Thailand
8 Chapter Labor
-
-
1 Chapter Basic knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.1 Strong Economic in Thailand
2.2 Trade Liberalization in Thailand
2.5 Advantages of Investment in Thailand
3 Chapter Incorporation
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.4 Investigation of entry schemes for each business type
3.5 How to establish a regional headquarters
3.6 Establishment of business base
3.7 Company liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter M&A
4.2 General M&A regarding to Corporate Law
4.3 Summary of applicable Laws for M&A
4.4 Difficulty of business and corporate evaluation
4.5 Foreign Investment Restriction
4.8 Securities and Exchange Act B.E. 2535
5 Chapter Corporate Law
5.1 Types of Thailand Business Structures
5.2 Annual General Shareholders’ Meeting in Thailand
5.3 Director and Board of Director
5.6 Dividend and Legal Reserve
6 Chapter Accounting System
6.1 Overview of accounting system
6.2 Person Responsible for accounting record
6.4 Problem and accounting system
6.5 Disclosure system and disclosure practice
7 Chapter Tax
7.2 Several issues on domestic tax law
7.3 File a Tax Return and Payment
8 Chapter Labor
8.1 Labor environment in Thailand
8.3 Social security system in Thailand
8.4 Points to keep in mind while having Japanese people in Japan
9 Chapter Q&A
-
-
-
Latest News & Updates
【About raising minimum wage】At the meeting on October 19, the Thai Central Wage Committee decided to raise the minimum wage of 300 Baht per day to 5-10 baht.It is scheduled to be implemented from 1 January 2017 after approval by the Cabinet.With regard to the amount raised, it is necessary to pay attention that different prefectures differ depending on the economic situation, such as the price level and corporate wage payment situation.For Bangkok, Nonthaburi, Samut Prakan and other 6 prefectures in the metropolitan area, 13 bahts are raised, 13 prefectures including Plazimburi, Songkhla, Chiang Mai and Ayutthaya will raise 8 baht, and other prefectures will raise 5 baht.In addition, the minimum wage increase in the eight prefectures of Sinburi, Chumphon, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Trang, Ranong, Narathiwat, Pattany, Yarra will be unchanged. -
Working environment
■ Working populationThe population of Thailand is about 67.01 million (2013 / the World Bank), of which the labor force population (over 15 years old) is about 54.87 million people and the employed workers are about 38.9 million (excluding seasonal workers) . Of the employed workers, agriculture, forestry and fishery workers account for about 13.21 million people, accounting for over 20% of the working population.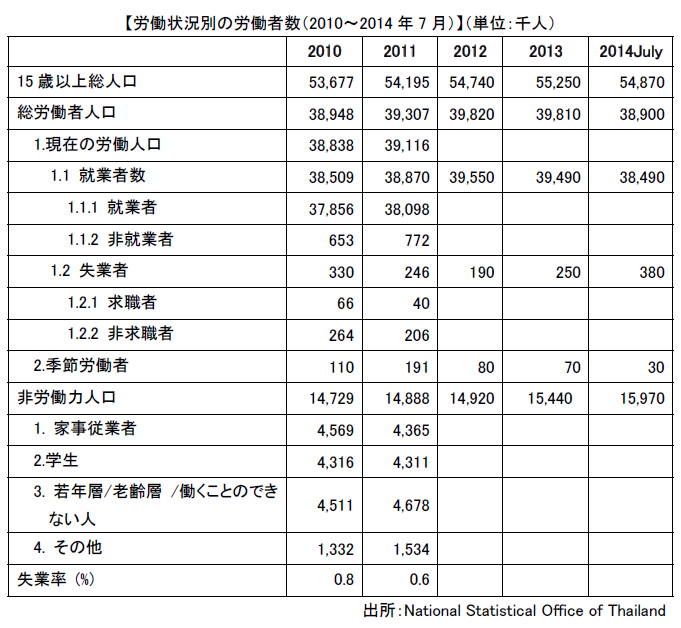 ■ Working Population by IndustryLooking at the employment structure of general workers by industry, the agriculture, forestry and fishery industry (13.21 million people) was the largest at 34%, followed by the wholesale and retail trade (690,000 people, 16%) in the manufacturing industry (649,000 people, 17% , Hotel drinking industry (2.55 million, 7%), construction industry (2.12 million, 5%), and so on. Recently the proportion of service industry is increasing.【産業別の就業人口】
■ Working Population by IndustryLooking at the employment structure of general workers by industry, the agriculture, forestry and fishery industry (13.21 million people) was the largest at 34%, followed by the wholesale and retail trade (690,000 people, 16%) in the manufacturing industry (649,000 people, 17% , Hotel drinking industry (2.55 million, 7%), construction industry (2.12 million, 5%), and so on. Recently the proportion of service industry is increasing.【産業別の就業人口】.png) Source: National Statistical Office of ThailandIn Thailand, the disparity in treatment such as wages due to academic background is large, so the higher educational level is progressing. Nonetheless, only about 16% of the regular workers are employed by college graduates or above. Currently there are few universities in Thailand with 78 national universities and 69 private universities. Recently, both excellent workers, professionals and other excellent talent are lacking, and for companies looking for talent, securing human resources and rising wages are serious problems.As of the end of 2014, it is said that about 1.5 million foreign workers are allowed to work in Thailand. However, it is said that about 300 to 4 million people including illegal workers not registered in the Ministry of Labor are included.Many foreign workers are migrant workers from Myanmar, Laos and Cambodia. Whether to prioritize the lack of labor force or crackdown on illegal workers is a very troubling issue for the Thai government.
Source: National Statistical Office of ThailandIn Thailand, the disparity in treatment such as wages due to academic background is large, so the higher educational level is progressing. Nonetheless, only about 16% of the regular workers are employed by college graduates or above. Currently there are few universities in Thailand with 78 national universities and 69 private universities. Recently, both excellent workers, professionals and other excellent talent are lacking, and for companies looking for talent, securing human resources and rising wages are serious problems.As of the end of 2014, it is said that about 1.5 million foreign workers are allowed to work in Thailand. However, it is said that about 300 to 4 million people including illegal workers not registered in the Ministry of Labor are included.Many foreign workers are migrant workers from Myanmar, Laos and Cambodia. Whether to prioritize the lack of labor force or crackdown on illegal workers is a very troubling issue for the Thai government.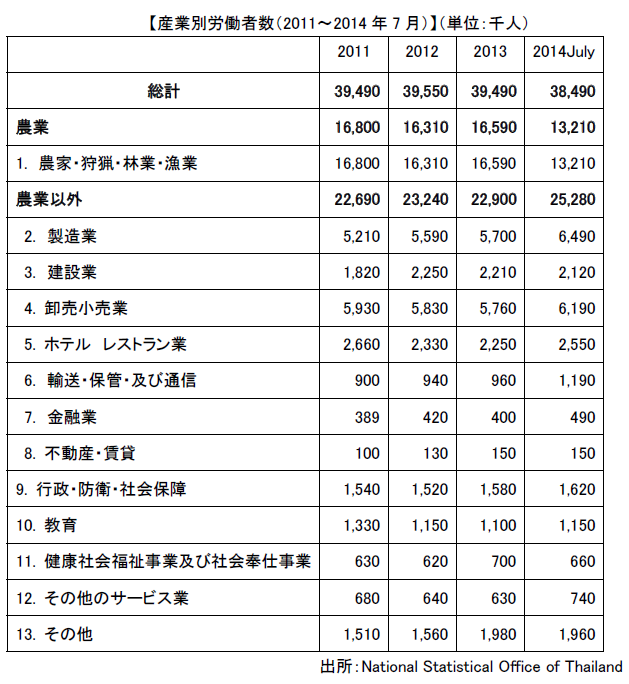 Especially in ASEAN countries, there are a lot of workers coming and going, and in order to acquire skilled workers from Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia and other ASEAN countries, companies in Thailand are expected to raise salary in the future.■ Unemployment rate
Especially in ASEAN countries, there are a lot of workers coming and going, and in order to acquire skilled workers from Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia and other ASEAN countries, companies in Thailand are expected to raise salary in the future.■ Unemployment rateIn Thailand, the seasonal fluctuation of the unemployment rate is characteristic, and as the new graduates enter the labor market from February to May, at the same time the unemployment rate of agricultural workers rises because it is dry season, but from June the unemployment rate tends to decline as it will be the busy season of.
In the investment boom season around 1995, temporary labor supply and demand was tightened, but after the 1997 currency crisis, the supply and demand of labor force relaxed with economic downturn, and in 1998 the number of unemployed people 1.41 million people, the unemployment rate worsened to 4.4%. However, after that, it recovered steadily, and in 2014 the number of unemployed was about 570,000 and the unemployment rate was 0.84%.As for the tendency, the number of unemployment of young workers aged 15 to 29 is the largest, and men are more unemployed than women. As of 2014, both Japan and the United States have about 3.6% unemployment rate, which means that in Thailand it is relatively low unemployment rate of 1% or less.■ Industrial average wage.png) The average wage level for all industries in FY2013 is 12,163 baht per month, and is generally on an upward trend. Furthermore, the average wage level for all industries in March 2014 has reached 12,773 baht per month, and has been rising for the past five years.Looking at the wage levels of major industries in FY 2013, the financial industry was 24,589 Baht, the electricity, gas and water supply exceeded the average level at 19,536 baht, while the manufacturing industry remained at an average level of 11,375 baht It is wage of 5,428 Baht for Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery Industries, which is less than half of all industry average.■ Comparison of wages with other countriesComparing Bangkok 's wage level with the major cities in neighboring countries, the wage levels of worker classes and engineers are higher than Jakarta and Ho Chi Minh, but there is not much difference from Shenzhen in China. Also, in recent years wage levels in intermediate management classes are rising sharply.
The average wage level for all industries in FY2013 is 12,163 baht per month, and is generally on an upward trend. Furthermore, the average wage level for all industries in March 2014 has reached 12,773 baht per month, and has been rising for the past five years.Looking at the wage levels of major industries in FY 2013, the financial industry was 24,589 Baht, the electricity, gas and water supply exceeded the average level at 19,536 baht, while the manufacturing industry remained at an average level of 11,375 baht It is wage of 5,428 Baht for Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery Industries, which is less than half of all industry average.■ Comparison of wages with other countriesComparing Bangkok 's wage level with the major cities in neighboring countries, the wage levels of worker classes and engineers are higher than Jakarta and Ho Chi Minh, but there is not much difference from Shenzhen in China. Also, in recent years wage levels in intermediate management classes are rising sharply.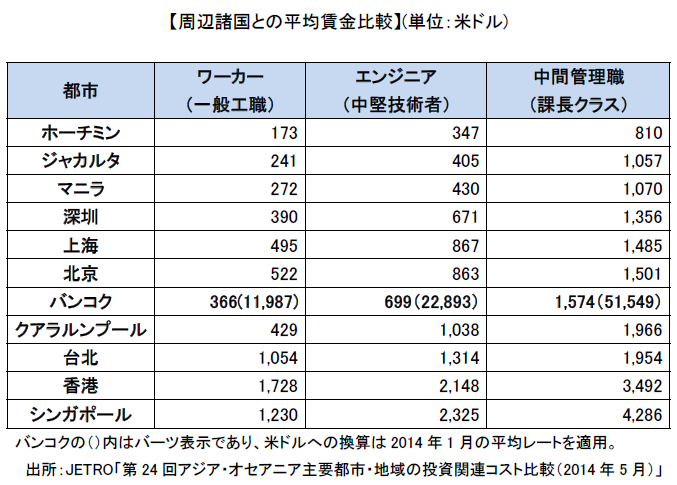 The salary system is determined by organization, department, or job title and worker skill level, background, and educational background. It may also be determined by the length of service. It is at least about 8,000 baht a month for inventory management and support jobs, sales and customer service in the clerical field, up to about 25,000 to 30,000 baht per month.Also, for accounting, finance and secretarial work, monthly salary is 40 thousand baht, while marketing and procurement department will have a minimum monthly salary of 15,000 baht. Looking at the senior position, the monthly salary is over 100 thousand baht in accounting and finance, in managers, monthly salary excluding secretaries is 150 thousand baht, and in accounting, finance and personnel department, monthly salary is 250 thousand Baht.By industry, young people in the aviation sector are about 8,000 baht per month, but up to about 150 thousand baht can be obtained depending on the type of business and qualifications and backgrounds of various types of international aviation. Monthly salary of banks and import and export businesses is 1 to 20 thousand baht, and in high-level jobs, they receive high salaries in the aviation sector, retail and FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods related) business and import and export business can do. At the senior management level, the highest standard salary is obtained in the pharmaceutical industry, oil and gas industry with a monthly salary of about 30-350 thousand Baht.Various skills and engineering are usually about 10 thousand Baht, and there is not much change even if you become a senior position. The IT department can earn approximately 15,000 baht for young people and approximately 30,000 baht for a maximum. 80,000 Baht for senior posts, 20-250 thousand Baht for managers and senior managers. Also, if you can speak Japanese, young people may cost 80 thousand Baht, depending on job class or nationality, 15 thousand to 350 thousand baht.It is necessary to pay attention that these salary schemes are only basic salary of employees, no other benefits or job allowances are included. The salary decision element includes the employee's qualification, career and educational background. They are also used for market credit when employees seek higher levels of occupation.
The salary system is determined by organization, department, or job title and worker skill level, background, and educational background. It may also be determined by the length of service. It is at least about 8,000 baht a month for inventory management and support jobs, sales and customer service in the clerical field, up to about 25,000 to 30,000 baht per month.Also, for accounting, finance and secretarial work, monthly salary is 40 thousand baht, while marketing and procurement department will have a minimum monthly salary of 15,000 baht. Looking at the senior position, the monthly salary is over 100 thousand baht in accounting and finance, in managers, monthly salary excluding secretaries is 150 thousand baht, and in accounting, finance and personnel department, monthly salary is 250 thousand Baht.By industry, young people in the aviation sector are about 8,000 baht per month, but up to about 150 thousand baht can be obtained depending on the type of business and qualifications and backgrounds of various types of international aviation. Monthly salary of banks and import and export businesses is 1 to 20 thousand baht, and in high-level jobs, they receive high salaries in the aviation sector, retail and FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods related) business and import and export business can do. At the senior management level, the highest standard salary is obtained in the pharmaceutical industry, oil and gas industry with a monthly salary of about 30-350 thousand Baht.Various skills and engineering are usually about 10 thousand Baht, and there is not much change even if you become a senior position. The IT department can earn approximately 15,000 baht for young people and approximately 30,000 baht for a maximum. 80,000 Baht for senior posts, 20-250 thousand Baht for managers and senior managers. Also, if you can speak Japanese, young people may cost 80 thousand Baht, depending on job class or nationality, 15 thousand to 350 thousand baht.It is necessary to pay attention that these salary schemes are only basic salary of employees, no other benefits or job allowances are included. The salary decision element includes the employee's qualification, career and educational background. They are also used for market credit when employees seek higher levels of occupation.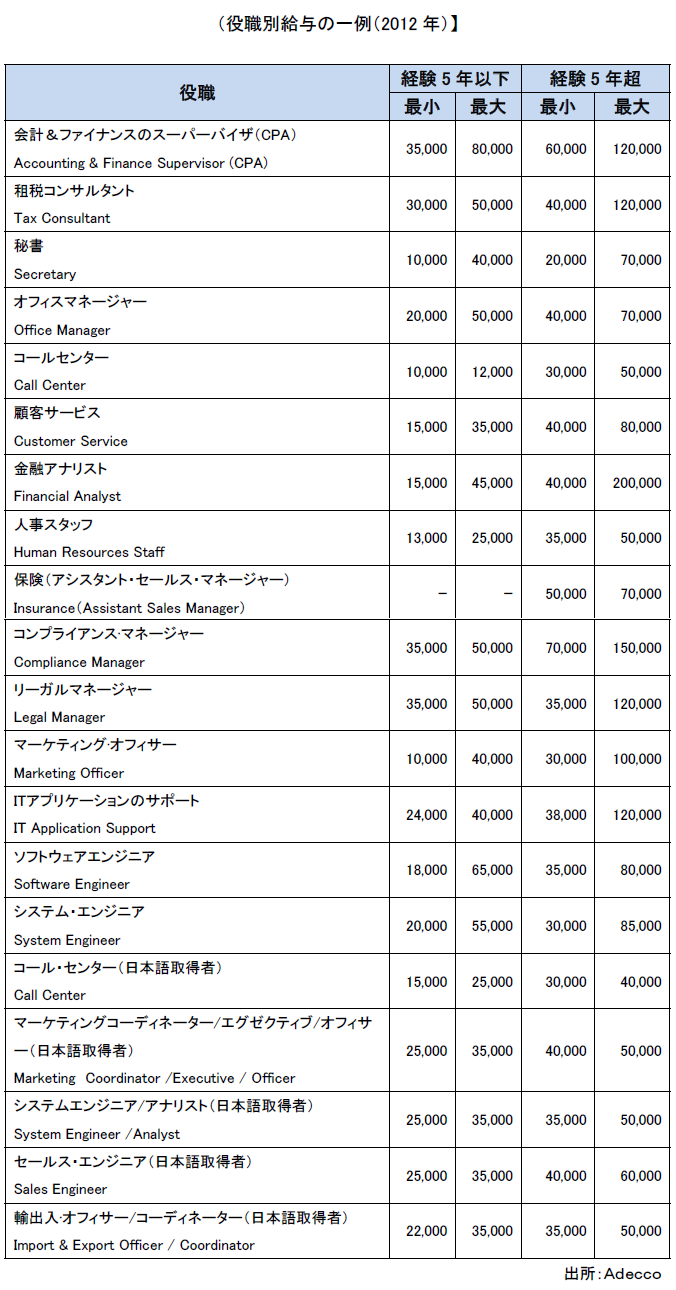 Especially senior management and foreign skilled employees of high skill professionals can obtain a significant amount depending on nationality, qualifications and backgrounds. Depending on the size of the company, international companies or global organizations, the salary system is very different. You have to be aware that you can present different benefits and warranties at the same level, the same post in two different companies.
Especially senior management and foreign skilled employees of high skill professionals can obtain a significant amount depending on nationality, qualifications and backgrounds. Depending on the size of the company, international companies or global organizations, the salary system is very different. You have to be aware that you can present different benefits and warranties at the same level, the same post in two different companies. -
Labor disputes with labor unions
Labor law in 1972 regulates worker protection, workers' compensation, minimum wage, etc. In 1975, Labor Relations Act was established enacting labor union and labor dispute resolution rules in 1975. Following the establishment of the Labor Relations Act, the Labor Congress of Thailand (LCT) was formed in 1976 by organizing domestic labor unions, but the military coup occurring in that year (Blood Wednesday In the issuance of martial law accompanying the incident), the effectiveness of these labor legislation ceased and strikes were prohibited.In 1981, this ban was lifted, and in 1990 the Social Insurance Law stipulating safeguards against injuries and unemployment of workers came into effect, but in 1991 immediately after that, the state workers' Union formation rights and strike right were deprived.Subsequently, in 1994, the Workers' Compensation Compensation Law, in 1998 shortened working hours and strengthened worker protection such as raising dismissal payments. The Workers Protection Law was enacted and in 2008 a revision was made to include obligation provisions to the temporary workers' right and welfare to be treated fairly and equitably by the employees of the dispatched workers.
■ Labor union etcIn the case of forming a labor union, based on the provisions of the Labor Relations Act established in 1975, it is necessary to have the founder of more than 10 workers, register the draft rules of labor union with the Labor Bureau, obtain permission Is required. If the cooperative agreement conforms to the purpose of the law and does not adversely affect national security and the economy, you will be able to acquire permission and act as a labor union under the Labor Relations Act.As a result, members of labor unions can have the right to submit requests, negotiations, accept arbitration decisions, and conclude agreements on the following contents to the employers and others.
·Working conditions· Working days, working hours·wage·Welfare· Dismissal· Worker complaints motion· Revision or renewal of labor condition agreement
As of 2014, the number of private industry labor conferences nationwide is 52 unions. The largest union organization has nationwide private industry labor conference and state enterprise labor federation each have about 150,000 members. Still, the organization rate is as low as a few%, the labor union organization by industry is weak, there are problems of the leadership of union leaders, and the current national center has not grown yet.Labor protection and welfare department of Labor Ministry regularly conducts inspections etc. in Thailand in compliance with labor laws and regulations and issues qualifications to users without problems.The establishment that employs more than 50 employees must establish a welfare program committee consisting of five or more workers' representatives, and the employer must establish at least every three months It is said that it is necessary to discuss consultation about benefits welfare of employee with welfare committee.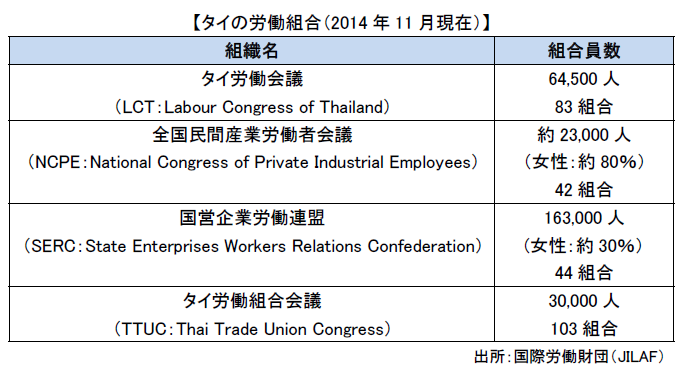
■ Conditions of Labor DisputesThe number of labor disputes occurred in 77 cases (number of participants: 58,611) in 2010, 119 in 2011 (73,573 participants), and 100 in 2012 (52,345 participants) It has been around 100 per year.In labor dispute, it is difficult to solve between the parties, there are cases where democratization is requested by the government or the government office to make it a social problem. For Japanese affiliated companies in 2009, Tostem · Thailand Factory and Mazda Joint Venture Factory are experiencing labor disputes demanding wage increase from 2009 to 2010 respectively.Also in 2012, the Japanese labor dispute has prolonged due to the prolonged labor dispute, the labor union hundreds have been demonstrating march by eliminating the dismissal of 178 executives including labor union officials and the payment of retirement payment, even at foreign-affiliated companies other than Japanese-affiliated companies There is a strike requesting a raise such as.
Procedure for resolving labor disputesIn Thailand, based on the Labor Court enacted in 1979 and the Labor Accident Procedure Law, a labor court has been established as the first instance court to expertly examine disputes between labor and management. The judge of the labor court, in addition to a judge with expert knowledge on labor issues, a person representing the worker side and a person representing the employer side will join the trial as a judge of the judge .The jury judge is asked to the presiding judge not to be on either the worker side or the employer side, and is required to swear to fulfill his / her duties fairly. Focusing on the promptness of the case, appeal is to be made to the Supreme Court rather than the appellate court of the second instance. However, the reason for appeal is limited to statutory matters.A series of procedures for solving labor disputes etc. occurring in the workplace are stipulated in the labor relations law as follows.1. First, when a worker submits a request relating to improvement of working conditions, signature of 15% or more of workers, more than one fifth of all workers when labor union presents labor union You are required to have each of them. At the time of labor negotiations, both labor and management can attend advisers qualified by the Labor Bureau.2. Labor and management must start negotiations between labor and management within three days from the date of receipt of the request, if negotiations can not be started within 3 days, or agreement has not been reached regardless of the reasons after the start of labor negotiations In case, labor dispute under the Labor Relations Act is considered to have occurred. The person who submitted the request must notify the Labor Bureau in writing within 24 hours from the point of failure to reach agreement.3. The mediation officer of the Labor Bureau enters into mediation within 5 days from the date of receiving notification. Unlike Japan, you must undertake procedures for mediation.4.When an agreement is reached by mediation, we announce the agreement contents for 30 days or more within 3 days from the date of reaching agreement in writing after signing both labor and management.5. If the consensus is not reached by arbitration,(A) agree to appoint a dispute arbitrator(B) Enter a strike from worker side or lockout from user sideWill be either.Dispute Since arbitration by arbitrators is an agreement between both labor and management, in reality most cases involve strikes or lockouts in (b). In the event of entering into exercise of strikes and lockouts, you must notify the Labor Bureau and the other party in writing 24 hours in advance. In addition, when a request form is not presented to the partner, or when one obeys the mediation of the Labor Office, it is forbidden to enter a strike or lockout.
■ Points of Labor DisputeThe main cause of the problem in labor dispute is mainly dissatisfaction with working conditions such as employee layoff, dismissal or wage amount. In 2013, 8,995 dismissals have been reported.Then, 4,736 illegal acts under the Labor Protection Act and 2,325 cases of labor condition agreement breakdown.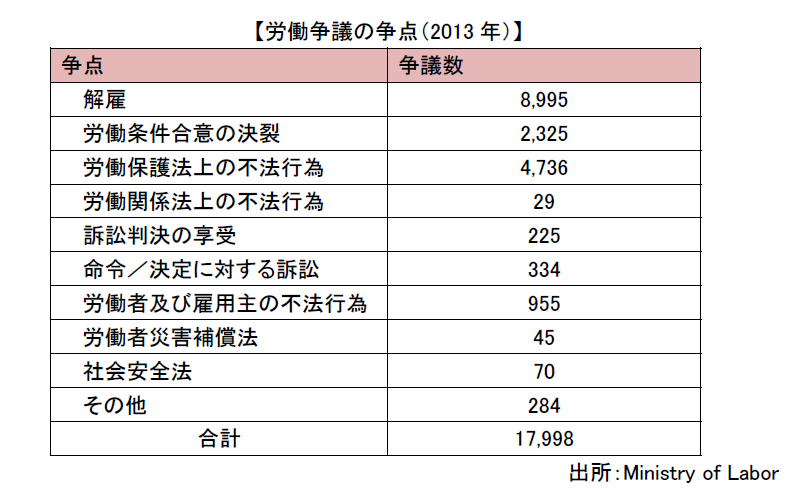 As a dissatisfaction with working conditions, salary levels may be significantly lower than other companies in the same area in the same area. In particular, in recent years, since the wage rise rate is as high as around 5%, it is necessary for labor management to grasp the level of other companies in the same industry and to review periodic salary levels. In order to retrain employees, companies also design payroll packages that meet the needs of each individual employee.
As a dissatisfaction with working conditions, salary levels may be significantly lower than other companies in the same area in the same area. In particular, in recent years, since the wage rise rate is as high as around 5%, it is necessary for labor management to grasp the level of other companies in the same industry and to review periodic salary levels. In order to retrain employees, companies also design payroll packages that meet the needs of each individual employee.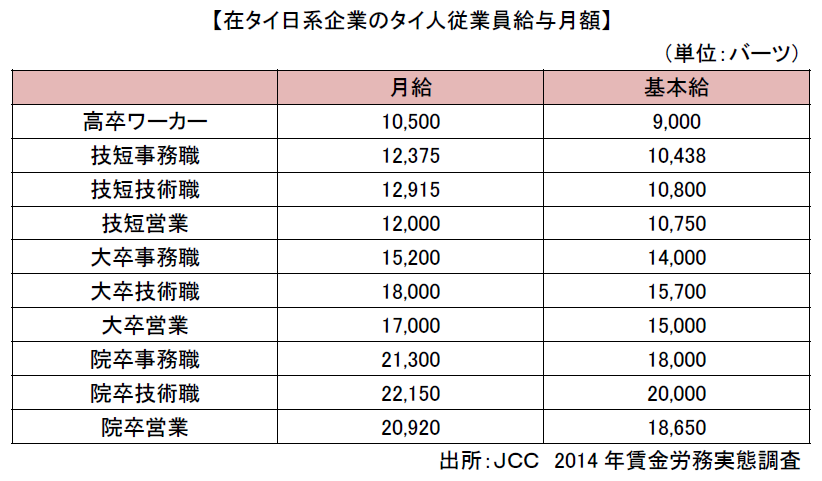 Elements such as job environment, corporate policy, relationships with superiors, career paths, etc., have become more influential to intention to join or continue to work. At the same time, as a factor other than the payroll level, it is important to tell workers how to benefit from working at the company. Especially for workers of advanced technology such as engineers to give their roles according to their skills and give dreams by giving a big challenge such as manager promotion opportunities also attracting technology workers to the company, In order to utilize it in a meaningful way, it is important.The concrete and long-term merit is an effective means of continuously hiring employees within the company. The long-term merit is necessary to match company goals and individual employee goals. It also leads to maintaining high productivity by knowledge and experience accumulated by employees.
Elements such as job environment, corporate policy, relationships with superiors, career paths, etc., have become more influential to intention to join or continue to work. At the same time, as a factor other than the payroll level, it is important to tell workers how to benefit from working at the company. Especially for workers of advanced technology such as engineers to give their roles according to their skills and give dreams by giving a big challenge such as manager promotion opportunities also attracting technology workers to the company, In order to utilize it in a meaningful way, it is important.The concrete and long-term merit is an effective means of continuously hiring employees within the company. The long-term merit is necessary to match company goals and individual employee goals. It also leads to maintaining high productivity by knowledge and experience accumulated by employees. -
Employment Practices and Labor Management
When employing Thai workers, it is necessary to think separately from workers and candidates for managerial positions (manager) and engineers. In Thailand, distinction between so-called blue color and white color is relatively clear. In addition, in the case of recruiting employees, means such as newspaper advertisement, bulletin in the industrial estate, posting at the nearest labor office, mediation of recruitment agencies, recruitment in relationships and reviews, etc. are taken Recently, posting on the Internet has also been actively performed.The major alphabetical daily newspaper with numerous advertisements (Thai and English) is Bangkok Post and The Nation, each with approximately 70,000 copies per day as of 2014. Also, to recruit graduates, it is also important to create a network with educational institutions such as universities at an early stage.In Bangkok, there are many recruitment companies both local and foreign companies, and these companies are also engaged in personnel labor consulting such as outsourcing of labor / legal procedures, corporate organization and labor relations, labor management in different cultures, etc. besides recruitment. When employing Thai workers, it is also effective to consult Japanese-affiliated companies with a Japanese recruitment company or consulting company.In the employment and job seeker protection law (1985) and the Foreign Employment Law, the employment placement system in Thailand is regulated, and job offers through companies that do not obtain a license in hiring workers are prohibited. License will be issued to recruitment company, introduction of company to job seeker, introduction of job seeker to company.Recently, workers and managers' class talent are both short and it is difficult to collect excellent talent. In Thailand, there is a tendency for so-called job hopping, which makes it easy to change workplaces depending on treatment (salary, post etc.), because there is little sense of resistance to job change regardless of the length of working hours, because of high liquidity of human resources. This trend is getting stronger especially in the manager and young people. Therefore, when deciding on employment conditions such as salary levels and company location conditions when recruiting engineers and managers, it is necessary to pay attention to competitors' terms and conditions.Also, you should pay particular attention to managing the local staff in Thailand to hurt your pride, such as adding scolding in front of other employees against staff with business mistakes Do not do it. Thai people tend to focus on the face, so if you take such actions immediately you change jobs or in some cases, other employees may be involved to develop into a big problem.
■BenefitsExamples of welfare programs in Thailand are listed below.· Fringe benefit (additional benefit)· Loan fund for workers· Implementation of educational program· nursery· Education on labor protection welfare· Establishment of management standard for HIV / AIDSEven for expatriates and workers in Thailand, implementing educational programs that enhance skills is an effective method for motivating employees. In particular, educational programs linked with individual career paths are effective, and participation in such programs is a great appeal for employees.It is actually used as an allowance, and representative ones are as follows.· Providing cars and benefitsThe company provides cars to employees for company use etc. Considering the risk of damages in case of trouble, whether to make it available for company or private use, or for use only for corporate use should be prescribed by regulations. In addition, it can be seen that the company pays gasoline fee and maintenance fee.· Transportation expensesIt is expenses for employee commuting, fixed amount per month, or it may be decided by discussion between employer and employee, or upper limit may be set.· Housing and Housing AllowanceWe will provide housing and housing benefits. These include provision of buildings and provision of housing allowances.· Education feeWe will bear all or part of the educational expenses of our employees' children. The type and burden range of the school vary from company to company.· Medical billsThe company will bear some or all of the medical expenses. Normally, we will submit a receipt for medical expenses etc. and we will pay medical expenses based on that. There are cases where it applies to the medical expenses of the employee's family.■ HolidaysOn Thailand's main public holidays, there are the following. Caution is necessary because the date may be different depending on region and year.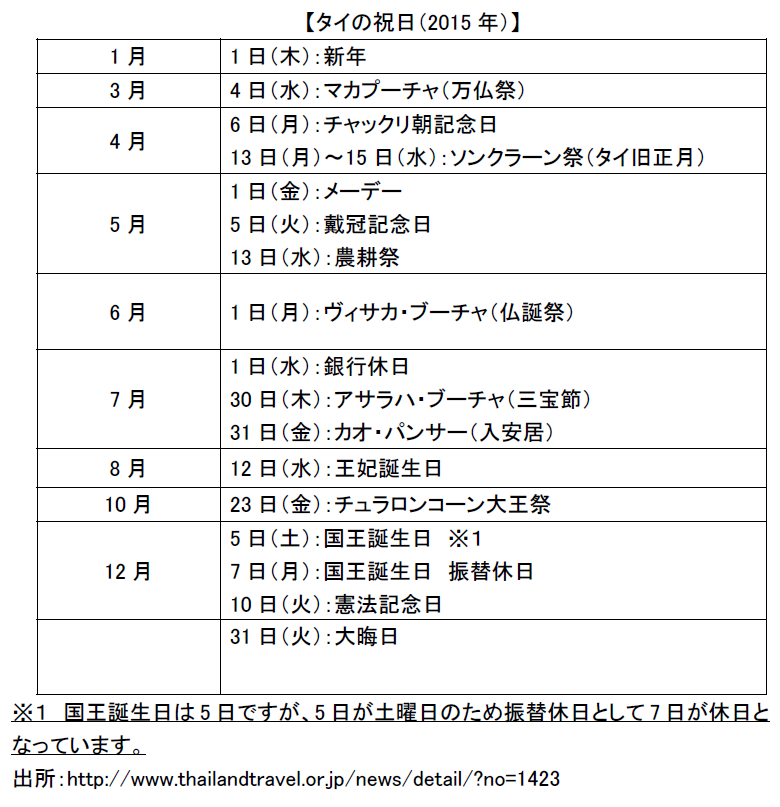
-
-
-
Labor Standards Related Laws
Regarding employment relations, in addition to the commercial trading law which is based on European civil code, the Worker Protection Law is the basic rule, entrusting to a free contract, protecting workers from the viewpoint of protecting the weak, This trend is strengthening in recent years. Specific laws and regulations include "Workers Protection Act (2008)", "Thai Civil Code and Commercial Code Chapter 3, Chapter 6 Chapter Regulations on Employment", "Employment Introduction and Job Seekers Protection Act (2001)" It is cited.These laws and regulations relate to employment contracts, dismissal, wages, hours worked, vacation, overtime, holiday work, overtime wage for overtime workers, young workers, female workers, minority workers, foreign workers, safety and health, Standards for outsourcing, rules on employment, etc. are stipulated.
■ Regulations related to labor standards【Laws related to labor standards】.png)
[Worker Protection Act]The Workers Protection Law is a law stipulating the rights and obligations between employers and workers, and it is a law that provides employment of workers, female workers and young workers, wages, welfare, workplace safety, dismissal allowances, labor welfare funds, We stipulate the minimum standards concerning how to implement workers protection of labor inspectors.Workers who are protected by the Workers Protection Law are said to be "those who agree to receive wages and work for the employer regardless of their name", and are regular employees, part-time employees, management Administrators who are in a standing position can also be protected if they fall under the above definition. Therefore, this law applies to users and workers of all business sites regardless of type of industry and number of employees. However, it is excluded in the following business establishments.
· Central public affairs, local public affairs, local government affairs· State-owned enterprises based on state-owned enterprise labor relations law· The following industries and occupations- Labor in the petroleum business under the Petroleum Act (including repair and service related to oil business, especially work in exploration areas and production areas)- Experts in labor, skill labor, service and administrative work, clerks, sales professionals, professionals in service, labor related to manufacturing, or labor related to these work- Labor at a food dealer or a beverage dealer whose sales or service hours are not continuous for each working day- Skilled or academic labor in exploration, drilling, refining and product manufacturing in petroleum or petrochemical- Managers, academic professionals, clerical workers, labor related to finance or accounting- Mobile sales or merchandising purchase invitation
In Article 77 of the Workers Protection Law, when employers do the following handling to workers, it is said that workers must obtain written consent in advance from the workers.
· When you want to work overtime· When you want to work on a holiday· Wage, overtime work allowance, holiday work allowance, holiday overtime work allowance and other benefits arising from labor are paid by check or foreign currency· When deducting more than one fifth by one tenth for one reason or wage etc.In addition, in order to comply with the Workers Protection Act, the Minister of Labor is to appoint a labor supervisory office to direct the work. In addition, the user is required to report to the labor inspector if it falls under the following, and in case of violation each will be fined.
· In case of hiring young people under 18 years of age (fine in case of violation: 20 thousand baht or less)· When the user is closed from business (fines when violating: less than 10,000 Baht)· When dismissing for reasons such as machine introduction or technical innovation instead of normal dismissal(Fines for violating: less than 20,000 Baht)
【Comparison of labor standards between Japan and Thailand】.png)
■ VacationIn Thailand, in addition to the annual paid vacation described in the above table, it is obliged to give the following vacation.[Sickness leave]For vacation due to illness (leave due to reasons other than business), 30 days of the year must be paid. However, if you are absent from work for more than 3 consecutive days, you will need to submit a medical certificate from the doctor to the company.
[Maternity leave]Holidays due to pregnancy must be given for 90 days including holidays. Also, 45 of them must be paid.
[Infertile Surgery Leave]For vacation due to infertility surgery, the period specified by the doctor can be absent, during this time you must be paid.
[Military leave]Vacation as a reason for military service etc. will always be accepted. Of these, 60 days must be paid.
[Training vacation]It is permitted to absent from work due to work training, and vacation for young people under 18 years of age must be paid up to 30 days.[Leave for labor union activities]Absenteeism will be recognized if you give notice in advance on your vacation due to the work of the labor union. Also, this absence must be paid.■Extra wageIf workers do overtime work, we have to pay more than 1.5 times normal wages as extra wages. With regard to holiday work within hours, wages of twice the normal wage and overtime on holidays will be three times the normal wage. In addition, extra wages outside hours, holidays, and holiday hours are not subject to payment in the case of administrative supervisors or workers who are paid as follows.
· Person with authority and obligation to decide worker bonus or dismissal as well as employer· Results such as visit sales or solicitation, workers receiving a fee according to the volumeHowever, if the above worker carries out holiday work, it is necessary to pay the same amount as the normal wage according to the time.■ Wages for monthly salaryFor Thai workers working on monthly salaries, it is necessary to deal with wages paid on holidays and holidays. Therefore, when calculating overtime work allowance, calculate hourly wage by dividing monthly wage by calendar day number and working hours, then multiply by the above-mentioned extra wage rate and calculate overtime work allowance etc.■ Competition obligationIn Thailand, there is no law stipulated with regard to the prevention of competition, so it is possible to decide on the prevention of competition on the employment regulations. However, employment contracts and employment rules unfairly advantageous to the user are not allowed.As a past judgment, only when the scope of the business prohibited to engage is reasonably restricted and the geographical scope of the business is reasonably restricted, it is necessary to decide to avoid competition Is allowed.There are cases in which employment regulations describe obligations to avoid competition due to job change to other companies in the same industry to prevent internal know-how from going outside the company or to prevent job change.
■Trial periodIn Thailand it is legally permitted to set a trial period. However, if you set a trial period of 120 days or more and you have dismissed after 120 days, you must pay dismissal allowance even during the trial period. Therefore, in Thailand there are many cases to set the trial period within 119 days.Also, even if you make a contract saying that you can dismiss without notice during the trial period, ending the trial period is deemed to be the same as dismissal, so if you do not officially adopt it after only the trial period You will need notification of one month before the expiration of the trial period. In Thailand as well as Japan, there must be a reasonable reason for dismissal of workers, but dismissing on the grounds of lack of abilities by looking at how to work and ability to work during the trial period It is accepted by the case.Many companies set a trial period and use it for recruitment because it is difficult to judge the abilities of employees just by employment interview.
■ BonusesIn Thailand as well as Japan there is no labor law rule on bonuses. However, unlike Japan, because it is a country where job change is actively carried out, there is a problem that workers will retire quickly unless they pay welfare benefits such as bonuses. In fact, it is common for many Japanese companies to pay bonuses equal to the salary of one to four months.■ Regulations related to labor management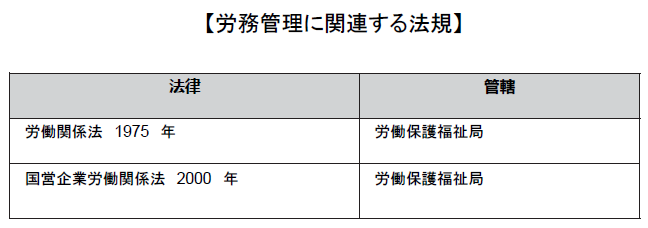 [Labor Relations Act]The Labor Relations Act stipulates labor standards that both employers and workers should observe. This law aims at a resolving and prompt resolution of labor disputes. Employers who have more than 20 employees in the Labor Relations Act of 1975 are supposed to have to prepare written agreements on labor conditions, but companies that have created work rules must register their labor regulations It can be substituted for the condition agreement.In the document of the Labor Condition Agreement, the following contents must be stated.·Working conditions· Working days, working hours·wage·Welfare· Dismissal· Worker complaints motion· Revision or renewal of labor condition agreementThe Labor Condition Agreement needs to be decided within three years from the date of agreement by labor and management. If there is no stipulation of validity period, one year from the date of agreement by labor and management or the employer starting to hire workers will be valid term.
[Labor Relations Act]The Labor Relations Act stipulates labor standards that both employers and workers should observe. This law aims at a resolving and prompt resolution of labor disputes. Employers who have more than 20 employees in the Labor Relations Act of 1975 are supposed to have to prepare written agreements on labor conditions, but companies that have created work rules must register their labor regulations It can be substituted for the condition agreement.In the document of the Labor Condition Agreement, the following contents must be stated.·Working conditions· Working days, working hours·wage·Welfare· Dismissal· Worker complaints motion· Revision or renewal of labor condition agreementThe Labor Condition Agreement needs to be decided within three years from the date of agreement by labor and management. If there is no stipulation of validity period, one year from the date of agreement by labor and management or the employer starting to hire workers will be valid term.
■ Regulations related to labor skill development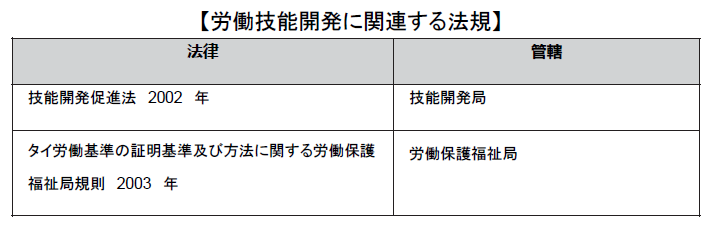 ■ Regulations related to employment work
■ Regulations related to employment work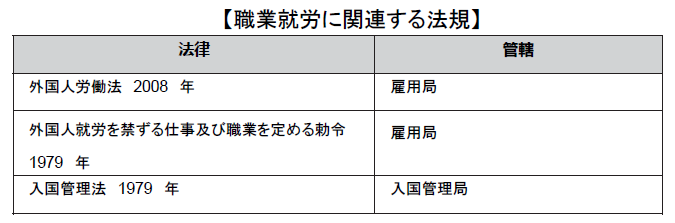 In Thailand, it is forbidden to hire workers under the age of 15 under the Workers Protection Law, and for young workers aged 15 to 18, prohibition of certain dangerous work, after 4 hours of continuous work There are restrictions such as a break for over 1 hour, work prohibition from 22 o'clock to 6 o'clock, ban on overtime work and holiday work.Regarding female workers, prohibition of sexual harassment, prohibition of dangerous work, worker recruitment advertisement (22 o'clock to 6 o'clock) in the midnight factory complex, restrictions on employment, prohibition of dismissal for pregnancy and other women protection provisions there is. Also, in the Official Gazette of January 17, 2011, the Occupational Safety and Sanitation Act of 2011 was promulgated, and in 1998, the Act on Amendment to the Workers Protection Act was promulgated on the same date.The occupational safety and health environmental law of this time was established in order to specify in detail the thing which had been included as a regulation concerning occupational safety in the worker protection law until now.The main provisions of the Occupational Safety and Health Environment Act are as follows.
In Thailand, it is forbidden to hire workers under the age of 15 under the Workers Protection Law, and for young workers aged 15 to 18, prohibition of certain dangerous work, after 4 hours of continuous work There are restrictions such as a break for over 1 hour, work prohibition from 22 o'clock to 6 o'clock, ban on overtime work and holiday work.Regarding female workers, prohibition of sexual harassment, prohibition of dangerous work, worker recruitment advertisement (22 o'clock to 6 o'clock) in the midnight factory complex, restrictions on employment, prohibition of dismissal for pregnancy and other women protection provisions there is. Also, in the Official Gazette of January 17, 2011, the Occupational Safety and Sanitation Act of 2011 was promulgated, and in 1998, the Act on Amendment to the Workers Protection Act was promulgated on the same date.The occupational safety and health environmental law of this time was established in order to specify in detail the thing which had been included as a regulation concerning occupational safety in the worker protection law until now.The main provisions of the Occupational Safety and Health Environment Act are as follows.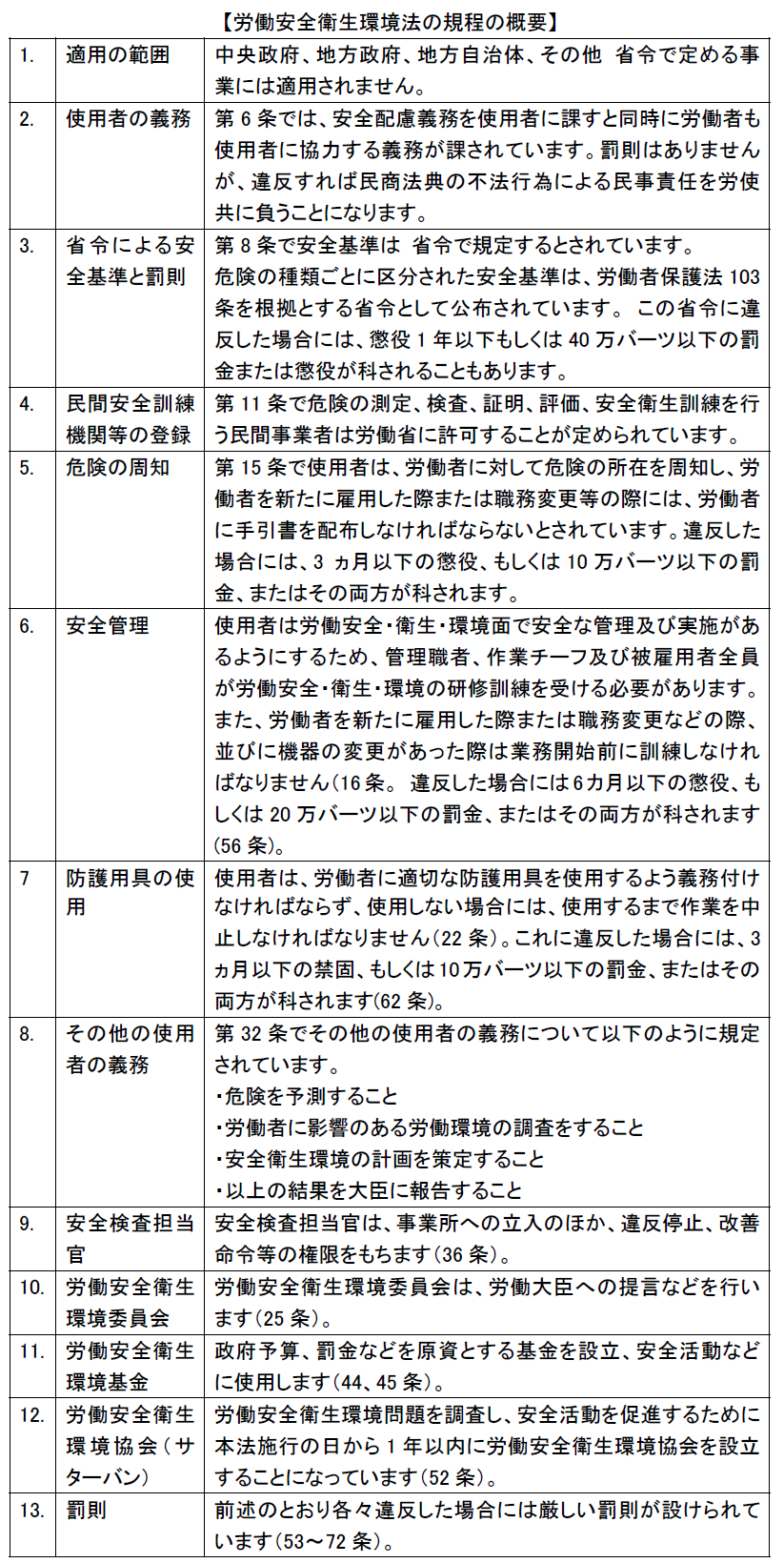
-
Legal system on wages
Under the Workers Protection Law, wages are defined as "consideration of labor based on employment contracts for normal working hours" and the following requirements are stipulated.· It must be at least the minimum wage· Payment must be made in cash※ However, if you have prior permission of workers, bank transfer is also possible· The same duties regardless of gender, same wage· The employer is obliged to pay wages at least once a month or at a time based on labor-management agreement· There is an obligation to pay 75% or more of wages (50% or more before the 2008 revision) at the time of non-work based on the force majeure of workers· Prohibition of deduction from regular wages, overtime work, holiday work allowance and holiday overtime labor allowance
However, individual income tax, labor union fee, savings cooperative association fee, reserve fund, damages to employers (requiring prior worker's consent) etc can be deducted from wages.If you do not pay wage in violation of these, you must pay 15% annual interest.
■ Minimum wageIn Thailand, according to the Ministry of Home Affairs Ordinance based on the 1972 Labor Law, from 1973 onwards, the minimum wage (daily amount) is stipulated for each region. Furthermore, with the amendment of the 2008 Workers Protection Act, the minimum wage for each function is decided by the Minimum Wage Committee. In recent years, the minimum wage has been rising in Thailand and the Commission's public notice on April 29, 2011 announced wage standards according to three levels of skill level with respect to eleven kinds of functions. As a result, level-specific wages between 275 and 510 Baht were enforced on August 1, 2011. In 2014, it was revised to 13 kinds of profession. There is concern about further wage increases in the future.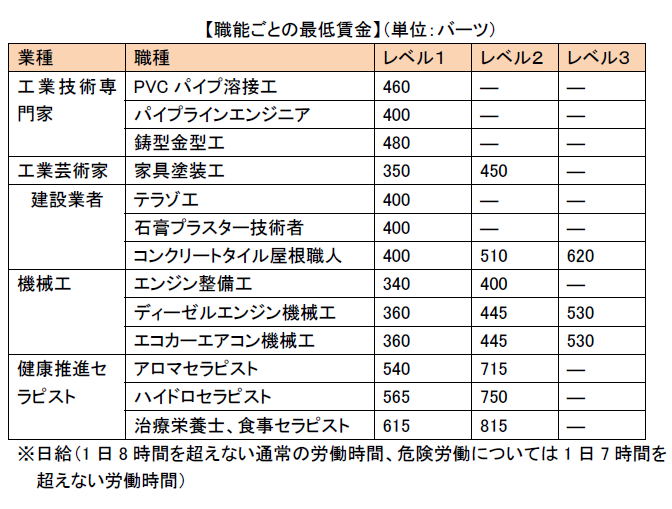 Employers are sentenced to imprisonment (within 6 months) or fined (up to 100,000 baht) if payment is not made based on the wage level by function specified above.Although the minimum wage by region was segmented as it was revised every year, it was decided to raise to 300 baht daily by the nationwide uniform by the policy of the Yingluck administration "turning into domestic demand led economy".However, since there are many merits other than wage cost (there are many families, there are many Japanese learning ratio in ASEAN, low corporate tax rate, market with population of 60 million, etc.), so it may be necessary to look only wage cost and not many elements.
Employers are sentenced to imprisonment (within 6 months) or fined (up to 100,000 baht) if payment is not made based on the wage level by function specified above.Although the minimum wage by region was segmented as it was revised every year, it was decided to raise to 300 baht daily by the nationwide uniform by the policy of the Yingluck administration "turning into domestic demand led economy".However, since there are many merits other than wage cost (there are many families, there are many Japanese learning ratio in ASEAN, low corporate tax rate, market with population of 60 million, etc.), so it may be necessary to look only wage cost and not many elements. -
Employment contracts and employment rules
Employers must make written or oral employment contracts when hiring workers. Regarding the conclusion of employment contracts, it is stipulated in Chapter 3 of the Ministry of Commerce and Business Code and Section 6 of the Workers Protection Act. Employment contracts include those that determine the period and those that do not specify the period. It is usual to prepare an employment contract documenting labor conditions etc ..In addition, users who regularly hire more than 10 people need to prepare Thai language rules of employment, employee ledger and wage register, and be inspected by the Labor Department. Also, in January every year, we have an obligation to report on the items described below to the Director of the Workers Protection and Welfare Department.
· Number of employed workers·working time·wage· Whether there is wage by function· Whether there is a plan to increase or decrease workers during the reporting year and the reason
The employment rules must submit copies of the employment regulations to the Labor Welfare and Public Welfare Bureau within 7 days after making or changing. Items that must be stated in the employment rules are as follows.
· Working day, normal working hours and break time· How to get a holiday, holiday· Regulations on overtime and holiday work· Basic salary, overtime work allowance, holiday allowance, payment method for holiday overtime duty allowance· Discipline and penalties· Applicants of complaints, methods· Elimination of employment contract, retirement allowance, special severance payment
As for "Requests for complaints, methods" which are items that need to be stated on the employment regulations, it is necessary to describe at least the following.
· Scope and contents of complaints· How to file a complaint· Complaint resolution procedure· Investigation based on complaints· Protection of complainants
Employment rules need to be announced to workers within 15 days from the day when the number of workers reaches 10 or more. In addition, after copies are kept at business establishments, workers must post it on business sites for ease of recognition. In addition, it is necessary to notify the Working Protection Welfare Bureau of the employment rules, but if the employment rules conflict with the law, you will be ordered by the Director of Labor Protection and Welfare Bureau to rectify.In addition, if you fail to compile, post, or notify employment rules, or neglect to create an employee ledger or wage ledger, a fine of not more than 20,000 Baht will be imposed.In addition to your name, gender, nationality, employment record, employment start date, job title or job, wage, etc. are described in the employee register, and labor day, working hours, wages, overtime allowance, holiday work allowance etc A statement of the amount of money and a signature of the worker are necessary. Employee ledger is obliged to save and keep for two years from employee's retirement date and wage register from payment date respectively. In addition, employers hiring workers will perform "user registration" and "insured person registration" within 30 days according to the provisions of the social insurance law and labor accident compensation law described later. The workers must pay the reserve funds and the employers pay the contributions to the funds respectively. -
Treatment of holidays
[Requirements for temporary closure]Under Article 75 of the Thailand Labor Protection Act, companies are permitted temporarily to close down when the company falls under the following requirements.
· A serious reason that hinders business activities to the extent that ordinary business operations become difficult· It is not based on force majeure· Being a pause for some or all of the project· Be temporary closed.· Advance notice to workers and labor inspector three working days before
[Payment of leave allowance]If any of the above requirements is met, the company is allowed to temporarily close the company. However, in case of suspension of work, employees are required to pay 75% of the salary at the time of the start of leave during the period of leave.The term of benefit for leave allowance will be between the start of leave and the beginning of work and the "salary at the start of leave", which is the basis of calculation of leave allowance, is not 75% of the base salary, but rather the monthly fixed amount of salary allowance and food expenses It becomes a thing including an allowance etc.
■ Reducing working hoursAs with temporary closure, we may consider shortening the working hours of workers to reduce personnel expenses. In Thailand, shortening working hours is not a disadvantage change of working conditions and can be shortened without obtaining consent from workers. However, with regard to reduction of wages of employees due to shortening of working hours, it falls under the unfavorable change of working conditions, so we can not reduce the amount unless workers' consent is obtained.For example, suppose that the work time of a company is reduced, and the worker's working hours are reduced from 8 hours a day to 6 hours a day. However, it is illegal to change the wage paid to workers from 8 hours to 6 hours unless workers' consent is obtained.Even if the company is in an economic crisis situation the above handling will be applied. Therefore, if the company is in a situation of economic crisis, it is necessary to communicate the situation to the workers, inform them of the necessity of reduction of wages due to shortening of working hours, and obtain consent.If a worker refuses to reduce wages, it will be possible for the company to dismiss that worker because the company did not agree to reduce wages in the event of a company emergency such as the economic crisis (legitimate It is recognized as grounds for dismissal. In this case, there is no problem if you pay dismissal allowance and dismiss.In the above cases, there is a possibility that the dismissed workers may appeal for reasons that they were unjustly dismissed by the labor court. Therefore, when the company falls into a situation such as the economic crisis, and the company wishes to reduce the wage of the workers, the company side needs to shorten the working situation, It is necessary to explain and prepare to avoid disadvantageous situation in the trial.
【Requirements for temporary closure】· A serious reason that hinders business activities to the extent that ordinary business operations become difficult· It is not based on force majeure· Being a pause for some or all of the project· Be temporary closed.· Beforehand notifying workers and labor inspectors 3 business days in advance
【Salary payment amount during temporary holiday period】Article 75 of the Workers Protection Act stipulates that the employer shall pay employees 75% of the salary at the time of leave beginning as a leave allowance as salary payment during the temporary holiday period.
【Handling in the case of leave of absence based on force majeure】If it is a holiday "not based on force majeure" in ② above, it is necessary to pay leave allowance during the holiday period, but if you are closed based on force majeure, you do not need to pay leave allowance.Whether or not natural disasters such as floods fall under "force majeure" is a problem. In Thailand, however, flooding happens every year, and it is highly likely that "foreseeing floods" can be considered as possible If you take a leave due to a flood, it is considered likely that a holiday allowance will be required. -
Employee dismissal
■ Normal dismissal (dismissal with dismissal allowance)Normally dismissed means to unilaterally dismiss employees due to company circumstances.In case of dismissing due to the circumstances of the company, according to Article 118 of the Workers Protection Act, we have to pay dismissal allowance according to the number of years of service to overtime workers over 120 days.However, as in Japan, prior notice is necessary, in the case of Thailand 1 prior notice before the wage period by notice in advance or in lieu of prior notice, the amount to be paid from the prior notice mentioned above until the day of dismissal by paying wages, you can be dismissed immediately (Article 17 of the Workers Protection Act).1 Prior payment period is understood to be prior notice to dismiss on the next salary payment date 30 days or earlier, for example if 30 days a month are salary payment days. In other words, there must be a payment date twice between the prior notice date and the dismissal date. Also, for unused paid holidays it is necessary to pay attention because they are obliged to buy (Article 67 of the Workers Protection Act).The severance allowance according to the number of years of service is as follows (Article 118 of the Workers Protection Act).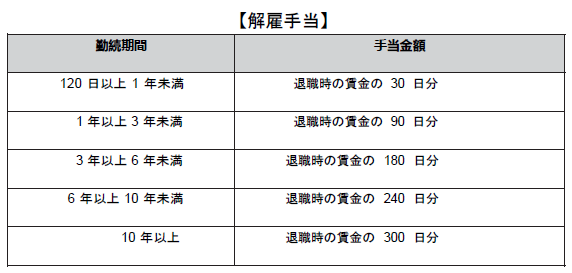 ■ Disarmament dismissal (dismissal without dismissal allowance)When dismissing a disciplinary dismissal with the following legitimate reasons, the company need not pay dismissal allowance (Article 119 of the Workers Protection Act).· When you are dishonest with your work, or you deliberately sinned against you· When deliberately damaging the user· In case of serious injury to the user due to carelessness· If you violate your employment rules, legitimate rules or orders of the user, or if the user has already issued a warning letter (unless it is a serious case that the user does not need to issue a warning letter) It is effective within one year from the day the worker committed the violation)· In case of abandonment of work in consecutive 3 working days without any valid reason regardless of whether there is a holiday between· In cases where you are ordered to imprison a final judgment, except for judgment on carelessness or minor offensesIn caseEven in this case, it is important to always include reasonable grounds in the dismissal notice.It will not be accepted even if we assert the reason for retrofitting at a later trial. In addition, concerning trivial violations etc., if you dismiss it suddenly without warning, there is a high possibility that the dismissal is not reasonable because it is not reasonable. Regarding trivial violations, it is necessary to perform disciplinary actions that are lighter than dismissal (verbal warning, issue of warning letters, suspension of work, reduction of salary).Also, as in seasonal labor, the period of employment is clearly stipulated, and when you terminate employment according to the provision, it does not fall under disciplinary dismissal, but it is not necessary to pay dismissal allowance .■ Other dismissal
■ Disarmament dismissal (dismissal without dismissal allowance)When dismissing a disciplinary dismissal with the following legitimate reasons, the company need not pay dismissal allowance (Article 119 of the Workers Protection Act).· When you are dishonest with your work, or you deliberately sinned against you· When deliberately damaging the user· In case of serious injury to the user due to carelessness· If you violate your employment rules, legitimate rules or orders of the user, or if the user has already issued a warning letter (unless it is a serious case that the user does not need to issue a warning letter) It is effective within one year from the day the worker committed the violation)· In case of abandonment of work in consecutive 3 working days without any valid reason regardless of whether there is a holiday between· In cases where you are ordered to imprison a final judgment, except for judgment on carelessness or minor offensesIn caseEven in this case, it is important to always include reasonable grounds in the dismissal notice.It will not be accepted even if we assert the reason for retrofitting at a later trial. In addition, concerning trivial violations etc., if you dismiss it suddenly without warning, there is a high possibility that the dismissal is not reasonable because it is not reasonable. Regarding trivial violations, it is necessary to perform disciplinary actions that are lighter than dismissal (verbal warning, issue of warning letters, suspension of work, reduction of salary).Also, as in seasonal labor, the period of employment is clearly stipulated, and when you terminate employment according to the provision, it does not fall under disciplinary dismissal, but it is not necessary to pay dismissal allowance .■ Other dismissalIf the employer wishes to terminate employment of workers because it is necessary for the user to reorganize the organization, manufacturing, distribution, service process and reduce the number of workers as a result of mechanization, machine change, technology improvement, the employer must inform labor inspectors and workers who terminate employment 60 days or more prior to the employment end date of the employment end date, the reason for termination of employment, the name of the worker.
If the user does not give prior notice to workers who terminate employment or does not notify before the legal deadline, the employer may, apart from the dismissal allowance under Article 118 of the Workers Protection Act, For workers who receive payment of unit wages based on the last wage for 60 days or based on labor results, special dismissal payment equivalent to the wage of the last 60 working days must be paid instead of notification (Article 121 of the same law).
In the event that the employer terminates employment of workers pursuant to Article 121 of the same Act and the worker has served for more than six years, the employer shall pay the final disposal allowance per year for workers who received payment of unit wage based on labor outcomes for more than 15 days of wages or pay more than the wages of the last 15 working days.
However, the total amount of dismissal allowance based on the same article shall not exceed the wage of the last 360 working days for workers who received payment of unit salary above 360 days of last wage or based on labor results Hmm.
With respect to the calculation of special dismissal allowance described below, if the fraction is less than one year, if the fraction exceeds 180 days, it is counted as one year's work (Article 122 of the same law).■ Termination of employment contract due to relocation of officeIn the case where the user relocates the establishment and it has a serious effect on the normal way of living of workers and their families, the employer shall notify the workers more than 30 days ago from the date of relocation of the establishment I must inform you to that effect.In this regard, if a worker does not wish to work at a new employment place, the worker has the right to notify the termination of the employment contract and the worker is under Article 118 of the Workers Protection Act You are entitled to receive a special dismissal allowance of 50% or more of the qualified dismissal allowance to receive.If the user does not inform the workers in advance of relocation of the establishment, the employer shall pay an amount equivalent to the last wage of 30 days, or for workers who receive payment of unit salary according to labor results You must pay special dismissal allowance equivalent to the wage of 30 working days of the day in lieu of notice.The worker shall inform the Labor Welfare Committee within 30 days from the date the employer relocates the establishment whether this is a case where the user has to make advance notice, whether the worker terminates the employment contract You can file a petition as to whether you have the right to notify you and whether you are entitled to receive a special dismissal allowance.The decision will be final unless the employer or worker sues the court within 30 days after receiving the decision notice of the labor welfare committee. In the event that the user sues, the user must deposit in the court the amount equivalent to the amount payable to the worker who filed the petition by filing the suit.When notifying the termination of the employment contract under the same Article, the worker shall grant the right within 30 days after the employer relocates the establishment, or after the decision of the Labor Welfare Committee or the court's ruling has been finalized (Article 120 of the same law).[Handling of employee dismissal]Severance allowanceIn case of more than 120 days of service, you will pay dismissal allowance according to the length of service (Article 118 of the Workers Protection Law). Generally, it seems that this dismissal allowance is often 30 days for one year of service.Unfair dismissalUnfairly dismissed means to unilaterally dismiss employees due to company circumstances even though employees are not involved. In this case, you must pay damages in addition to the dismissal allowance. In Japan, when it is judged to be unfair dismissal, there are cases that it returns to the original workplace, but in Thailand the monetary solution by compensation is common in consideration of the human relationship after returning. If dismissal is not approved it will be as followed.· When I am pregnant· In case of labor union· When workers or labor unions are engaged in union activities· Firing of workers committee members without permission of labor court· During treatment with occupational accidents or when labor capacity becomes impossibleIn Thailand, it is easier for judges to take advantage of judgment on labor side, so it is important to prepare a situation that can be proved assuming case of trial.
-
-
-
Social insurance law
■ Scope of applicationIn Thailand, the social insurance law was established in 1990, and now, guarantee system concerning seven types of benefits such as injury, disability, childbirth, death, child support, old age, unemployment other than worker's work is maintained. Initially, it was obliged to join a workplace that employed more than 20 people, but from April 2002 all the offices that employ employees have to join.
Also, benefits were only for health insurance (injury, disability, childbirth, death, 4 types), but from April 1999, child support, old-age pension, unemployment insurance from January 2004 have been added.
The insured is an employee of a private company and is regarded as an employee aged 15 to 60 years old and is also targeted for foreigners. However, domestic workers are not included. For work injuries and illnesses, there is a workers 'accident compensation fund system based on the Workers' Compensation Law described later. Social insurance law and labor accident compensation law the competent authority is the social insurance secretariat of the Ministry of Labor.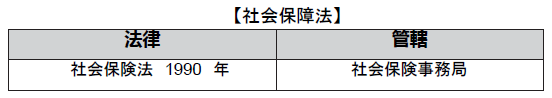 ■ Insurance premiumThe company is stipulated to deduct the social insurance contribution from the monthly salary of employees who join social insurance. The current insurance premium rate is 5%, but the target monthly wage limit is 15,000 Baht. Therefore, it is maximum 750 Baht per month.Because Japan and Thailand have not concluded a social security agreement, Japanese expatriates will join social insurance in both Japan and Thailand, but for Japanese companies and Japanese expatriates because of the upper limit It is not that much additional cost. The company will pay the same amount of insurance premiums and will pay to the Social Insurance Secretariat by the 15th day of the following month. In addition, for insurance benefits, the government is responsible for 2.75%.
■ Insurance premiumThe company is stipulated to deduct the social insurance contribution from the monthly salary of employees who join social insurance. The current insurance premium rate is 5%, but the target monthly wage limit is 15,000 Baht. Therefore, it is maximum 750 Baht per month.Because Japan and Thailand have not concluded a social security agreement, Japanese expatriates will join social insurance in both Japan and Thailand, but for Japanese companies and Japanese expatriates because of the upper limit It is not that much additional cost. The company will pay the same amount of insurance premiums and will pay to the Social Insurance Secretariat by the 15th day of the following month. In addition, for insurance benefits, the government is responsible for 2.75%.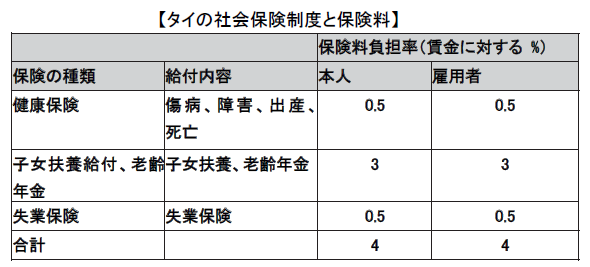 ■ Qualifications and benefits of social insurance benefitsThe requirements for receiving seven social insurance benefits and the contents of benefits are shown in the table below.
■ Qualifications and benefits of social insurance benefitsThe requirements for receiving seven social insurance benefits and the contents of benefits are shown in the table below.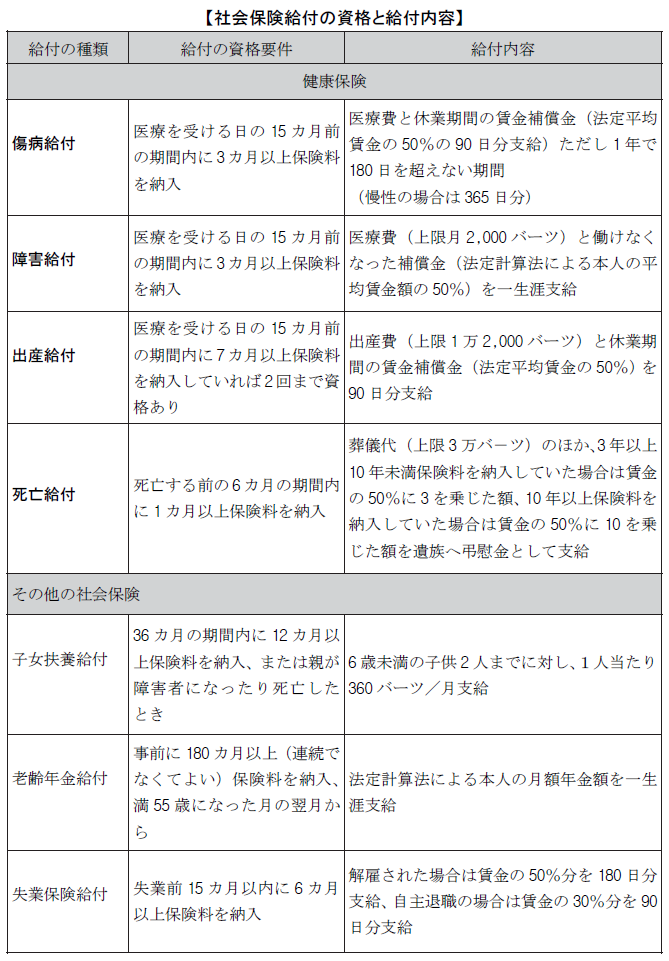
-
Workmen`s Accident Compensation Insurance Law
■ Overview
In 1973, the Workers 'Disaster Compensation Fund was established with the purpose of providing insurance benefits for workers' work disorders, diseases, and deaths, protecting and compensating for workers. Currently, the Ministry of Labor Social Security Administration manages this fund based on the Workers' Compensation Act revised in 1994.
 ■ Insurance premiums and insurance benefits
■ Insurance premiums and insurance benefitsThe company has to pay insurance premiums stipulated by the law for injuries during work, illness, insurance benefits necessary for the deceased employees. As with Japan, the premium is fully borne by the user, and the rate is set within the range of 5% of the maximum annual wage for each type of industry according to the incidence of occupational injury accidents.
Contents of insurance benefits are compensation money, medical expenses, rehabilitation expenses, and funeral expenses. Compensation will be paid at the rate prescribed by the law according to the degree of disability, disease, etc., but generally it will be paid monthly within 60% of the monthly salary, not less than 2,000 Baht and not more than 9,000 Baht. Self-care expenses are actual expenses, usually 35,000 Baht, and in the case of heavy weigh up to 50 thousand Baht. Rehabilitation expenses will be paid at the statutory rate (up to 20,000 Baht) as necessary.
In case of death, funeral expenses will be paid in the range up to 100 times the daily salary. However, the specific amount of insurance benefit is calculated from the statistical data of accident rate of accidents and accidents for each type of industry, and the burden / fund balance of the fund at that time.
In Thailand, the level of unemployment insurance is low, so in addition to the social insurance and industrial accidents mentioned above in order to compensate for it, some companies have set up a retirement funded fund system by voluntary participation of the Retirement Fund Law, but among Japanese companies, There are also cases where a corporate original system is established as welfare benefits for workers.
-
-
-
Visa and work permit
■ Obligation to Obtain Visa and Work PermitFor foreigners to work in Thailand, you need to obtain a visa and work permit. In order to obtain a visa, the Immigration Bureau and the Ministry of Labor will be judged according to the respective standards in order to obtain work permit.Visa: Permits required for foreigners to stay in ThailandWork Permit: Permit required for foreigners to work in Thailand■ Visa ProcedureFor Japanese, visa is required for visitors unless they are planning to stay in Thailand for more than 30 days for sightseeing purposes. In entering Thailand for work purposes, it is necessary to first obtain a nonimmigrant visa (Non Immigrant / Business Visa) at a Japanese embassy or consulate in Thailand, and the number of days the nonimmigrant visa can stay is 90 days Has become.Documents necessary for applying for a nonimmigrant visa in Japan are as follows.(A) One visa application form (available on the Embassy website)(B) Photo (3.5 x 4.5 cm) 2 sheets color (pasted on application form)(C) Passport (more than 6 months remaining valid term, one with visa margin more than one page)(D) Airline ticket or confirmation of reservation(E) Original 1 copy of English curriculum vitae (available on the Embassy website)(F) English letter invitation from the company in Thailand (original) Part 1 (In particular, the applicant's purpose of staying, title, period of office, salary etc in Thailand is used and the company's letterhead paper is used, Attaching the registry, applicant name, company name, planned entry date, planned stay period, representative's autograph signature etc. are necessary)(G) Thai Party Register Copy (Capital, Company Representative Register Listed, Thai Language Allowed)(H) English letter recommendation letter (original) from a Japanese company 1 part, (If English company letter of recommendation can not be prepared, one copy of English letter guarantee letter and guarantor passport copy)(I) Copy of Thai Work Permit (Only those who previously worked in Thailand)(J) Application fee Single 9,000 yen (multiple entries of 22,000 yen, basically single entry in case of employment purpose)■ Procedure for acquiring work permitForeign nationals who have received permission to stay in Thailand with a nonimigrant business visa are required to comply with the Investment Encouragement Act or other laws and regulations in accordance with the period permitted by relevant authorities, you can obtain a work permit of. The maximum period will be two years.
For foreign nationals who are temporarily stayed, especially those who have received permission without the deadline, 30 days from the date of issuance of work permits will be the permitted period.Documents necessary for applying for a work permit are as follows.(A) Passport(B) 3 pictures(C) Employment / Certificate of employment certificate(D) Graduation certificate (English)(E) Health certificate (by Thai physician)(F) Company Registered Certificate(G) Taxpayer registry certificate(H) Factory installation permit (for manufacturing industry)(I) Explanation of company's business (corporate profile etc.)(J) Map of company location, organization chart, number of employees, etc.(K) latest accounting audit document (unnecessary in case of new company)(L) Applicant's planned salary(M) Applicant's address in Japan and Thailand(N) List of employees who already have work permits at company(O) Corporate tax, VAT, personal income tax declaration and receipt (unnecessary in the case of new company)(P) Description of the applicant's position and dutiesIn addition to the above, there are cases where you are required to submit additional documents separately.If the employment period is as short as 15 days or less, you can obtain the work permit on the same day by submitting the application form and necessary information filled in to the Labor Bureau or the One - Start One - stop Investment Center. In the case of a BOI company (a company approved by the Thai Investment Promotion Act), a work permit of 30 days is approved. In this case, application documents are different from normal, so you need attention.Work permits must apply for renewal of work permits before the permission period expires. If you apply within the deadline, you can continue to work until the results of the application are notified by the Registrar.Work permits must always be carried or managed in the work place. In case of retirement, it is necessary to return the work permit within seven days from the day of retirement. In addition, if conditions such as employment form, employment, work place, etc. change, you must apply immediately to the Registrar.① Submission of short-term employment report to Ministry of Labor etc.② Japanese headquarters etc. pay the salary during stay③ Declaration of personal income tax in Thailand · Tax payment is unnecessaryIt will be that.① Application / Acquisition of Work Permit② Declaration / tax payment for personal income tax is required in Thailand.The problem here is when. ① Application and acquisition of Work Permit are required② When the Japanese headquarters pays salary during stay in Thailand → declaration · tax payment in Thailand in Thailand is "unnecessary"③ When the Thai corporation bears the salary during stay in Thailand → The personal income tax declaration · tax payment in Thailand is "necessary".In case of Japanese citizens, you must apply salary of 50,000 baht in Thailand when applying for work permit.■ Banned employment of foreignersRegarding the acquisition of work permit, the following 39 industries are prohibited from working by foreigners regardless of the area by the Foreign Employment Regulation Law.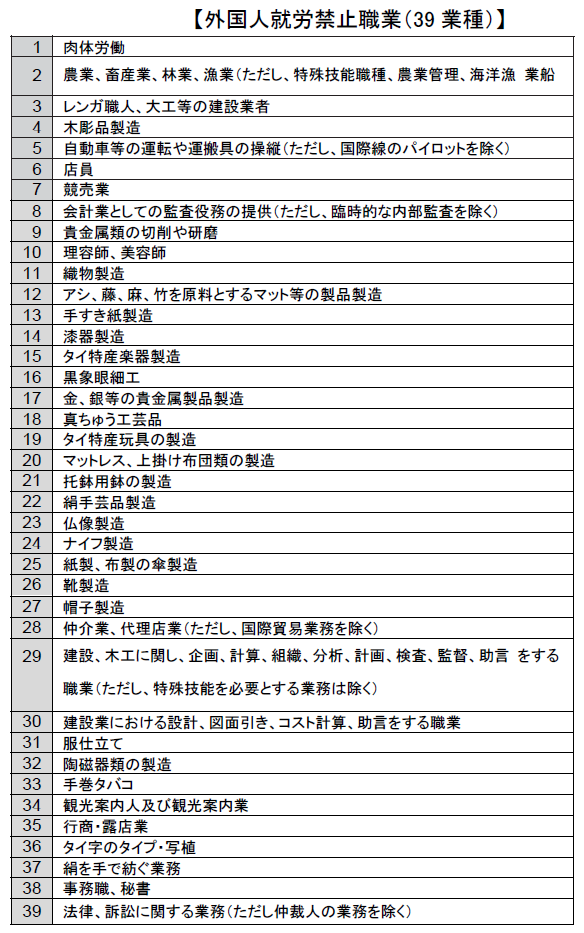 ■ Conditions for acquiring work permitIn order for a foreign corporation like a Japanese company to acquire the work permit of a foreign worker (including a Japanese worker), a company that is an employer for each worker must pay at least 2 million baht payable capital It is necessary to register money and it is possible to hire up to 10 foreign workers. However, in order to hire foreign workers beyond 10 people, in addition to paying capital of 2 million baht per person, it is necessary to satisfy one of the following requirements.· The income tax paid by the employer in the previous year is at least 3 million baht· The employer has been engaged in export business and has brought foreign currency equivalent to at least 30 million baht to Thailand in the previous fiscal year· The employer has engaged in the tourism industry and brought at least 5,000 foreign tourists to Thailand in the previous fiscal year· Employers hire at least 100 Thai peopleIn addition, even if it does not satisfy any of the above requirements, there will be no restriction on the number of people who can obtain work permit if it meets any of the following requirements.· To be a foreigner who can not use Thai people or Thai people who can use it are able to use technology that is very limited, but transfer technology to at least two Thai people by the deadline· Be a foreigner with expertise to achieve time-limited projects· Be a foreigner engaged in entertainment business with temporary contract■ Requirements for work permit and visa renewalWhen updating work permits, it is necessary to update visa at the same time. The following items are the basis for renewing your visa, so confirmation in advance is required.(A) Monthly salary is not less than 50 thousand baht(B) The paid-up capital of the company is 2 million baht or more per foreigner(C) It is clear that the business is able to continue soundly by the financial statements of the previous fiscal year(D) Four foreign employees have four full-time Thai employees* However, the above (b) (c) is not applicable to branches or resident offices, and for (d) the ratio of one Thai person per foreignerSpecifically, the judgment is based on the following criteria regarding "(c) It is obvious that the business can be maintained soundly by the financial statements of the previous fiscal year".· The auditor has not expressed a limited opinion on the continuation of the project to the financial statements· It is clearly indicated that there is movement in the business by the balance sheet and income statement· Make monthly declaration of VAT or specified business tax· Withholding personal income tax every month· Make social insurance premium declaration every month
■ Conditions for acquiring work permitIn order for a foreign corporation like a Japanese company to acquire the work permit of a foreign worker (including a Japanese worker), a company that is an employer for each worker must pay at least 2 million baht payable capital It is necessary to register money and it is possible to hire up to 10 foreign workers. However, in order to hire foreign workers beyond 10 people, in addition to paying capital of 2 million baht per person, it is necessary to satisfy one of the following requirements.· The income tax paid by the employer in the previous year is at least 3 million baht· The employer has been engaged in export business and has brought foreign currency equivalent to at least 30 million baht to Thailand in the previous fiscal year· The employer has engaged in the tourism industry and brought at least 5,000 foreign tourists to Thailand in the previous fiscal year· Employers hire at least 100 Thai peopleIn addition, even if it does not satisfy any of the above requirements, there will be no restriction on the number of people who can obtain work permit if it meets any of the following requirements.· To be a foreigner who can not use Thai people or Thai people who can use it are able to use technology that is very limited, but transfer technology to at least two Thai people by the deadline· Be a foreigner with expertise to achieve time-limited projects· Be a foreigner engaged in entertainment business with temporary contract■ Requirements for work permit and visa renewalWhen updating work permits, it is necessary to update visa at the same time. The following items are the basis for renewing your visa, so confirmation in advance is required.(A) Monthly salary is not less than 50 thousand baht(B) The paid-up capital of the company is 2 million baht or more per foreigner(C) It is clear that the business is able to continue soundly by the financial statements of the previous fiscal year(D) Four foreign employees have four full-time Thai employees* However, the above (b) (c) is not applicable to branches or resident offices, and for (d) the ratio of one Thai person per foreignerSpecifically, the judgment is based on the following criteria regarding "(c) It is obvious that the business can be maintained soundly by the financial statements of the previous fiscal year".· The auditor has not expressed a limited opinion on the continuation of the project to the financial statements· It is clearly indicated that there is movement in the business by the balance sheet and income statement· Make monthly declaration of VAT or specified business tax· Withholding personal income tax every month· Make social insurance premium declaration every month -
Social insurance of expatriates
■ Social insurance[Continuity / Loss of Social Insurance Insured Personnel Qualification]When you go overseas from Japan, the handling differs depending on whether the employment relationship with companies in Japan continues (enrollment transfer or non-continuation).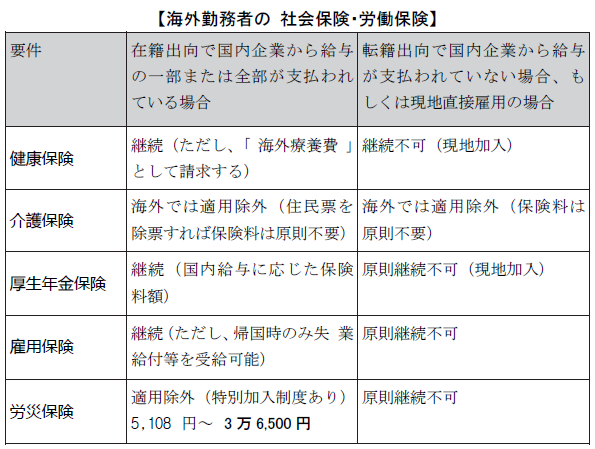
In the case of being registered as a second-time employee, if part or all of the salary is paid by the employee of the second-party, the insured person's qualifications such as health insurance, employee pension insurance, employment insurance etc. continue even while he / she is abroad.
Meanwhile, in the case of a transfer to a transferring company that terminates an employment relationship with a Japanese employer on a secondary basis and has an employment relationship with overseas subsidiaries, employment relationships with secondary companies are not continued, so health insurance, employees' pension insurance, employment the insured qualifications such as insurance will be lost.
[Optional subscription of the National Pension]In the case of a transfer to another company, we can not continue the insured qualification of the employee's pension insurance. If it is planned to arrive within one year, you will be a resident in Japan, so you will join the National Pension.However, if you are planning to move over a year, you will be a non-resident of Japan, so in principle you do not need to join the National Pension. If you wish to join the Japanese pension system, you can make a voluntary proceeding of the National Pension Plan (Article 5, paragraph 3 of the National Pension Act).The national pension's optional entry requirement is as follows.
1. Have Japanese nationality and be between 20 and 65 years old2. Payment of insurance premiums in Japan※ Alternative payment by relatives etc[When using the Japanese health insurance system abroad]Even if you receive medical practices abroad while you are overseas, you can apply for "medical expenses" to the health insurance association etc. to join as long as the insurance qualification of Japan's health insurance continues.However, when applying, you need to pay attention to the following two points.
1. In order to become an application at "medical expenses", the full amount of overseas medical expenses will be fully redeemed once and applied to the Japanese health insurance union etc2. With regard to medical practices received overseas, an amount obtained by deducting the self-payment amount from the amount calculated by converting it into the insurance medical treatment point when receiving insurance medical treatment in Japan is provided
Documents necessary for health insurance overseas medical expenses application are as follows.· Medical treatment expenses application form· Certificate of medical treatment contents· Receipt statement· Receipt (Original)However, if the documents to be submitted are written in languages other than Japanese, it is necessary to attach a Japanese translation after clearly describing the name and address of the translator.
[Continuation of health insurance system in Japan]If the employment relationship with a company in Japan does not continue, the insurance qualification of health insurance will be lost. However, you can join the health insurance system in Japan by using the health insurance optional continuous insured system or by joining the National Health Insurance (Health Insurance Law Article 37).As for the optional continuing insured system of health insurance, it is necessary to do within 20 days after the loss of the qualification and the National Health Insurance must be completed within 14 days after the loss of the qualification, so urgent response is required.
1. Health insurance Optional continued insured's insurance premium(1) Standard fee monthly fee at retirement(2) Average amount of standard remuneration monthly fee determined for each insured person who subscribedAmount by multiplying insurance premium rate to any of the above lower amounts* Unlike in office, the insurance fee paid by the establishment will also be borne by you.
2. National Health Insurance PremiumDepending on the income etc. of the insured, the amount calculated by the provision of the municipality
[Special subscription system for workers compensation insurance]Workers' accident insurance will be excluded from workers who are temporarily transferred to overseas business because workers who work at a business office in Japan are eligible for insurance benefits.Therefore, it is possible to receive insurance benefits for workers' compensation accident insurance by using overseas dispatcher special enrollment system for workers who go to overseas (Article 33 Insurance premium of special subscribers Is the amount obtained by multiplying the insurance premium calculation basic value by the insurance premium rate, which is at least 5,108 yen per year, maximum 36,500 yen (as of March 2015) per year.Special participants are listed below.
1. Workers who are dispatched from projects (excluding fixed term projects) to be conducted in Japan and engaged in overseas projects2. Employers who are dispatched from projects (excluding fixed term projects) conducted in Japan and who engage in small and medium-sized enterprises always using a certain number or fewer workers overseas and those other than workers* The size of SMEsFinancial industry · insurance industry · real estate industry · retail business ... less than 50 peopleWholesale · Service industry ... 100 people or lessOther than the above industries ... 300 people or less
3. Project for implementing technical cooperation for developing countries such as the International Cooperation OrganizationThose who are dispatched from organizations conducting projects (excluding fixed term projects) and who engage in businesses undertaken in the developing country area
■ Overseas travel accident insurance[Treatment at the Time of Appointment of Representative]When transferring overseas, it is desirable to consider subscribing to overseas travel accident insurance besides the state of subscription to public insurance. Overseas travel accident insurance can receive medical treatment without cash when treatment is done at a hospital where insurance company has a contract. Also, unlike public insurance, actual costs of actual medical expenses are paid up to the contracted insurance amount. Since it is not possible to proceed after leaving Japan when new overseas travel accident insurance is added, it is necessary to complete the enrollment procedure before departure.
[Handling at the time of returning from a liaison office]If an expatriate is to return, it will be subject to the year-end adjustment of that year. The target salary is the salary paid since the day you became a resident (the day you returned). In addition, if income other than salary is more than a certain amount, you need to file a final return for that year in addition to the year-end adjustment.
■ Salary design and calculation example of expatriate's salary[Japan - salary inequality problem between Thailand]When paying salary to a Thai expatriate, since there are differences in the method of calculating personal income tax in Japan and Thailand, even for that payment it can not be said that it is the same as Japan, and the salary amount setting and form of payment are preliminarily determined It is necessary to carefully consider.There are differences in applicable tax rates between Japan and Thailand, so if you pay the same salary as in Japan, the salary may be lower or higher.
■ Comparison of tax rates between Japan and Thailand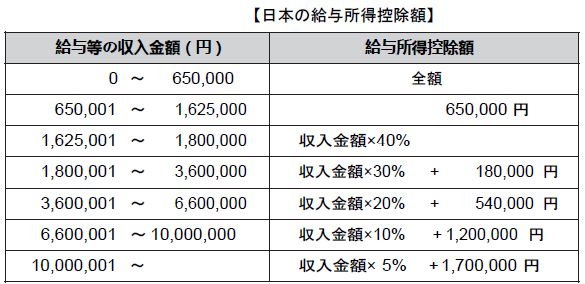
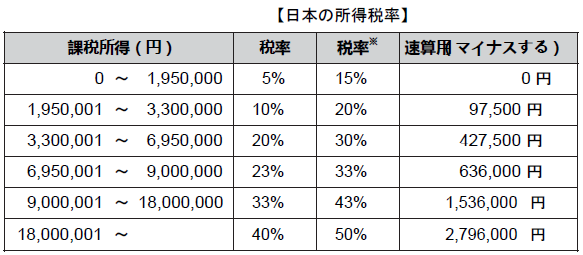
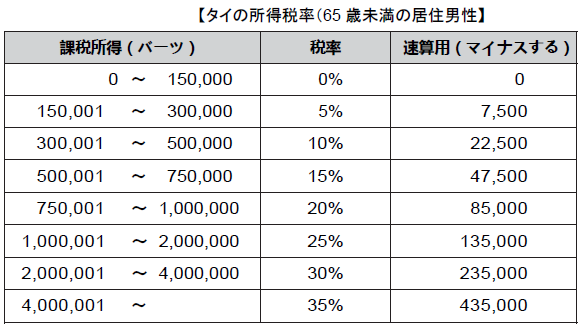 On the Japanese side, there are salary income deduction (650,000 yen) and basic deduction (380,000 yen), so income tax will not be applied if it is within 1,300,000 yen on an income basis. In Thailand, the amount of salary income deduction is very low, but the tax rate is lower than in Japan, so unless the salary amount is low so much, the proceeds will not be lower than in Japan. Therefore, it means that there is no need for gross up calculation for overseas employees in Thailand.Let's compare the taxable amount when Japanese expatriates actually receive salary in Thailand with Japan.
On the Japanese side, there are salary income deduction (650,000 yen) and basic deduction (380,000 yen), so income tax will not be applied if it is within 1,300,000 yen on an income basis. In Thailand, the amount of salary income deduction is very low, but the tax rate is lower than in Japan, so unless the salary amount is low so much, the proceeds will not be lower than in Japan. Therefore, it means that there is no need for gross up calculation for overseas employees in Thailand.Let's compare the taxable amount when Japanese expatriates actually receive salary in Thailand with Japan.
(Preconditions)40-year-old man Annual income in Japan: 648 million yen Dependent: NoneProposed date of assignment: 3 years* Social insurance fee will be subject to social insurance fee deduction, but as mentioned above it is 2,025 yen at maximum, so we will not consider it here.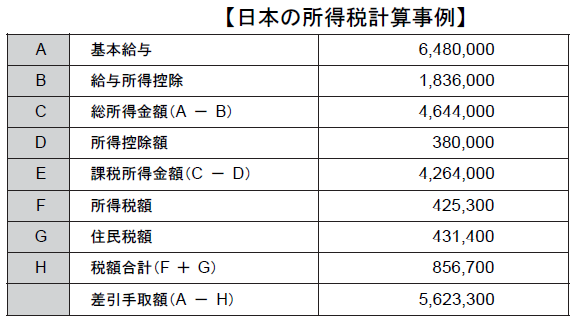
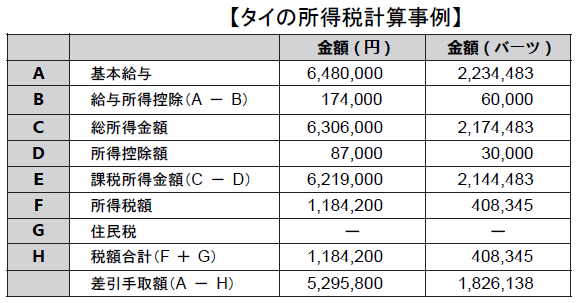
Thus, when a salaried employee with an annual income of 6.48 million yen receives a salary in Thailand, the number of handsets will be reduced by 568,900 yen.
■ Gross Up Calculation Matching Committed AmountsTherefore, you need to do a gross up calculation to match the proceeds. In order to make the take amount equal to the previous 5,623,300 yen, payment of about 7,300,000 yen is necessary, so it is necessary to adjust about 820,000 yen by adding it to the payment amount. The amount to be added depends on the amount of salary, but since it is necessary to add about 800,000 yen or more, it is necessary to consider the payment in advance.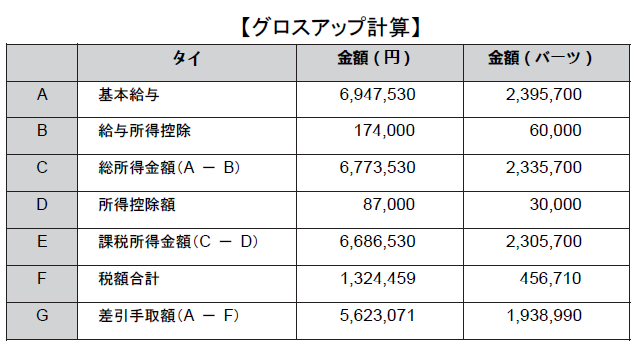
-
-
-
Other
[1] タイ国経済データベース
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya