Thailand
9 Chapter Q&A
-
-
1 Chapter Basic knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.1 Strong Economic in Thailand
2.2 Trade Liberalization in Thailand
2.5 Advantages of Investment in Thailand
3 Chapter Incorporation
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.4 Investigation of entry schemes for each business type
3.5 How to establish a regional headquarters
3.6 Establishment of business base
3.7 Company liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter M&A
4.2 General M&A regarding to Corporate Law
4.3 Summary of applicable Laws for M&A
4.4 Difficulty of business and corporate evaluation
4.5 Foreign Investment Restriction
4.8 Securities and Exchange Act B.E. 2535
5 Chapter Corporate Law
5.1 Types of Thailand Business Structures
5.2 Annual General Shareholders’ Meeting in Thailand
5.3 Director and Board of Director
5.6 Dividend and Legal Reserve
6 Chapter Accounting System
6.1 Overview of accounting system
6.2 Person Responsible for accounting record
6.4 Problem and accounting system
6.5 Disclosure system and disclosure practice
7 Chapter Tax
7.2 Several issues on domestic tax law
7.3 File a Tax Return and Payment
8 Chapter Labor
8.1 Labor environment in Thailand
8.3 Social security system in Thailand
8.4 Points to keep in mind while having Japanese people in Japan
9 Chapter Q&A
-
-
-
Q&A1
Q
I am considering establishing a corporation in Thailand in the future. We are considering establishing at a trading company and factory, and we have grasped conditions and establishment procedures in general. It is a place to report on future investment to the head office. Please tell me if there are points that are likely to be a blind spot when establishing a trading company or factory.
A
Since we are already summarizing conditions and establishment procedures, you know about capital controls.
There are the following points as well that misunderstanding that those who investigate capital regulation to some extent are often misunderstood.
Trading company: Wholesale and retail businesses can capitalize at 100% foreign capital with a capital of 100 million baht or more
Manufacturing industry: Manufacturing industry is not subject to negative list, so you can invest at foreign investment 100%
None of the above is a mistake.
However, on the other hand, it is insufficient as information, and that is in some cases it may be a legal trouble after establishment.
1. In wholesale and retail businesses, you can capitalize at 100% foreign capital by paid capital of 100 million baht or more.
However,
· Retailers with minimum capital of 100 million baht or more and minimum capital per store of 20 million baht or more
· Wholesale business with minimum capital of 100 million baht or more per store
It is an accurate definition, especially when deploying multiple stores, it is necessary to pay attention to the point that additional capital is required.
It is also worth noting that when conducting both retail and wholesale business, each will cost 100 million baht or more.
2. It is the so-called forecast production type manufacturing industry that 100% foreign investment can be made, the manufacturing industry in contract manufacturing and contract processing is regarded as a contracting business, widely as a service industry and it is possible to become a subject of negative list there is. Therefore, it is necessary to confirm beforehand whether manufacturing activities carried out by the company are stuck on the negative list.
In any case, I think that consideration should be taken not to be such a thing after the establishment.
-
Q&A2
QWe plan to set up a joint venture with a local company in Thailand. I think that I will make Thai director, but I am a bit worried if I am a trustworthy person. Is there any good way to do it?
AIn Thailand there are foreign investment restrictions, especially for the service industry, there are options such as applying for BOI, establishing with a local partner, etc.In the case of establishing as a joint venture with a local partner, in many cases we will take the partner Thai director as director. Japanese people often become directors, but it is also seen that they are not resident in Thailand.The Japanese director is in Japan, leaving all the business to the Thai director.I think that it is one management method, but I think that I often find myself a little uneasy about leaving everything.In Thailand you can limit the signature authority.For more than a certain amount of payment, you can not sign if you are not a Japanese director. In addition to delegating daily work, it is possible for Japanese people to make a decision on serious business decisions by making decisions in Japan.In addition, there are also a signature method in the signature method, but signature with a common name is necessary even for a small settlement etc, so we can not recommend it much because the speed of daily work is delayed. It is important to delegate authority to a certain extent and keep speed control and important decision-making control. -
Q&A3
QCurrently I would like to advance into industrial park in Thailand. There are many industrial parks in Thailand, but where is the industrial area where Japanese companies enter a lot?
ARayong, Chonburi, Ayutthaya, which are the major areas around Bangkok, are regions where many Japanese companies enter the market after Bangkok. -
Q&A4
QWhen establishing a company in Thailand, is it necessary to certify the document at the notary office or embassy as a procedure on the Japanese side?
ANotary of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, certification is basically necessary. However, practical treatment varies depending on accounting firms, law firm offices, etc. Please consult us before proceeding. -
Q&A5
QI am planning to establish a joint venture company in Thailand, but how can I grant the signature right?
AIt is common to set requirement that it will not be effective unless there are multiple names of all or a part of the directors holding signing rights of each invested company. By doing so, you can equally grant signing rights to each investor. However, there is a disadvantage that the daily work also needs to be renamed, making it inefficient. In order to avoid such a situation, it is considered preferable to use properly such that it is possible to use a common name for certain things, a single signature for daily business things, and so on. -
Q&A6
QThe registration of the company was completed and a foreign business license was obtained. When starting business operation, is there anything to be surprised about registration and registration of foreigner's license?
AIn order to operate the business after establishment, it may be necessary to acquire a separate license depending on the type of industry. Unless these licenses are acquired, there is a risk that business operation will not proceed or business will be allowed without permission, so you need to confirm which license acquisition is required beforehand. Here is a list of the main licenses.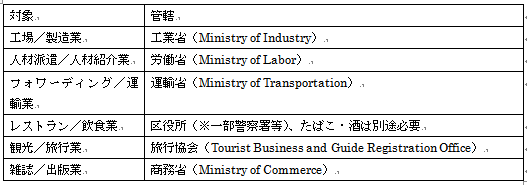 Although the acquisition period of each of the above licenses is different, for example, it takes 1.5-2 months for food and drink.
Although the acquisition period of each of the above licenses is different, for example, it takes 1.5-2 months for food and drink. -
Q&A7
QI often hear that Japanese companies are easy to do business in Thailand, but in order to make it a starting point for considering in-house what kind of cost it will cost to start a business on the ground, Please tell me.
ADepending on the type of industry, this time I would like to estimate assuming the case of a trading company in Bangkok, the service industry. I think that you can check the market price based on this and calculate your own items etc.<Initial cost>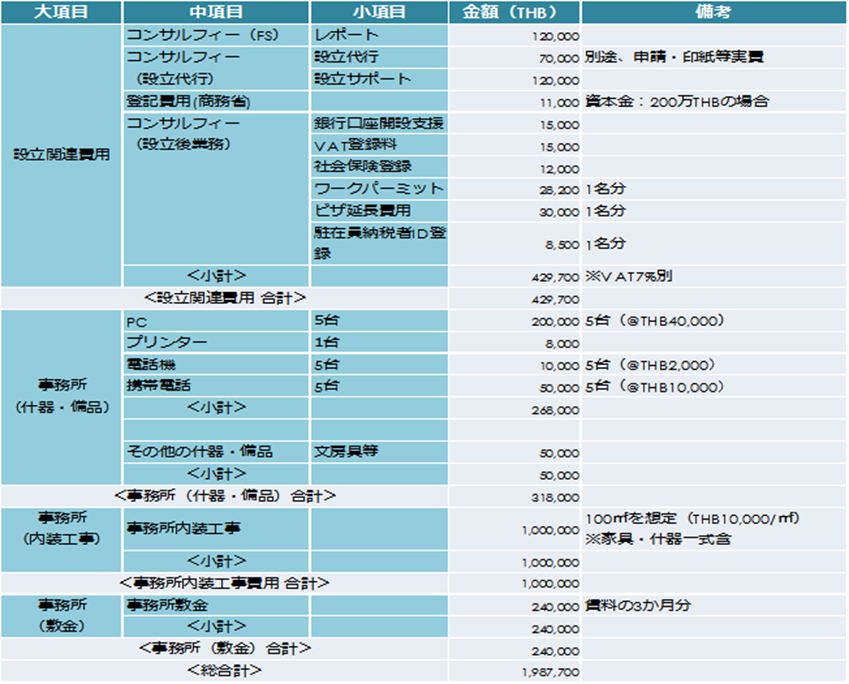 <Running cost ①>
<Running cost ①>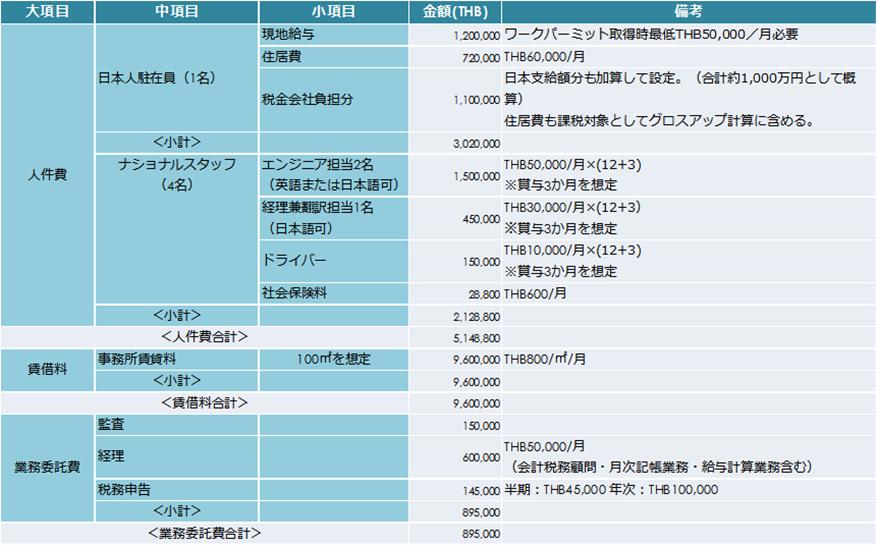 <Running cost ②>
<Running cost ②>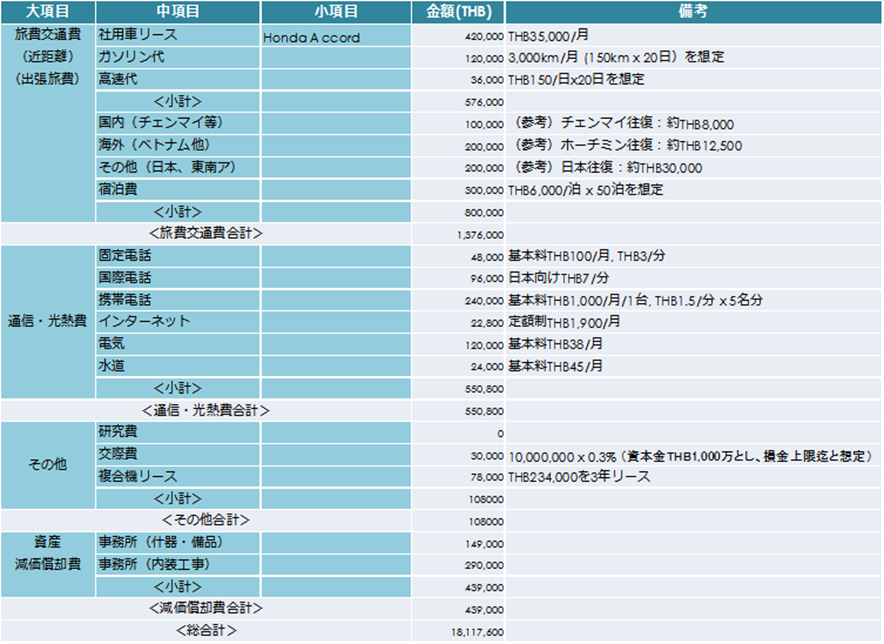
-
Q&A8
QWhen establishing a joint venture company C in Thailand where 49% of Japanese corporation A and 51% of Thai corporation B invests, will company C be subject to the regulation of the Foreign Business Act?AUnder the Foreign Business Law, if foreign capital accounts for 50% or more of the total capital, the company is defined as a "foreign corporation" and is subject to regulation. In this case, the foreign capital ratio of Company C is less than 50%, so it does not fall under the definition of "Foreign Corporation" and Company C will not be subject to the Foreign Business Act.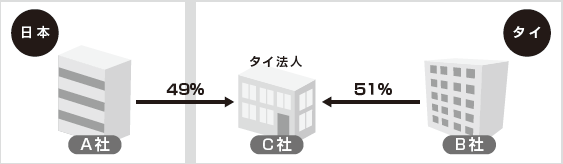
-
Q&A9
QI am planning to establish a joint venture company C in Thailand, which owns 51% of Japan A company and 49% of Thai B company. In this case, is Company C subject to the regulation of the Foreign Business Act?AAs explained in ①, entering foreign capital of 50% or more is subject to regulation. In this case foreign capital will be 50% or more, so it is deemed to be a "foreign corporation" and Company C will be subject to the Foreign Business Act.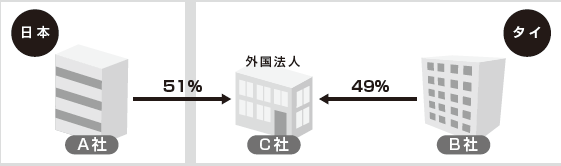
-
Q&A10
QWe have established a joint venture company C in the scheme of case 1). In addition, Company C wants to establish a new company in Thailand with (1) a joint venture company D of 51% C, a joint venture company D 49% Japan A, and a company E of 100% owned company C). Will D and E companies be subject to the regulation of the Foreign Business Act in the cases of (1) and (2) above?AFirst of all, as for case (1), company C is regarded as "Thai corporation" as in case 1). Therefore, company D will become a joint venture company of Japan A company 49%, Thail C company 51%, it will be considered as "Thai corporation" and will not be subject to regulation.Also in case (2), Company E is established as a 100% investment by Company C regarded as "Thai corporation", so it is regarded as "Thai corporation" and is not subject to regulation.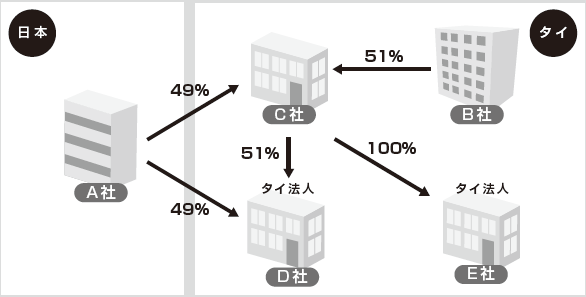
-
Q&A11
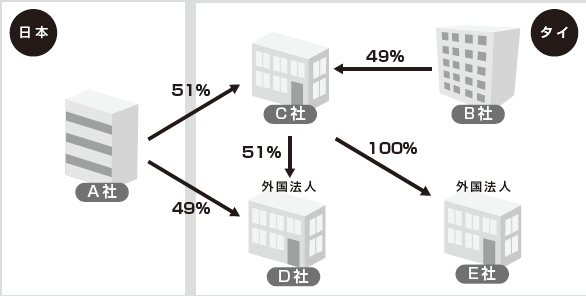
Q
We established a joint venture company C in the scheme of case 2). In addition, Company C wants to establish a new company in Thailand with (1) a joint venture company D of 51% C, a joint venture company A 49% of Japan A, and an E company 100% owned by ⑵ C company. In the cases of (1) and (2) above, will it be subject to the regulation of the Foreign Business Act?
A
First of all, as for case (1), company C is deemed to be a "foreign corporation" as in case 2). Therefore, Company D will be a joint venture company of Japan A Company 49% Japan C Company 51%, it will be regarded as "100% foreign corporation" and subject to regulation.
Also in case (2), Company E is established as a 100% investment by Company C regarded as a "foreign corporation", so it is considered as "100% foreign corporation" and subject to regulation.
-
Q&A12
QI have a subsidiary in Thailand, but I am considering whether to make a capital increase or borrow from a parent company. What are the merits and demerits of each?
AIn Thailand there are no special restrictions on parent-child loans. Therefore, if a local subsidiary in Thailand raises funds, it may be possible to increase capital from the parent company, borrow from the parent company, or borrow from a local financial institution. In consideration of each merit and demerit, it is necessary to decide the procurement method.png)
-
Q&A13
QWe have been a company that has been encouraged by BOI until now, but it is included in the business to be abolished according to the new BOI encouragement. There are various benefits for BOI encouragement, but will these benefits be maintained?
A.Basically it is to be maintained about non taxable benefits. Specifically, it has the following benefits.· Land ownership· 100% foreign capital contribution· Relaxation of requirements for obtaining work permitsHowever, as stated above, it is limited to the benefits under "Non taxation". Tax exemption for corporate income tax and exemption from import duties on exported raw materials is not applicable, so pay attention. -
Q&A14
QAs a requirement of BOI, there is a condition to add value of 20% or more, but how do you calculate the added value ratio in the application?
AThe calculation formula of the value added rate is as follows.Value added = [(ex-factory price of the product) - (raw material cost) - (utility cost)] / (ex-factory price of the product) * 100
The value-added rate is a criterion, but it does not depend on that alone. The process of production and processing is also emphasized, and production and processing processes need to be done in Thailand. Therefore, only attaching the seal, it will not be accepted by addition of value added by granting patent or trademark right.As a background, promotion of employment is also necessary, which may not be satisfied in the above.Even in the definition of manufacturing, it seems that it does not become a manufacturing industry, such as attaching a seal as described above. In reality, we need to import raw materials into Thailand, leaving production and processing process, and produce or process in Thailand. -
Q&A15
QIs Thailand a domestic corporation (Thai capital 51% or more) possible to acquire land and condominium?
ARegarding land and condominiums, it is possible to acquire it in Thai domestic corporation (Thai capital 51% or more and majority shareholders are Thai citizens or Thai domestic corporations) and BOI companies. Foreign corporations or individuals with foreign nationals can only acquire condominiums. For houses etc., foreign corporations and BOI enterprises can not be acquired, but Thai domestic capital enterprises are available for purchase.In addition, service apartments are handled in the same way as condominiums if the ownership of each room or facility can be distinguished. -
Q&A16
QWhat taxes and fees are involved in obtaining land?
ASpecific business tax and stamp duty will be charged as tax related to land acquisition.Similar to VAT, the specific business tax is paid by the payor in addition to the purchase price, and the receiving side declares / pays the tax. Specified business tax on real estate will be 3.3% of purchase price.In addition, the stamp duty will be 0.001% of the purchase price.On the other hand, the fee to the government at the time of land purchase will be 2% of the purchase price or value. Usually we calculate by purchase price. Since this fee is capitalized together with the normal purchase price, it will be processed on land accounting in the land (in case of expenses it will be Government fee).
-
-
-
Q&A1
QWe are currently considering establishing a joint venture corporation in Thailand. I think that the resolutions that shareholders can influence will change depending on the investment ratio, but what should be decided on the basis?AFor private companies, the quorum is 25% or more in ordinary resolution such as election of directors, dividends, approval of financial statements, resolution is a majority of attending shareholders, special resolution such as change of articles of incorporation, capital increase, merger is quorum, resolution requirements Both are 75% or more.Although there is a balance with foreign investment restrictions, we recommend considering the shareholding ratio based on the majority and 75% as a standard.Also, when issuing preferred stock in Thailand, it is possible to arbitrarily set voting rights as well as dividends. For example, it is possible to occupy a majority in voting rights regardless of the ownership ratio by setting one common share as one vote per share and one as 10 votes per preferred share.Issuance of preferred stock and its requirements can be stated in the articles of incorporation.For reference, an example of the items to be stated in the Articles of Association and the Articles of Incorporation is described.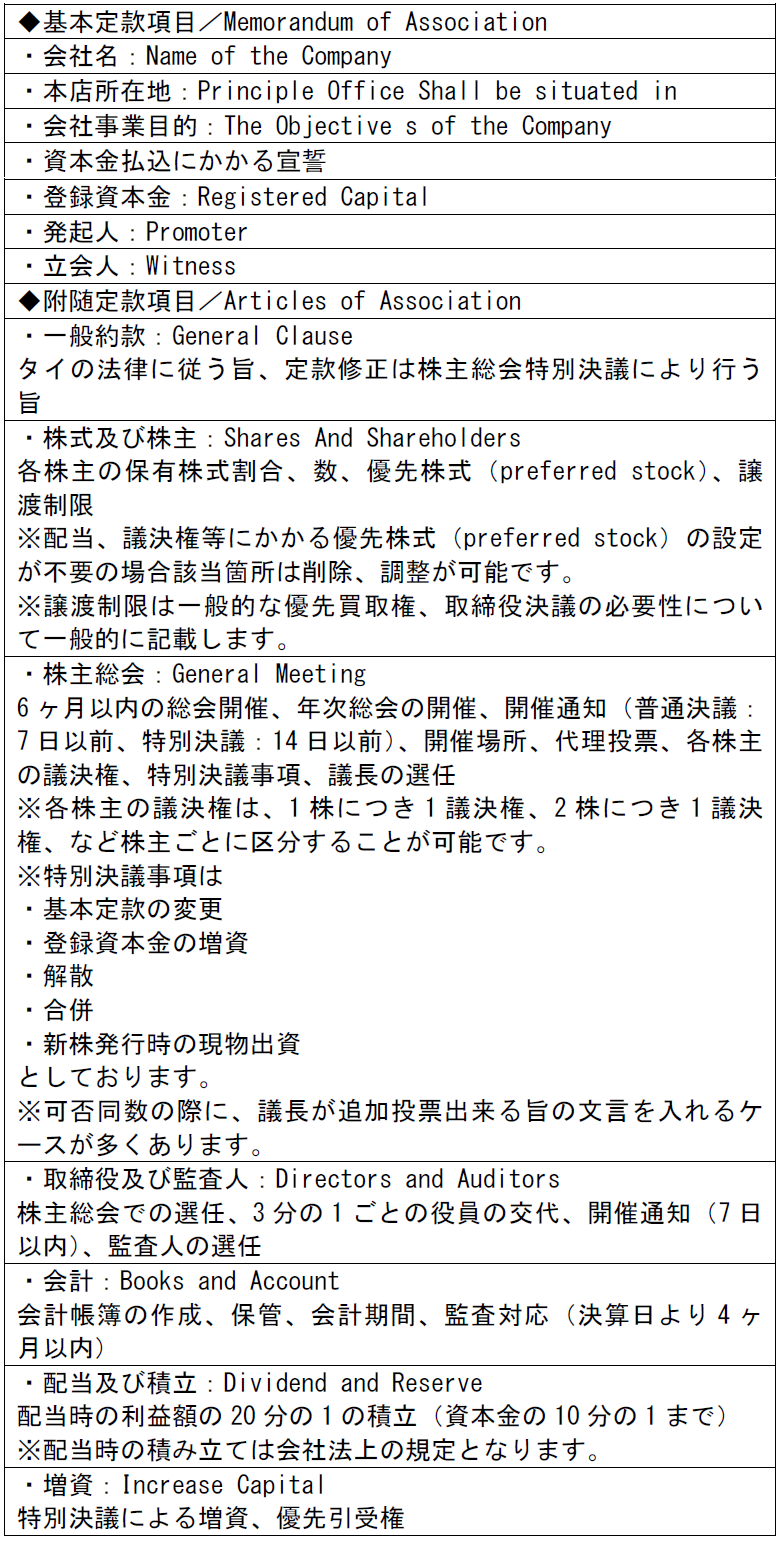
-
Q&A2
QDoes the president or director of a Thai local corporation need to live in Thailand?AIn the case of a private company, there is no legal obligation of the director to live. Therefore, nonresidents can become presidents or directors.However, as it is necessary to sign autographs of bank authorities, administrative procedures, monthly tax returns, etc, which occur on a daily basis, it is desirable to give certain authority to others.Also, as a precaution, in order to prove that the regular shareholders' meeting was conducted correctly in Thailand, it is sometimes required to submit a copy of the passport of the director (1 person) You must stay in Thailand for the period during which the general meeting of shareholders is held. -
Q&A3
QIn Japan, there is a corporate auditor system, but is there a similar system in Thailand?AThere are no provisions in the Commercial Code and Public Corporation Law. However, under the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Commission, there is an obligation for public companies to establish a board of auditors. The Board of Corporate Auditors consists of three or more persons outside the company, one of whom is supposed to have members of financial and financial knowledge to join the members, and is working to strengthen the corporate governance of the public company. -
Q&A4
QIn establishing a corporation in Thailand, we have established a joint venture with a Thai company, with 49% of Japanese companies (and Japanese individuals) and 51% of Thai enterprises constituting shareholders.51% of Thai companies are preferred shares, but we are planning to change the dividend ratio this time. Please tell me how to proceed and change your dividend ratio.AIn Thailand it is stipulated that under Article 1142 of the Commerce Code of Civil Code, it is impossible to change the conditions on preferred stocks issued once.Therefore, in order to change the dividend ratio, we will issue new preferred stock (capital increase) and then proceed with redemption (capital reduction) of the existing preferred stock once.In other words, you need to do both procedures of increasing and decreasing capital.If we redeem the preferred stock held by a Thai company first, we will contravene foreign investment regulation due to capital composition.Therefore, as one of the procedures, it will be slightly complicated, but you need to follow the steps below.1. Capital raising procedure (issue of preferred stock according to new dividend ratio) * Even if the old preferred stock is redeemed, capital increase will be made so that Thai capital will be 51% or more2. Payment of Capital Required for Capital Increase ※ It is necessary to consider how to raise funds for capital increase.3. Capital reduction procedureWith regard to capital reduction, in Thailand it is not possible to reduce the capital reduction to less than a quarter of the total capital. In that case, it is necessary to divide capital by dividing it twice.Taking the above procedure, it is important to prepare such as consultation and written concluding, so as not to cause trouble, since the investment ratio of Thai companies is higher than the original ratio, even temporarily. -
Q&A5
QIs there anything to be aware of when raising capital? In caseAWhen making a capital increase, procedures must be taken against several administrations, such as changing the capital of the registry, changing the register of shareholders, notification of changes in the capital at the tax office. Also on taxation, attention should be paid to the risk of taxation on the benefits received.In 2012, S company in Osaka made a capital increase by a Thai subsidiary and underwent by the parent company with par value, Osaka National Taxation Bureau told the Osaka National Taxation Bureau that there was a failure to file a 1.4 billion yen gift benefit declaration.In this case, it is considered that the taxation on the incentive was given as if the actual underwritten value assumed by the parent company was lower than the market price of the subsidiary stock (favorable issue) and that the economic benefit from the former shareholder was transferred . The judgment as to whether or not it corresponds to advantageous issuance is considered to be a case where a difference of about 10% or more of the stock occurs between the market price of shares at the date of payment determination and the actual amount to be paid.In Thailand, it is necessary for three or more shareholders to be mandatory, so when you make a capital increase you need to keep in mind that there is always a risk of income taxation. -
Q&A6
QIn Article 1202 of the Commercial Code of Commerce and Industry in Thailand, provision of profit funds at the time of dividend is written, and it is a funding of one-twentieth (5%) of the profit, but at the time of dividend it is necessary to accumulate one twentieth of the profit Is it necessary to do?
AAccording to the law of 1202 of the Commercial Code, it is wording that it is one twentieth of the profit."When distributing dividends, it is necessary to accumulate more than one-twentieth of the profit as legal reserve until it reaches a large amount, either one tenth of the capital stock or the amount specified in the articles of incorporation, whichever comes first (Article 1202 ) "However, there are the following two methods as practical handling and views.
(a) To make it one-twentieth as strictly as stipulated by law(b) To make it one-twentieth of the amount to be distributed from the profit amount
If you read the legal sentences in writing, it becomes (a), but because the large reserve is required according to the view of (a), the amount to be allocated to the dividend among the profits rather than the profit is taken as the calculation standard There is also a view that it is reasonable in practice.In fact, there are cases where it is based on the view of (b) in practice.On the other hand, as the accounting auditor often points out and requests on the street (a) by law, in practice it is desirable to check opinions with the accounting auditor and respond.In this way, since the interpretation is divided, it is necessary to take into consideration the attitudes of lawyers and accountants, business practices, risks, etc., respectively.
-
-
-
Q&A1
QWhat kind of accounting software is common in Thailand? Also, in preparing the financial statements, is it possible to use languages other than Thai, such as English, or to use currencies other than Thai Baht such as USD?AIn Thailand, Express, CD Organizer, Quick Books, etc. are common as accounting software, it is common that Thai language and English can be set as software setting. In Japanese companies, there are many cases set in English. However, the declaration of the annual tax return is Thai language, and the audit report is Thai language.Even if you set it in English on accounting software, it is necessary to prepare a Thai audit report by the accounting auditor when preparing the audit report.In addition, since the currency for booking is Thai baht, if you want to manage with US dollar or yen, you need to convert Thai Baht at each period end rate and convert it for internal management only. -
Q&A2
QHow can we account for the payment of goods owned as inventory as samples to customers and suppliers without charge?AFrom the conclusion, it is common to post it in selling and administrative expenses.For example, if you provide it as a sample to customers, it can be said that it is appropriate to post it as sales promotion expenses. On the other hand, in the case of suppliers, it is common to record as expendable item costs.Because processing varies depending on the supplier, it is necessary to pay attention.Also, once it is recorded as an inventory item, it will be transferred from the inventory item to one of the above account items.Risk is deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be deemed to be In particular, if you cross the fiscal year end, it is better to leave vouchers of free provision to customers and suppliers. -
Q&A3
QI am planning to adopt accounting and management staff when setting up a company. What kind of scope should be covered as a theme for confirming what kind of work I was involved in before and educating staff?
AI think that there are the following contents as guidelines for adoption of accounting management staff and education.
AccountingOverall image of transaction, purchase from supplier, sales to customers and issuance of each voucher related theretoVarious payment methods and their managementBookkeeping work in accounting software and output of financial statementsCreating and reporting internal analysis materialsTaxOutline and schedule of VAT, withholding taxMonthly tax payment, social insurance treatmentAnnual tax return and shareholder meetingStatutory audit correspondence (interaction with the auditor)· Other administrative tasksSocial insurance registrationPayrollMonthly voucher summary, cash deposit, small cash management -
Q&A4
QThe accounting staff is meeting the settlement of accounts, but the settlement report is late and the audit is likely to be delayed. What kind of measures are there?AIt is important to keep points schedule and points where staff is stuck and to constantly update the situation.First of all, let's review the schedule concerning the settlement of accounts.In the case of the January - December account settlement,· Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders: End of April· Tax return: End of May· Submission of audit report: Within one month from ordinary general meeting of shareholdersHowever, I think that there are many companies in the March closing date in Japan, so in that case, we will audit in late February - early March, there are many schedules to submit an ordinary shareholders meeting and an audit report think.Next, it is a point that is likely to get stuck.1. Settlement mattersThe details of settlement arrangement are largely unchanged from Japan, but there are mainly the following points.·Inventory· Depreciation and amortization expenses· Accrued allowance· Account processing· VAT payment2. Statutory audit issues pointed outAlthough the items pointed out in the statutory audit are related to the above-mentioned settlement arrangement matter, in Thailand, paying particular attention to the following points.· Charge replacement process with parent company· Parent / child loan processing· Fixed asset management and accounting standard· Handling of inventory wear and tearAs stated above, it is necessary to take measures to maintain evidence of contracts, etc., to handle expenses with respect to expenses change and parent / child loan handling with the parent company. Recently, it is important for the auditor to take responsibility for compliance aspects, so it may be confirmed compliance aspect in statutory audit.Regarding the recording of fixed assets in Thailand as mentioned above. As for principles to use for more than one year, fixed assets are counted regardless of the amount, so it is necessary to pay attention.In addition, when inventory is different from the actual stock and the book value, it is generally more likely to process with inventory difference gains or losses. However, it is also necessary to pay attention to the point that the inventory depletion is not deductible for tax purposes.It is important to grasp the schedule that points out easily, points of dealing with large impacts in the business this coming in the company, how it is being processed, and whether there are pending matters or not. -
Q&A5
QWe have settled accounts in the January - December accounting period, but there is a difference between the inventory quantity in the physical inventory and the quantity in the book. If the quantity is large, what kind of response is necessary in case of few?AIn the case where inventory differences are occurring like this time, it is common to process with inventory difference gains, etc. when the actual quantity is large, or inventory reduction when there is little difference.<When the actual quantity is large>Inventory / inventory difference gains<When the actual quantity is small>Inventory depleted loss / inventoryRegarding inventory wear and tear, it is classified as either cost of sales or non-operating expenses depending on the cost or not, or excess or deficiency adjustment by miscellaneous income or loss. However, in Thailand, treatment of non-inclusion of deduction is common in both cases of inventory depletion and miscellaneous goods. Therefore, it is unnecessary in this case to handle stand-ups by tax authorities, auditors, etc.Also, with regard to inventory depletion loss, due to VAT calculation it is possible to treat tax as deemed sales, so pay attention to it.For example,Book value: THB 1,000Actual price: THB 800In case of THB 200 difference, THB 300 THB 300 If THB 300, THB 300 × 7% = THB 21 must be recorded as Output VAT on sales on VAT Report.This means that VAT is calculated as deemed sales. In this case, issuance of an invoice is unnecessary.Regarding market prices, we usually refer to them if there is sale of the same / similar products. If the selling price of the same / similar product as the amount declared as deemed sales diverges greatly, it may be pointed out, so it is necessary to pay attention. -
Q&A6
QDo you have a general payment period in Thailand? I would like to confirm the conditions and notification method in Thailand in general when deciding payment terms and notifying.AThere are no statutory on payment due date and payment period, so some patterns can be seen in 50 days. There are many closing days at the end of the day, payment is at the end of the month or 5, 15, etc. are increasing.The payment period is 30 days / 45 days / 60 days is increasing. There are not many discounts on payment within a certain date, but it can be seen. On the other hand, if you exceed the due date, you may be asked for a penalty.Notification of payment terms can be handled by putting them in estimates, contracts, invoices, etc. However, there may be cases where a separate notice is sent.As for the accounts receivable at the time of the monthly closing, there are uncollected receivables if the accounts exceed the approximate sum of the monthly sales plus the past monthly payment period of more than 30 days on a gross basis Therefore, I would like you to make a payment request based on the age table of accounts receivable so that long-term uncollected loan will not remain.
-
-
-
Q&A1
Q.Is there anything to pay attention to when introducing or setting up the personnel system in Thailand?A.You need to check the following points first.◆ Industry (factory / trading company): Depending on the type of industry, the organizational structure is different and the complexity of required accuracy also changes.◆ With or without labor union: The presence or absence of labor union has a big influence on wage system and its operation, especially decision.Whether or not to acquire ISO etc. If ISO exists, it is necessary to adopt ISO as a criterion for personnel evaluation, to take consistency, etc.◆ Region: You should consider wage differences by region.◆ Purpose of system introduction / change and problem of current system: The composition of institution changes depending on the purpose of introducing / changing for purpose.◆ Improvement of Internal Human Resources Related Provisions: In the case where there are provisions so far, it is necessary to adjust the consistency.◆ Target Category and Organization Chart (Including Number of Employees)· Manufacturing control·Manufacturing technology· Production line·Sales· Sales staff· Trade·accounting· General affairs personnel affairsGeneral affairsTogether with the type of industry, what kind of system to apply in what range is a point in building.◆ Covered System· Wage system· Grade system·Rating system· Others (welfare, division of duties, career path, evaluation manual)In light of the above object, it is related to what kind of configuration and complexity to build.Also, from the viewpoint of comparison with Japan and other countries involved in personnel affairs, the features of Thailand are summarized below, so please refer..png) Source: National Statistical Office of ThailandFirst of all, I think that I can take the first step in introducing and changing the system by understanding the difference between Japan and each country like the one mentioned above, holding down the points at the time of what I have to tackle.
Source: National Statistical Office of ThailandFirst of all, I think that I can take the first step in introducing and changing the system by understanding the difference between Japan and each country like the one mentioned above, holding down the points at the time of what I have to tackle. -
Q&A2
QWhat is the general personnel evaluation system in Thailand, the characteristics of pay raise?AIn Thailand, it is common to raise salary according to so-called emotion such as job attitude and attendance and years of service. Recently, some companies introduced performance-oriented principles, mainly in European and American companies, and the number of cases introduced by Japanese companies is increasing.
Similarly to Japan, absolute evaluations and relative evaluations are performed using absolute evaluation of primary evaluation, and relative evaluations are performed more frequently for secondary adjustment (for example, adjustment between departments) after secondary evaluation.
Although it is common to pay full-time allowance, ability to supply salary, salary, allowance, it is not common to add a lot of allowances. Considering the purpose to be attached, it is necessary to consider. There are many cases where you can attach a deductible allowance for the purpose of preventing frequent injury vacation.
In raise payment it is common to multiply the salary increase by the salary increase rate. Because there are many cases where the salary increase rate for each type of job is not defined, there is a harmful effect of raising the salary according to the length of service regardless of the degree of contribution to the company.
Also, in Thailand where there are many December settlements, the following evaluation schedules are more frequent..png)
-
Q&A3
QAlthough we are a factory in the industrial estate, we are planning to complete the establishment half a year ago and hiring personnel for future operation. At the beginning, it is an organization of ten or so people, but I would like to hire recruitment activities with a certain salary rate down. Could you tell me the image of salary price?AThe salary price will also change slightly depending on the location of the industrial estate. Also, since there are salaries to some extent depending on duties and positions, I think that it is better to adopt a salary range for each job and position.Also, at the time of the actual interview, it is necessary to check the present salary and desired salary beforehand and light up the expected salary width. In some cases, we will offer higher salaries, but because negotiations are usually possible, please decide in consideration of the expected salary range in the company and future pay raise.Below is an image of salary range for each region..png)
-
Q&A4
QFor the first time, I am planning to give an assignee to Thailand. Those who are assigned are worried about Thai security. Actually, what is the security of Thailand?AIn Bangkok and Phuket the security problem is not serious. Many Japanese are staying in Bangkok, Thailand and Phuket in Thailand for sightseeing purposes, and many Japanese staff and their families are staying at work.According to the US Thinktank Economic and Peace Institute, Thailand ranks eighth according to the 2012 survey "World Terrorism Index". (1st place is Iraq)This is caused by the conflict between Murray Islamic extremists in Thailand and Thai authorities. Religious circumstances in Thailand are 94% Buddhism and 5% Islam, although Muslims are overwhelming in areas close to Malaysia although Buddhists are mostly occupied, situations where security is not good is.Also, in Thailand you can possess a handgun if you apply (you need a certain position). There are shooting ranges in Phuket as a tourist destination. It is necessary to tell them not to go to dangerous areas when putting out an assignee including such points. -
Q&A5
QThe expatriate said that he would like to drive a car in Thailand. Is it common for companies to lend automobiles etc? In the first place what kind of procedure is necessary for Japanese people to drive a car in Thailand?AIf you acquire an international driver's license in Japan, you can drive a car in Thailand. (It is possible to obtain it at the driver's licensing center in Japan etc.)However, the percentage of traffic accidents is very high compared with Japan, and the local people's driving is also rough, so it is getting more involved in problems. As a result, many companies are banning driving locally, and few cases lend automobiles.Instead, there are many companies that make it possible for expatriates to use cars and drivers borrowed for business by the company on holidays and other occasions. -
Q&A6
QAlthough I am setting up a factory in Thailand, I am planning to match salaries and allowances of employed employees with other countries of my company, but I also want to know the situation of other companies in Thailand. What types of salaries and benefits are common in Thailand is common?AIn factories in Thailand, in addition to basic salary, there are many cases where the following benefits are paid.· Food Expenses / Living Expenses Allowance: Especially when overtime workers occur in workers or shift work is on the rise.· Commuting expenses: In Thailand, it is difficult to calculate a fixed amount of commuting expenses because there are few public transportation facilities except in the city center, so it is common to set in the company how much per month in Thailand. Approximately 5,000 Baht is common.· Housing allowance: There are cases where you only pay for executives. Between 5,000 and 10,000 baht is increasing.· Position allowance: It becomes allowance for executives.· Technical Allowance: When using a specific technology at a factory, you often work on a company for a certain period of time and pay for it when you acquire skills.· Language allowance: It is payment to successful applicants for language tests such as Japanese and English, and to certain level of employees.· Full-time allowance: There is also a meaning to prevent abuse of injury and disease allowance.In addition to the above allowances, there are cases where payment is paid when making improvement proposals. It is increasing that it is set at around 50 Baht per proposal (one serving is a standard), 500 baht if adopted, etc. (for a salary of 1 day as a guide) etc. -
Q&A7
QI am considering joining Thailand's PF (Provident Fund) as part of welfare program. Please tell me about details.AFor the Provident Fund, the company specifies a certain rate, and the company and employees pay the respective premiums.Depending on the operation of the premium, you can receive benefits at the time of retirement.In principle, all employees are eligible, but employees can choose not to join.As premium rate, 3% - 5% of salary is common, 3% is more in companies with less than 300 people.There is also an option to change the above-mentioned premium if the length of service exceeds a certain number of years.It can be set like 3 years for 1 - 5 years, 5% for 5 years etc etc.Depending on the risk / return, fund management is divided into several types by the Provident Fund Investment Company.As an example of high risk / high return, 35% of reserve funds are fixed, only a certain degree of interest is set, and the remaining 65% is in accordance with the result of operations.As an example of low risk / low return, 95% of reserve funds are fixed, only a certain degree of interest is set, and the remaining 5% corresponds to the result of operations.In addition, there are also the types with the lowest risks and returns with all interest as extent of interest.The type of these products varies depending on the provider's investment institution.For companies with 300 or fewer people, there are many companies that choose low risk / low return.Especially for companies that are 20-50 customers and are subscribing to the Provident Fund, there are cases where 3% choose a low-risk / low return type and approximately 80% of the employees are subscribing It is getting more. -
Q&A8
QDo you have labor laws or customary special, Thai unique holidays?AIn Thailand, we have the following holiday system.· Vacation leave: Paid vacation up to 30 days per yearMaternity leave: Up to 90 days before and after childbirth (paid up to 45 days) Vacation· Military leave: Paid vacation up to 60 days per year· Employee's leave: Employees who worked for more than one year can only get one leave for their birth (unpaid)· Business leave: Unpaid leave by self-circumstances (Article 34 of the Workers Protection Act)In particular, vacation due to injury or sick leave is commonly referred to as "Sabay leave", but there are cases where you frequently take a rest after regular use. In order to prevent this normalization, it is an effective measure because we have taken measures to raise the motivation to add a plus if you work when giving a full-time allowance.Also, leave of absence is not legal, but there are many cases that are usually established. Also, although there is no obligation to paid, there are many cases that are paid. As for the period of the birth, in general, it is about two weeks, but as regulations it regulates in about 1 to 3 months and some companies regulate such as paid for a certain period . -
Q&A9
QIn Thailand, there was no prescription for annual paid leave of employees, I heard that it is necessary to carry out the paid vacation not used in the next year to the next fiscal year or to buy it according to labor-management agreement, but when annual paid vacation is retired at the time of retirement If it remains, what kind of treatment do you do?AIn Thailand, if paid vacation remains at the time of retirement, you must pay wages for the remaining days of paid vacation. (That means you have to buy it.)However, for employees who have been dismissed due to disciplinary reasons, even if annual paid holidays remain, it is not necessary to pay wages for that number of days. -
Q&A10
QWe will do business in the showroom. Regardless of weekdays or weekends, I'd like to have duty work with a shift system of about 5 to 6 days a week. Will it be necessary to pay holiday allowance in case of working on weekends?AUnder Thai labor law, in Thailand it is said that workers must be given a holiday for more than one week per week. However, it is not stipulated that holidays must be set on Saturdays and Sundays, so if more than one day off is secured per week, you do not need to pay holiday allowance even if you let you work on Saturdays and Sundays . (It is necessary to obtain consent beforehand to workers.)In addition, since Thai legal hours are 8 hours per day, 48 hours per week, for example, if you set the working hours of each day from Tuesday to Sunday as 8 hours for every Monday as a holiday It is not necessary to pay extra overtime wage or holiday allowance.However, when Monday is set as a holiday as described above, holiday allowance becomes necessary when it is made to work on Monday, and depending on the type of business, depending on the type of business, it is necessary to pay holiday allowance regardless of the above handling Please be careful. -
Q&A11
QCurrently, we are planning to relocate our factory overseas. At that time Thailand is also listed as a candidate, but in Thailand I am concerned that the wage is rising. What is the appeal of Thailand other than cheap labor force?AEconomic growth is expected in Thailand in the future, and there is concern about rapid price rise and wage increase accompanying it. Along with that, it is true that there are an increasing number of companies considering relocation of factories in Vietnam and Indonesia. -
Q&A12
QI am planning to establish a manufacturing factory in Thailand, but how do I deal with the situation when it suffered from natural disasters such as floods and it is inevitable to take a leave of absence?AIt is possible to close the factory due to floods etc.However, depending on the circumstances, it is necessary to pay leave allowance for employees during the holiday period. -
Q&A13
QPerformance deteriorated due to the damage caused by the flood, and employees have to be dismissed. What points do you need attention to?AIn Thailand it is permitted to do the dismissal if there is a justifiable reason. As a result, in principle, dismissal of employees due to deterioration in business results caused by damage such as floods and other disasters is deemed to be a justifiable reason. However, unlike in Japan it is necessary to pay dismissal allowance so be careful.Also, even if the company dismissed for reasonable reasons, attention should be paid to the labor court as an unfair dismissal from an employee who has been dismissed (in that case, it is recognized as a legitimate reason as a matter of fact) Whether it will be an issue). -
Q&A14
QCompanies with more than 20 workers in India will receive a Provident Fund (Retirement Benefit Plan), but will Thailand have a Provident Fund?A.The Provident Fund also exists in Thailand. However, in the case of Thailand, it is a matter of voluntarily joining for each company, and it is not a compulsory enrollment system.The Provident Fund in Thailand refers to the retirement benefit plan under the Retirement Fund Act (1987).The Provident Fund was established under the agreement of workers and employers, basically workers and employers fund the funds by half each month, the fund managers operate in the market, retirement of workers Sometimes a combination of principal and investment returns will be paid as retirement allowance.Employees can choose whether to join the Provident Fund at the time they enter the company, but because they are often benefits for employees, they will mostly join. The merit of the company side is that it is tax deductible for all part of the employer's share of the Provident Fund for tax purposes, and it makes it easier for excellent employees to gather by making arbitrary welfare benefits such as Provident Fund etc. It is cited.Meanwhile, as an advantage of employees, tax incentives can be received with an insurance premium of up to 500 thousand Baht per year, insurance premiums of up to 10 thousand baht per year are subject to income deduction, exceeding 10 thousand baht For insurance premiums as well 490 thousand baht or 15% of wage, whichever is smaller, is tax-exempt.In Thail, which is said to be a shortage of workers, it is necessary to carefully consider measures such as welfare benefits. -
Q&A15
QEstablished a corporation in India and Thailand. In India it was meant that we had to obtain personal payment number PAN (Permanent Accounting Number). Is there such a number in Thailand too?AAlso in Thailand, you need to obtain a tax identification number (TAX INDENTIFICATION NUMBER). If you do not get this and you receive a salary from a local corporation, you may be deemed illegal. The assignee must apply before paying the first withholding tax on income. -
Q&A16
QSince we set up a new base in Thailand, we plan to dispatch staff from the Japanese headquarters for that support. Is there anything to pay attention to other than staying days?ARegarding the length of stay, I think that many people are grasping the criteria of 180 days, but it is also necessary to pay attention to the requirement to acquire Work Permit in Thailand. -
Q&A17
QWe are considering business correspondence on business trips from Japan for business for customers in Thailand. Since it is business correspondence, I think whether it is necessary to obtain business visa and work permit, but is it the same as normal procedure? Are there any other points to keep in mind?AAccording to your inquiries, you need to obtain business visa and work permit when doing business even in case of business trip. In applying, we will apply under the company name of the employee (customer). If the customer is applying for the BOI encouragement project and the work concerns the BOI promotion project, it will be applied at OSOS. On the other hand, if you do business other than BOI promotion project, you apply to Labor Department.As you apply, the customer will become the company of the applicant, so the customer will bear the risk of applying. Also, since it is interpreted that there is an employment relationship between the customer and the business traveler, in view of the labor risk of the customer, it is concluded that a temporary contract / outsourcing contract is signed, It is desirable to set a separate contract to the effect that no salary payment or labor risk will be borne by the side. -
Q&A18
QWhat kind of procedures are there when Japanese people return from Thailand?AAs a procedure for Japanese returning from Thailand the following things are needed.· Visa / Work PermitVisa and work permit will expire automatically when expiration date expires.However, when additional personnel comes in the future, we will acquire work permit, in that case capital / number of people etc.If it can not be added with the requirement, you need to cancel the work permit first.In cases where there are no problems with the capital requirements and the number of people requirements, there are many cases where they are automatically extinguished.In addition, there are cases to cancel at the company from problems such as staying at the site as it is on site hiring etc.·personal income taxAt the time of returning, we will make a final declaration for the relevant fiscal year.Depending on the timing of returning, we will make a final tax return with no taxable income up to the salary of April payment without March.Target taxable income is the same as in 2013.In Thailand, the income tax rate is retroactively determined at the end of the year, and the timing of the declaration is the following year. Therefore, income of 2014 will be declared by January 2015 to the end of March.If there is a refund and you do not already have a bank account, it is also possible for the company or someone else to receive it on your behalf.In other countries, cancelation of Tax ID is required, but in Thailand cancellation is unnecessary.· OthersIf you have notified your residence status, you need to apply for exclusion.In addition, the procedures at the Japanese side such as a transfer notice in Japan are not different from the handling at the time of returning from another country. -
Q&A19
QIn the future, I am planning to take out appointees to Thailand. I would like to refer to the living expenses normally required in Thailand in setting up the local salary of the assignee. How long will it cost to live in Thailand?APrices in Thailand (Bangkok) will generally be one-third to one-third of Japan, but in living standards equivalent to Japan, equivalent living expenses will be charged. Local meals are cheap for restaurant meals, but at restaurants like Japanese restaurants it is set at the same price as in Japan.Regarding local housing, at the level where Japanese expatriates live, it is 25,000 Baht in one room and 35 thousand Baht from 2 LK.In general, if you have a local salary of about 50,000 Baht, you can do enough for one person's living, but if your family is occupied, a salary above that will be required. Charges also depend on the number of children. In order to bring a child to a Japanese school, about 7,000 Baht per month and other entrance fee and bus fee will be charged.When setting up local salary, we decide after considering these. As for housing and school expenses, there are also cases where it is taken as the company burden, so consideration for each company is necessary. -
Q&A20
QAre the minimum wages of expatriates stipulated by the law?AFor the Japanese (relocated and locally recruited Japanese) under the requirement of obtaining a work permit and extension of visa, the Thai corporation will pay a salary of at least 50,000 Baht at the Thai corporation side.Also, this system applies not only to Japanese but also to European countries, Australia, New Zealand, the United States and Canadians, the minimum wage of the same amount (50,000 baht) is applied, the amount is different for other countries, The system is applied first.Example)· More than 45,000 Baht for Korea, Singapore, Taiwan and Hong Kong· Asia (excluding the above 4 countries), Eastern Europe, Central America, South America, Mexico, Russia and South Africa, more than 35,000 Baht· For Africa (excluding South Africa), Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos and Vietnam, over 25,000 BahtIn Thailand, when using non-Thai citizens workers, pay attention to the above system. However, since it is not so strictly practiced, there are many cases where you are using non-Thai citizens without observing the above minimum wage. -
Q&A21
QWe established a subsidiary in Thailand and we intend to place Japanese representatives in the future. I think that Japanese representatives will continue to join Japanese social insurance in order to pay some salaries from Japanese corporations even after their assignment. Do I have to join Thai social insurance?AIt is not necessary to join as long as it is a position of officer at a local corporation, but if it is any other position, you need to join the local social insurance.Therefore, in case of a question, you will join both social insurance in Japan and local social insurance in Thailand and pay insurance premiums respectively.In order to receive pension in Thailand it is necessary to have insurance for 15 years or more, so if you are appointed for a period less than that, the burden of insurance premium payment will increase.Depending on the company, there are cases where employees' burden is not increased as a company burden for local insurance premiums. -
Q&A22
Q
It is the first year since I got an assignee to Thailand. If it is in Japan, January - December will be the taxable period of personal income tax and I think that we will have year-end adjustment in December, but what about the taxation period of personal income tax and tax payment in Thailand Do you think?
A
Thai taxation period is 1/1 ~ 12/31 same as in Japan.
In Japan, as a general rule, the company side will do the year-end adjustment, taxpaying will be done by the company side, except for those who satisfy certain requirements, but in Thailand individuals need to file a final return . The final declaration will be made by the end of March.
In addition, you can receive income deductions such as spouse deduction described below when calculating personal income tax at the time of final return.
· Spouse deduction · · THB 30,000
· Child deduction · · THB 15,000 / person
(Minors under the age of 20 or students under the age of 25, up to 3 people)
· Parents' dependency deduction · · THB 30,000 / person
(Over 60 years old, with income limit)
However, in order to receive deductions relating to the families mentioned above, it is necessary for the Japanese side to prepare a family register and certify it at the embassy in Thailand. Even those who can receive deductions for reasons that such procedures are complicated and because the amount deducted is small is also increasing for expatriate staff who have not applied deduction.
-
Q&A23
QAbout 300 people Manufacturing companies, how many people in accounting, personnel affairs, general affairs, secretarial / interpreter generally how many people? Also, although there is currently a representative office in Bangkok, is it possible to recruit staff and establish a new company at the current representative office, then let them transfer?AWith the above scale, it can be said that there are many cases of about 10 people or less.The borrowing will be after 4 accountants, 2 personnel affairs, 2 general affairs, secretarial / interpreter 1 name.Regarding transfer, the transfer like the one above is possible. However, it is necessary to include in the employment contract when hiring at a representative office, a statement on transfer to an affiliated company. In addition, we should prevent trouble at the time of transfer by explaining firmly not only in writing but also verbally.In addition, it is necessary to explain beforehand when treatment such as welfare benefits changes due to transfer. Please note that consent is necessary especially when it becomes disadvantageous condition. -
Q&A24
Q.We may hear that Japanese salary salary is not taxed unless it is brought in Thailand. Will salaries actually paid in Japan do not matter as a tax exemption in Thailand unless brought in Thailand?A.From the conclusion, Japan salary must be treated as taxable."I am not taxed unless I bring my Japanese salary salary to Thailand", I think that there are cases where judgment is made based on Article 41 of the Thai Revenue Law. In this section, it is stated that income brought to Thailand out of foreign source income is taxable for Thai residents. However, all domestic source income of Thai residents are subject to taxation.In other words, whether the Japanese side salary is domestic source income or foreign source income is a problem. However, if you work in Thailand and work, regardless of the place of payment, you can see the difference between domestic source income in Thailand It is treated. Therefore, for Thai residents, Japan salaries are taxable in Thailand.So, what kind of income is applicable to Thai foreign source income? This includes real estate income, dividend income, etc generated in Japan. Therefore, these incomes will be subject to taxation only when brought in Thailand.Since it is a point with many misunderstandings, I think that you can confirm once again. -
Q&A25
Q.We may hear that Japanese salary salary is not taxed unless it is brought in Thailand. Will salaries actually paid in Japan do not matter as a tax exemption in Thailand unless brought in Thailand?A.From the conclusion, Japan salary must be treated as taxable."I am not taxed unless I bring my Japanese salary salary to Thailand", I think that there are cases where judgment is made based on Article 41 of the Thai Revenue Law. In this section, it is stated that income brought to Thailand out of foreign source income is taxable for Thai residents. However, all domestic source income of Thai residents are subject to taxation.In other words, whether the Japanese side salary is domestic source income or foreign source income is a problem. However, if you work in Thailand and work, regardless of the place of payment, you can see the difference between domestic source income in Thailand It is treated. Therefore, for Thai residents, Japan salaries are taxable in Thailand.So, what kind of income is applicable to Thai foreign source income? This includes real estate income, dividend income, etc generated in Japan. Therefore, these incomes will be subject to taxation only when brought in Thailand.Since it is a point with many misunderstandings, I think that you can confirm once again. -
Q&A26
QThailand's personal income tax is a progressive taxation of 5-35%, but is the same tax rate for bonuses and retirement allowances?AThe personal income tax rate on Thai salary is 5-30% progressive taxation as you asked.Bonuses' tax rate will be treated the same as salary tax rate (calculated as progressive tax as annual income).On the other hand, the tax rate of severance payment is separately prescribed as separate taxation, and it becomes service years × 7,000 Baht + (retirement payment - (years of service × 7,000 Baht)) × 50%. However, the retirement income tax rate in Thailand is the case of receiving retirement payment maintained under the company regulations, and can be selected if the length of service is 5 years or more.
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya