix 5 of the Company Ordinance in 1984 (excluding private companies that are subsidiaries of listed companies) (Article 234 (2)).
In the case of a listed company, further creation and disclosure of the following quarterly report is required. With respect to the deadline, the first to third quarter must submit to the registering authority and the Securities and Exchange Commission in addition to the shareholders and listed stock exchanges within one month after the end (Article 245). The contents of the quarterly report are composed of the following documents based on International Accounting Standard IAS 34.
· Quarterly balance sheet· Quarterly income statement· Quarterly Cash Flow Statement· Statement of changes in quarterly shareholders' equity· Quarterly notes· Quarterly Management Report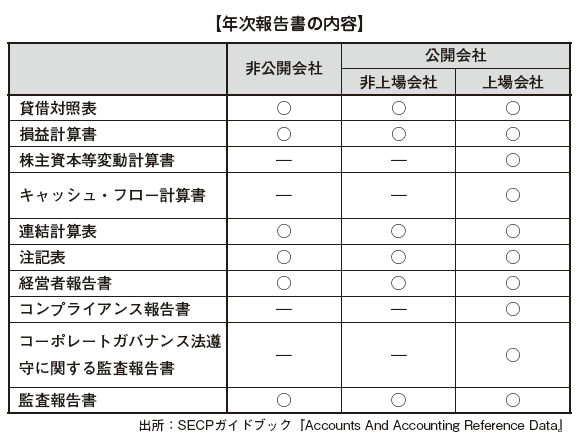 ■ Audit systemPakistan requires the appointment of an auditor (Auditor) for all companies under the company regulations of 1984 (Article 252 (1)). International auditing standards (ISA) are applied to Pakistan's auditing standards.
■ Audit systemPakistan requires the appointment of an auditor (Auditor) for all companies under the company regulations of 1984 (Article 252 (1)). International auditing standards (ISA) are applied to Pakistan's auditing standards.
-
-
-
References
・1984年会社条例
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya