Mongolia
6 Chapter Accounting
-
-
1 Chapter Basic knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.4 Investment regulation and incentives
3 Chapter Establishment
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.2 Establishment of business base
3.3 Liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter M&A
4.2 Laws and regulations concerning M & A
5 Chapter Corporate Law
5.1 Organization of the company
6 Chapter Accounting
7 Chapter Tax
7.2 Individual Issues of Domestic Tax Law
7.5 Tax survey and tax penalty
8 Chapter Labor
8.4 Foreign Employees in Mongolia
9 Chapter Q&A
-
-
-
Outline of Mongolian accounting system
In Mongolia, various laws have been enacted since the market economy in 1990, and from 1993 revisions have been made so that the accounting system approaches international standards. Also, in May 1997 we adopted the auditing law (Law of Mongolian Auditing) and in December 2001 the Law of Mongolian Accounting was adopted and it followed this law until 2016, but in June 2015, a new accounting law was enacted. In the year of 2016, we decided to abide by. Therefore, this Accounting Part contains the provisions of the Accounting Act of 2016.
According to Article 4.1 of the Accounting Act, the company must comply with the following accounting standards;
1. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
2. International Financial Reporting Standards for SMEs (IFRS for SMEs)
3. International Financial Reporting Standards for State Enterprises
Until 2016, all companies operating in Mongolia made financial reports in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), but were divided into three according to the new accounting law. In addition, all companies record income and expense based on accrual basis (Accounting Act 6.1).
The company must prepare accounting books and financial statements in accordance with the Company Law and Accounting Law and disclose it to shareholders (Article 95, paragraph 1 of the Companies Act). In the case of a listed company, it is necessary to submit financial statements together with the financial regulation committee (Financial Regulatory Commission) and documents required by the stock exchanges and to publish them..png)
Post period
Under the accounting law of Mongolia, the accounting period of the company is from January 1st to December 31st (Article 10 paragraph 1 of the accounting law), it is not permitted to set the other period as the accounting period. Therefore, in order to prepare the consolidated financial statements by the parent company in the March financial year, it is necessary to deal with temporary closing of subsidiary of Mongolia at the end of March within the company.
■ obligation to keep account books
The company has an obligation to keep necessary documents such as accounting books (Article 97 paragraph 1 of the Companies Act). The accounting book must be kept for 10 years from the date of creation, and after 10 years has elapsed, it will be kept at the National Archives (General Archival Authority) (Article 11.1), which is the national and enterprise. It is a government agency that stores and manages documents created by the private sector. The necessary documents such as accounting books that need to be kept in the company and maintained so that they can be read by shareholders at any time.
The accounting book must be recorded in local currency Tugguru (Article 7). Or, if you obtain permission from related institution (Mongolian bank and financial regulation committee), it is possible to record with overseas exchange.
Accounting penalty
According to the accounting law, if a company fails to fulfill its obligation, it is subject to a penalty and classified as follows according to the content of the violation (Article 27 of the Accounting Act).
1. If you violate the following provisions, you will need to pay an amount equivalent to five times the minimum wage; (192,000 Tugulg / September 2013).
4.1 Accounting books comply with accounting standards
Article 7 Accounting books are created in Mongolian and recorded in Tuggle
Article 8.4. The executive officers and accountants sign the financial statements and press the seal
9.1. Report financial statements in electronic form to relevant organizations within the time limit of the law
Section 9.2. Obligations of Financial Management Organizations Reported in Electronic Form
9.5. In the case of electronic reporting, an executive officer or an accountant electronically signs it
Article 10.3. Companies that comply with International Financial Reporting Standards report interim financial statements (January - June) by 20th July and electronic filing of tax returns to financial management organizations by February 10 next year
Article 10.4. Companies that prepare consolidated financial statements report the final declaration electronic form to the financial management institution attached to the parent company by March 1 of next year
10.5. Companies other than the above 2 will report the final return in electronic form by February 10 next year
10.6. Conditions financial institutions related to rural areas, the governor of the capital, shall submit a final return to the financial management organization by 20th March next year
11.1. The company keeps the financial statements for more than 10 years
14. Rules for accounting records, etc.
2. If you do not memorize accounting, if you are not preparing a financial report, give the employee a penalty of Togguru which is equivalent to 5 times the minimum wage and 5 to 10 times the low wage of the company to the company (27.1. 2 articles).
■ Mongolian accounting standards
Mongolia does not have its own accounting standards and adopts International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) as it is.
According to Article 4.1 of the Accounting Act, the company must comply with the following accounting standards;
1. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
2. International Financial Reporting Standards for SMEs (IFRS forSMEs)
3. International Financial Reporting Standards for State Enterprises
In recent years, the number of companies investing in Mongolia from abroad has increased, and the transparency of accounting standards is also required. Especially the qualitative improvement of accounting report is also strongly requested for comparing accounts with other countries. It is expected that it will be possible to attract investment from overseas markets by improving the transparency of these accounting standards and the qualitative improvement of the report contents.
-
-
-
Disclosure Schedule
Disclosure of information to shareholders based on the Company Law
Companies in Mongolia must hold annual shareholders' meetings by April 30 every year and disclose the following documents to shareholders (Article 59.4 of the Companies Act).
· Company's annual financial statements
· Audit report by the accounting auditor
· Report on conflict of interest by the accounting auditor
· Information on candidates for director
· Shares held by special interested persons of the company
· Director's report
- Information on remuneration of directors and business executives of the company
- Report on business activities (in the case of a corporation)
- Other information on resolutions
As a general rule, the annual financial statements must be prepared by March 20, the audit report of the financial statements must be prepared by March 31, and other documents should be prepared by the opening date of the general meeting of shareholders. Companies subject to audits such as foreign-affiliated companies are obliged to complete the audit by February 10.
■ Tax return filing schedule
Regarding tax returns, there are "Quarterly Declaration" and "Tax Return".
The income tax quarterly declaration must be declared until the 20th day of the following month, and the final return must be declared by February 10 (Article 21 paragraph 4 of the Income Tax Law).
In other words, the quarterly declaration is due April 20, July 20, October 20, and the final return till February 10 are deadlines.
In addition, for companies that prepared consolidated financial statements, the quarterly declaration form must be declared by the 25th day of the following month, and the final return form must be declared by February 25 of the following year.
For tax payment, the corporate income tax must be paid by 25th of the month (Article 21 (4) of said Article).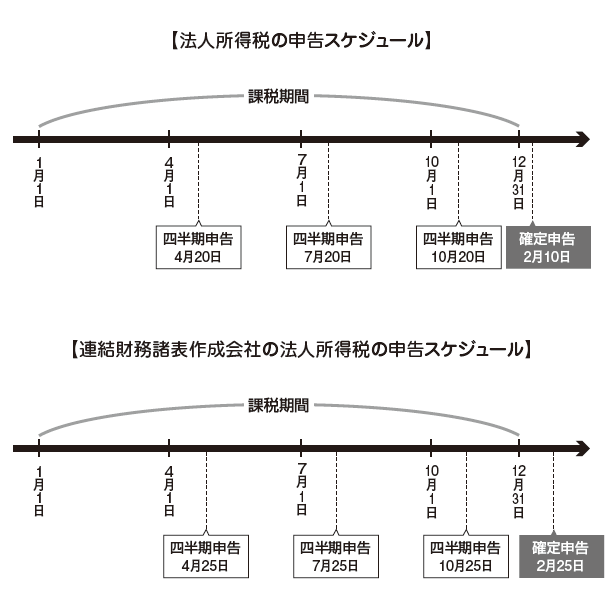
-
Disclosure contents
■ The composition of financial statements is stipulated in the Accounting Law and the Company Law.
Please see the description below..
The financial statements of companies that record accounting in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) consist of the following documents; (Accounting Act 8.1).
·Balance sheet
·Profit and loss statement
· Statement of changes in shareholders' equity
· Cash flow statement
· Supplementary schedule (contents of important transactions and conflicting interests carried out during the accounting period · amount, amount of officer compensation etc.)
Companies with one or more subsidiaries will prepare consolidated financial statements. In addition, if the parent company is a company registered overseas, it is necessary for the first parent company among subsidiaries to be registered in Mongolia for them to prepare intermediate consolidated financial statements (Accounting Act 8.3).
The financial statements consist of the following documents; (Article 96, Paragraph 1 of the Companies Act).
·Balance sheet
·Profit and loss statement
· Cash flow statement
· Statement of changes in shareholders' equity
· Notes table
· Supplementary schedule (contents of important transactions and conflicting interests carried out during the accounting period · amount, amount of officer compensation etc.)
In addition, the Board of Directors is required to submit a "Director's Report" on shareholders regarding annual activities, organizational structure, and important asset conditions.
Director's report should include the following content; (Article 96 (4)).
· Contents of the business that the company did, changes in important organizations and status of assets
· Amount of bonus paid to officers of the company
· Information requested by the Financial Regulatory Committee
· Other information established in the articles of incorporation
■ Creating and Approving Financial Statements
The business executor and accounting person of the company signs and stamps the financial statements and the executing officer is responsible for the accuracy of the financial statements (Accounting Act 8.4). In addition, we must undergo an audit by the accounting auditor (Article 96, paragraph 6 of the Companies Act). After that, it is necessary to submit the audited financial statements to the shareholders meeting and obtain approval by shareholders (Article 96, paragraph 5 of the Companies Act).
Partial abbreviation of financial statements of limited liability company
In the case of a limited liability company, it is possible to omit a part of the documents to be included in the financial statements by the articles of incorporation (Article 96, paragraph 2 of the Companies Act). However, the following documents must be created;
·Balance sheet
·Profit and loss statement
· Cash flow statement
· Statement of changes in shareholders' equity
· Notes table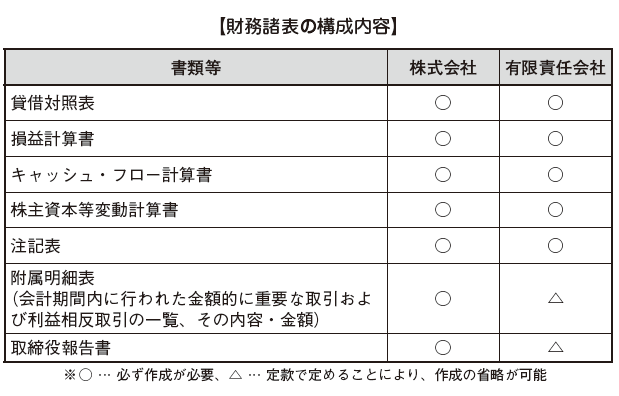
■ Information disclosure of listed companies
In the case of a company listed on the stock, the following information disclosure is required. In addition to disclosure of financial statements, it is also necessary to disclose the status of shareholders. (Securities Market Law Article 9 (6), Article 10 (1)).
· Submit an interim declaration and tax return prepared according to the accounting law to the Financial Regulatory Committee and the Stock Exchange
· The minutes of the General Meeting of Shareholders at the Annual General Meeting of Shareholders shall be submitted to the Financial Regulatory Committee within 20 days after the General Meeting by June 1st and the minutes of the Extraordinary General Meeting of Shareholders
· Publish summarized financial statements prepared pursuant to the provisions of the Financial Regulatory Committee
· When the sale of shares is done, submit a stock trading report including the following contents to the Financial Regulatory Committee within 30 days
- Start date of sale of shares and completion date of proceedings
- Number of shares sold and amount
- Gain / loss on sale of shares
- Name of the shareholder who purchased 5% or more of the stock
-
-
-
Audit system
In May 1997, the Auditing Act (Law of Mongolian Auditing) has been adopted and followed the law until 2016, but a new auditing law was enacted in June 2015 and it was decided to comply with 2016. Therefore, the auditing system puts the text of the audit law of 2016.
-
External audit system
■ Audit and its regulatory agencies
The state agency that supervises the audit is the financial regulatory committee. The financial regulatory committee grants auditing authority to an audit corporation or an auditor. Therefore, if the audit corporation violates the audit law, the financial regulatory committee may cancel authorization as an auditing corporation under its authority.
■ Companies to be audited
Companies and organizations that satisfy the following requirements must always undergo an audit (Article 10 para. 1 of the Audit Act). In addition, if the amount of investment from Japan establishes a subsidiary based on more than 25% of the total capital, it must be audited as it falls under a foreign-affiliated company;
· Companies that comply with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
· Companies that prepare consolidated financial statements
· When changing the form of the company and dissolving it
· Foreign companies
· Fund
· Companies that need auditing in other laws and contracts
The above companies need to be audited within the following period; (Article 10.2).
· Stock company is held two weeks before the general meeting of shareholders
· Companies that sell the form of the company, dissolution and all assets in auctions are notified 1 month ago
· Banks will file a final return by March 31 next year
· Other companies will declare the final return by April 30 next year
■ Requirements for auditing firms and accounting auditors
When conducting the auditing business, the auditing firm conducts the form of a limited liability company or partnership (Article 19.1 of the Audit Act). In addition, the audit project must acquire a license and must satisfy the following requirements;
· The founders and shareholders are Mongolian accountants
· Business executors and partners have an unlimited license for accountant's term
· Two or more full-time employees have an unlimited license for an accountant's term
· No violation of the auditor's professional ethics rules
· Be equipped with offices and facilities that conduct business
· If the promoters and shareholders are foreign companies, more than one-third of all accountants of the company are Mongolians
· If the promoters and shareholders are foreign companies, Mongolian accountants have more than one-third of all shares of the company
· Audit projects comply with international standards
· Requirements stipulated by other laws
Auditing firms that audit companies conducting accounting records in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) must have an unlimited license for an accountant for at least 4 auditors (Audit Act 19.4). Here, the term unlimited term of accountant is the license of the Mongolian Accountant exam. In the Mongolian School of Accountancy Exam if you take and pass the exam for the first time, you will be qualified for 4 years and if you pass the second exam, afterwards, you will be able to obtain unlimited period qualification (Accounting law 25.1).
In addition, the requirements to take an accountant exam are as follows; (Article 24.1 of the Accounting Act).
· Person who graduated from university in accounting department and has a working experience for more than 2 years accounting specialization
· Those who have graduated from university in finance, economics, management department, have acquired necessary accounting unit, and has a working experience for more than 4 years and have practical experience
An audit corporation that meets the following conditions cannot be appointed (Article 94, paragraph 13 of the Companies Act). In addition, audits by persons who fall under these disqualification reasons will be invalid (Article 94 (14)).
· Persons who have certain interests with the company
· Officers and employees of the company
· A person who holds shares in a company or who has a claim or obligation in a company
· Persons who have contracted with this company in addition to audit work
Also, please be aware that companies that comply with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) cannot request one audit firm to audit for more than five years. In order to ask the same company, it is necessary to free up a period of three years (Article 8.2 of the Audit Act). This regulation has nothing to do with SMEs and state-owned enterprises (Audit Act 8.3).
■ Appointment / dismissal of accounting auditor
In the General Meeting of Shareholders (in the case of a Company with Board of Directors, the Audit Committee) the audit committee needs to appoint an audit corporation and concludes an audit agreement (Article 94 paragraph 3 of the Companies Act). It is necessary to determine the rights, obligations and responsibilities of the Audit Corporation, and remuneration in this contract. In addition, the auditor may be dismissed by a resolution of the general shareholders' meeting (in the case of a company with a board of directors, the Audit Committee).
■ Legal audit and compensation
Legal audit is required for tax return of the company. Optional audits can be requested by the Board of Directors, the Audit Committee, or shareholders holding 10% or more of the common stock (Article 94.7 of the Companies Act). In the case of statutory audits, the company pays audit fees, but in the case of voluntary audits, shareholders who requested audits must pay. (Article 94, paragraph 8 of the Companies Act). In addition, it is forbidden to decide the amount of remuneration (performance fee) according to the result of the audit (Article 94 15).
A penalty concerning auditing
The following penalties are imposed on accounting auditors and auditing firms who violated laws and regulations; (Audit Act Article 22).
A warning
· License of audit service suspended for 3 months or infinite stop
· Deprivation of certified public accountant
·fine -
Internal audit system
Although the external audit has been established as an institution, the development of the internal audit system has been delayed, and since 2010 the necessity has been discussed. In December 2011, the government established internal audit provisions under the Budget Law, and internal government audits were obligated for all state-owned enterprises operating in Mongolia. In addition, it is necessary to establish an internal audit at the stock company, but for a limited liability company, it can be arbitrarily installed. When establishing an internal audit, it conforms to international auditing standards.
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya