Mongolia
5 Chapter Corporate Law
-
-
1 Chapter Basic knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.4 Investment regulation and incentives
3 Chapter Establishment
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.2 Establishment of business base
3.3 Liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter M&A
4.2 Laws and regulations concerning M & A
5 Chapter Corporate Law
5.1 Organization of the company
6 Chapter Accounting
7 Chapter Tax
7.2 Individual Issues of Domestic Tax Law
7.5 Tax survey and tax penalty
8 Chapter Labor
8.4 Foreign Employees in Mongolia
9 Chapter Q&A
-
-
-
Difference between Limited Liability Company and Corporation
The company law of Mongolia was first codified as a law in July 1999. Although a partial amendment was carried out thereafter, while investment from foreign countries increased little by little, revision was required to bring it closer to international standards, and in October 2011 the new company law was born.
Under the Corporate Law, two types of companies, limited liability company and corporation, are established (Article 3, paragraph 4 of the Companies Act). A limited liability company is a company form in which trading of shares is restricted by the company's articles of incorporation. On the other hand, a company is a form in which stocks are freely traded on the market. For foreign-affiliated companies entering Mongolia, it is common to choose a limited liability company.
■ limited liability company
The limited liability company is a company form in which the investor's liability is limited only to the contribution amount and the rights of the investor is restricted by the law and the articles of incorporation (Article 3, paragraph 5 of the Companies Act). Therefore, the risk of failing in the project is limited to the loss of the contribution amount, and we will not bear further responsibility.
Regarding institutional design, a wide range of articles of incorporation autonomy is allowed, and it is also possible to design similar to the company by prescribing in the articles of incorporation. For example, it is possible to set up a board of directors. Principal institution design consists of investors, business executors. In general, the establishment of the accounting auditor is optional, but in the case of a company that falls under the audited company such as a foreign-affiliated company, even a limited liability company will require an accounting auditor (if the investment amount from Japan is the total capital stock For overseas affiliates with over 25%, it is a foreign-affiliated company, accounting auditor is required).
■ Co., Ltd.
A corporation is classified into a public company (Open Public Company) and a private company (Closed Public Company) (Article 3, paragraph 6 of the Company Law). A public company is a company form that allows stocks to be registered at stock exchanges and to be traded freely on the market (Article 3, paragraph 7). On the other hand, a private company is a company form that registers shares on the stock exchanges, but only traded within the counter market (OTC: Over the Counter) (Article 3, paragraph 8).
The merits of the company are publicly available, and because we can publicly invite shareholders, it is advantageous in terms of financing.
For institutional design, Japan is required with the same institutional design as the company with the committee. In other words, it consists of shareholders, business executives, directors (auditors) and accounting auditors, and the board of directors must establish three committees of the audit committee, the nomination committee and the remuneration committee. It is necessary to appoint an outside director for more than two-thirds (2/3) of the total number of director’s because ownership and management are clearly separated at the stock company. The interests of the shareholders and directors may not necessarily match. The Mongolian Corporate Law emphasizes strengthening the monitoring system over limited liability companies in order to adjust the interests of both parties.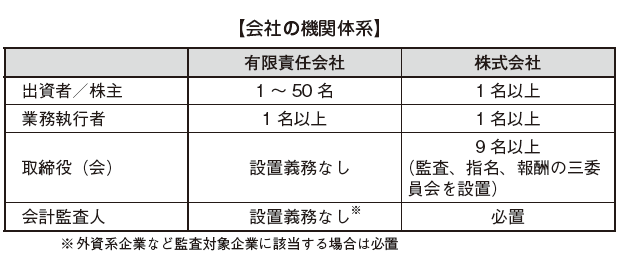
-
-
-
Investor
■ Number of investors
Under Mongolian company law, there is no regulation on the number of investors. As long as there are one or more investors, individuals and corporations are not questioned.
Meanwhile, the incorporators who carry out the establishment of a company have a maximum of 50 persons in the case of a limited liability company (Article 5, paragraph 1 of the Companies Act). There is no obligation to hold shares of the company after the establishment, as regards the incorporators as well as the requirements of individuals, corporations, nationality, residence, etc., but usually the founders will be the investors as they are.
When a company is founded by one initiator, the founders can decide to establish a company (Article 13 (2)). In the case of two or more founders, a contract can be established between the organizer, and the rights and obligations, the type of stock, the number, the purchase deadline etc. are specified (Article 13 paragraph 3).
General shareholders meeting
As with Japan, there are three kinds of shareholders general meetings such as ordinary general shareholders meeting, extraordinary general shareholders meeting, and organizational general meeting (Article 14 of the Company Law, Article 59 (3) of the Company Law). The provision concerning general shareholders' meeting applies to both limited liability company and corporation.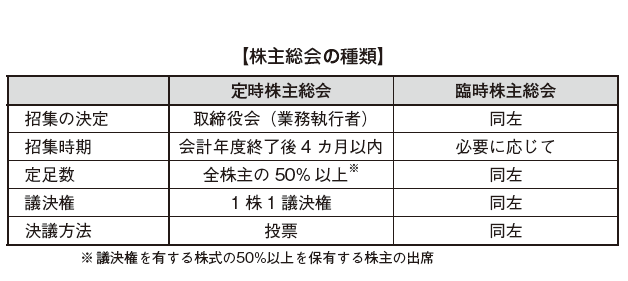
[Organization]
The sponsor must hold a general meeting before the establishment of the company. And must be register within 30 days. If there is no other provision in the agreement between the founder, the foundation shall require all attendees to attend and a resolution is made by a majority vote (Article 14, paragraph 4 of the Companies Act). The chairperson of the founding general meeting will be appointed from among the promoters (Article 14.5).
Matters to be resolved at the Organizational Meeting are as follows; (Article 14 (3)).
· Approval of company establishment
· Determine the content of the articles of incorporation
· Issuance of common stock and preferred stock and determination of its issue price
· When establishing a director, appointment of directors, remuneration etc.
· Establishment costs that the company should pay
· Payment deadline of contribution
In addition, in case of investing in kind in the spot, it is necessary to conduct evaluation by the evaluation organization as necessary and obtain approval at the foundation meeting concerning the evaluation value (Article 14 (6)).
[Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders]
An annual general meeting of shareholders should be held within four months after the end of the fiscal year by resolutions of the Board of Directors (executors if not established) (Article 59 (4) of the Companies Act). Also, within a period of 5 business days from the date of decision of holding the general meeting by the Board of Directors (business executor), we will report to shareholders through newspaper etc., and after 40 days from the date, we decided to hold the general meeting, the ordinary general shareholders meeting will be on hold. (Article 60 (3)).
[Extraordinary shareholders meeting]
An extraordinary general meeting of shareholders can be held voluntarily by convocating directors (Article 61 (1) of the Companies Act). Provided, however, that an extraordinary general meeting of shareholders shall be held if it falls under the following;
· When the number of directors making up the Board of Directors falls below the majority
· When two or more outside directors request holding
· Shareholder holding 10% or more of voting rights shares requests holding
· When loss becomes 30% or more of shareholders' equity
· If the liability exceeds shareholders' equity for the second consecutive year
· When a meeting is resolved at the Board of Directors meeting
· When the accounting auditor requests an event
· When matters stipulated in the articles of incorporation arise
Two or more outside directors or shareholders who hold 10% or more of the voting stock shares can request the extraordinary shareholders meeting (Article 61 (2)). In the case where the Board of Directors (business executor in the case where it is not established) decides to hold the general meeting within 10 business days after receiving the request (Article 61 (4)) and holds an extraordinary general meeting of shareholders at the request of shareholders, It must be held within 45 business days from the date the host request was made (Article 61 (9)).
■ Convener and the convocation notice
The Board of Directors (business executor if not set up) must notify all shareholders who hold voting rights of holding a general meeting of shareholders (Article 65 (1) of the Companies Act). In the case of a limited liability company, it is possible to specify the convocation notice method and the convocation time in the articles of incorporation (Article 65 (2)). If not stipulated in the Articles of Incorporation, it is necessary to notify the shareholders within five business days after resolution of the general meeting of shareholders (Article 60 (4)).
The following items are stated in the convocation notice of limited liability company; (Article 65 (4)).
·company name
·Street address
· Date and time, location
· Matters to be resolved at the shareholders meeting
· Issue date of the shareholders list attending the general meeting
· Other items stipulated in the articles of incorporation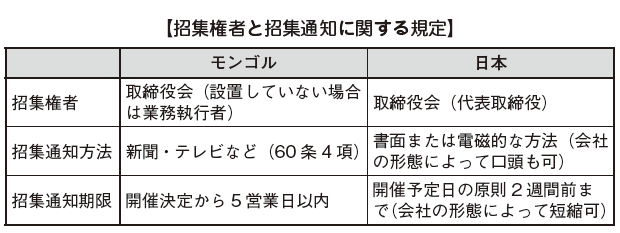
■ Resolution of general shareholders meeting
[quorum]
In principle, attendance of shareholders holding 50% or more of the voting shares is a quorum requirement (Article 69 paragraph 1 of the Companies Act). However, it is also possible to specify provisions in which the quorum exceeds 50% in the articles of incorporation (Article 69 (2)).
If it is less than the quorum, the general meeting of shareholders will be postponed and the postponement of shareholders' meeting must be held within 20 business days. Even if the general meeting of shareholders is postponed, resolutions will not be changed. In addition, it is necessary to notify the date, time and location by 7 business days prior to the scheduled shareholders' meeting scheduled date (Article 69 (6)).
Resolutions at the general meeting of postponement of shareholders will be effective upon the attendance of shareholders who hold 20% or more of the total shares, but the following will be resolved at the general meeting of postponement shareholders due to the attendance of shareholders holding one-third (1/3) or more of the total shares (Article 69 paragraph 5).
· Change and renew the company's articles of incorporation
· Company merger, division, etc.
· Issuance of shares, change of stock type
· Change of corporate form
· Company liquidation and liquidator appointment
· Stock split, consolidation
[Voting Right and Resolution Requirements]
Regarding voting rights, if there is no other provision, one share becomes one voting right (Article 63 paragraph 2 of the Companies Act). The resolution of the General Meeting of Shareholders is made by a majority of the voting rights of the attending shareholders (Article 63 paragraph 5), and the resolution requirements can be weighted according to the articles of incorporation (Article 63 (8)). The biggest feature is that there are no concepts like ordinary resolution or special resolution. In the case of important matters such as amendments to the Articles of Incorporation or mergers of the company, In principle, a resolution will be made with approval of a majority. Matters to be resolved at the general meeting of shareholders are stipulated as follows; (Article 62).
· Change and renew the articles of incorporation
· Company merger, division, etc.
· Issuance of shares, change of stock type
· Change of corporate form
· Company liquidation and liquidator appointment
· Stock split, consolidation
· Election and dismissal of officers of the Board of Directors
· Issuance of preferred stock
· Approval of financial statements
· Approval of important transactions
· Conflict of interest transactions
· Stock rebate
· If there is no other provision in the articles of incorporation, decide the remuneration of the directors
· Reports from the Board of Directors
· Matters to be resolved by resolution of other board of directors
· Other matters stipulated by the Companies Act and the Articles of Incorporation
In addition, in the case of a limited liability company that does not establish a board of directors, in addition to the above, the following matters can be resolved; (Article 62 (2)).
· Issuance of shares
· Determining the scope of the rights of directors
· Appointment of officers and directors, retirement
· Remuneration of Directors
· Election and dismissal of auditors
·Dividend
· Establishment of branch office and representative office
· Determining the market value of property and property rights (stocks and other securities)
■ Minutes of General Meeting of Shareholders
We will prepare minutes within 15 business days after the shareholders meeting is closed. At that time, the chairman's signature is required, and the chairman takes full responsibility for the minutes. In the minutes, the following items need to be stated; (Article 74, paragraph 2 of the Companies Act).
· Date and time, location
· Chairperson's name
· Resolution
· Number of voting rights, attendance rate
· Form of ballot forms (when ballot forms are used)
· Number of approvals for each resolution matter, opposite number -
Business executor
The Mongolian Company Law also imposes business executives (Executive Bodies) as in Japan, and one or more must be elected. Business executives will be appointed / dismissed by a resolution of the Board of Directors (or general meeting of shareholders if not established). You can concurrently hold a shareholder and a director, but you cannot concurrently serve as the chairman of the board of directors (Article 83, paragraph 4 of the Companies Act).
A business executor can perform business without a power of attorney on behalf of the company by negotiating, concluding a contract within the authority given by the company's articles of incorporation and the Board of Directors (if not established, general shareholders meeting) ( Article 83 (8)). In general, the business executor is an individual and is a company representative (Executive Director), but it can also be decided as an organization in the articles of association (Article 83 9). -
A director
Directors are the institutions established to conduct the business of the company (Article 75, paragraph 1 of the Companies Act), in the case of a limited liability company, there is no obligation to appoint if the articles of incorporation do not specify otherwise (Article 75 (2) Section). Therefore, it is common for ordinary companies to appoint only executives and not to have directors. -
Accounting auditor
Under the Corporate Law, for the limited liability company, there is no obligation to establish the accounting auditor. However, since all foreign-affiliated companies need to undergo a certified public accountant audit by an auditing method, whenever investment from Japan is made, it must be installed.
-
-
-
Shareholder
Number of shareholders
Under Mongolian corporate law, there is no regulation on the number of shareholders. Therefore, as with a limited liability company, it is only necessary for one or more shareholders. Meanwhile, more than one employee at the time of establishment of the company has become shareholders, and the requirements of corporation, individuals, nationality and residence place are not questionable.
General shareholders meeting
Most of the provisions concerning general shareholders' meeting are the same as limited liability company. However, there are differences regarding the notice of convocation of the shareholders meeting. Regarding the convocation of a stock company, it is determined by the rules of the Financial Regulatory Commission (Article 65, paragraph 3 of the Companies Act).
[Convocation Notice]
The notice of convocation shall give notice of the general meeting of shareholders to the Financial Regulatory Committee and the Mongolian Stock Exchange within three days from the day when the general meeting of shareholders is decided and notice of convocation to shareholders within five days (after the resolution) (Article 2, paragraph 6, 3.2 of rule). The notice of the general meeting of shareholders should state the following contents;
· Announcement of holding of shareholders meeting
· Copy when notifying shareholders through newspaper, website, etc.
· If there is a proposal proposed by shareholders holding 5% or more of the voting shares, its contents
· Documents concerning matters to be resolved at the shareholders meeting
Notice of convocation to shareholders requires at least two public notices. First is to notify the shareholders over two or more media, such as newspapers, radio, television and stock exchanges website, 30 days or more prior to the scheduled meeting date, and notify the shareholders 15 days after the notification. In addition to the above media, it is also possible to notify by telephone, facsimile, e-mail, etc. (rule 3, paragraph 5).
The convocation notice must include the following information; (rule 3, paragraph 7).
· Company name, registered address, date and time of holding, venue
· Shareholder list with voting rights
· Resolutions at the general meeting
· Resolved projects, regulations in resolution, location, opening hours
· Chairperson to implement general meeting · Telephone number, e-mail address, address, business hours of members (for corporations)
· Documents required by shareholders
As in Japan, Mongolia has established a record date to determine who is the shareholder with voting rights. This must be at least 45 days prior to the scheduled date of the general meeting of shareholders (Article 64 paragraph 2 of the Companies Act).
The General Meeting of Shareholders will not be able to resolve matters other than the agenda and after the date and time of the general meeting is decided, the schedule cannot be changed (Rule Article 2, paragraph 4). In holding the general meeting of shareholders, in the event that the quorum is not satisfied, prepare minutes and postpone the general meeting of shareholders. We will notify the notice of deferral shareholders meeting notice to the financial regulation committee within 4 days. The general meeting will be held within 20 days after the postponement resolution, but it is necessary to notify the location of the postponement shareholders meeting, the date and time, etc. 10 days before the meeting.
After the shareholders 'meeting is held, the company must submit resolution documents of the annual shareholders meeting to the financial regulatory committee before 1st June, and within 20 days after the extraordinary general meeting of shareholders' meeting is held (Rule 2, Article 10 Section). -
Board of Directors
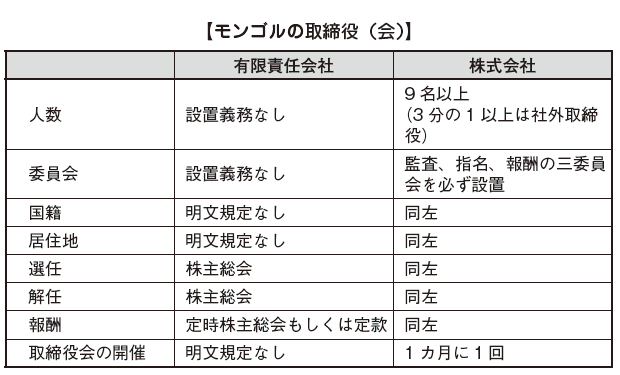
The company must appoint a director.
■ Number of Directors (Associations)
Regarding the number of directors, more than 9 people are required for the company, and more than one quarter must be an outside director (Article 75 (4) of the Companies Act). The number of directors shall be determined in the articles of incorporation (Article 75 (3)).
If you cannot appoint an outside director of a corporation at a general shareholders meeting, the director of the company cannot execute the authority (Article 75 (6)). In this case, the director will decide to hold an extraordinary general meeting of shareholders within five (5) business days after holding the general shareholders meeting, and will re-resolve the election of directors (Article 75, paragraph 7).
■ Requirements for Directors
As a requirement of the director, it is not possible to appoint a civil servant as a director. There is no stipulation clearly about nationality and residence.
■ Election / dismissal of directors
Directors are elected at the ordinary general meeting of shareholders pursuant to the Company Law or the rules of the articles of incorporation (Article 77, paragraph 1 of the Companies Act). If there is no other provision in the articles of incorporation, the term of office of the directors will be until the date of the next general meeting of shareholders, but re-appointment is also possible (Article 77 (2)). In addition, directors can be dismissed at the ordinary general meeting of shareholders or the extraordinary general meeting of shareholders (Article 77 (3)).
■ Representative
The representative will be appointed from among the directors by a resolution of a majority of the directors. If there is no other provision in the articles of incorporation, the representative will manage the operations of the directors, hold general meetings of shareholders and manage the minutes (Company Article 78, paragraph 2). Also, executives cannot concurrently serve as directors.
■ Obligation to set up external directors
In the case of a corporation and a state-owned enterprise, it is necessary for the number of directors to be nine (9) or more and one-third (1/3) or more to be an outside director (Article 75 paragraph 4 of the Companies Act). Outside directors must meet the following requirements; (Article 79 (1)).
· The shareholding ratio of the target company is 5% or less
· Not being an employee of the target company, or not working for the target company within 3 years
· Does not work for state enterprises
· Do not deal with the target company
· Other requirements established by other laws and the articles of incorporation of the company
■ Rights and responsibilities of directors
The rights and responsibilities of the directors are as follows; (Article 76, paragraph 1 of the Companies Act).
· Determining the company's business policy
· Ordinary shareholders meeting and Extraordinary general shareholders meeting
· Content of resolutions at general shareholders meeting, creation of shareholder list with voting rights
· Types of authorized shares of the company, Issuance of shares within authorized shares
· Evaluation of the market value of assets and property rights in accordance with Article 55 of the Company Law
· Purchase and redemption of shares
· Election and dismissal of executives and determination of scope of executive officers' rights
· Determination of contract terms, remuneration, bonuses, liability limits of Executive Officers
· Appointment of accounting auditor, determination of terms of contract
· If there is no other provision in the articles of incorporation, determine the amount of dividends, terms of payment
· Determination of regulations concerning business and corporate governance of directors and business executives
· Establishment of company branch and representative office
· If you decide to change the company form at the shareholders meeting,
· In accordance with Chapter 11 of the Company Law, approval on important transactions
· Acceptance of conflict of interest transactions in accordance with Chapter 12 of the Company Law
· Other matters stipulated by the Companies Act and the Articles of Incorporation
When resolving on the next agenda, an outside director must attend and must vote; (Article 76 (2)).
· Evaluation of the market value of assets and property rights in accordance with Article 55 of the Companies Act
· Appointment of accounting auditor, determination of terms of contract
· Approval concerning conflicting transactions in accordance with Chapter 12 of the Company Law -
Board of Directors
A corporation is obliged to establish a board of directors and must be held at least once a month (Article 80 paragraph 1 of the Companies Act).
The Board of Directors will be held at the request of the chairman of the Board of Directors, directors, executives and other persons specified by the articles of incorporation (Article 80 (3)).
The resolution of the Board of Directors requires attendance of more than a majority of the directors, one person and one vote number of majority vote. However, as with the Japanese Corporate Law, voting rights are not granted to directors who have special interests in resolutions. In addition, if the number of votes is the same, it is possible to set up a system that the chairperson has the right to cast an additional 1 vote in the articles of incorporation and the provisions of the Board of Directors.
If the number of board of directors falls below half of the number of persons to be set, the company will hold an extraordinary general meeting of shareholders for appointment of directors within three months (Article 80 (8)).
The minutes of the Board of Directors should include the following contents; (Article 80, paragraph 11).
· Date and time when the Board of Directors was held, place
· Attendees of the Board of Directors
· Resolution of the Board of Directors
· Resolutions decided by voting, result of voting
· Final resolution
Committee
In the case of a corporation, the Board of Directors must establish the Audit Committee, the Nomination Committee and the Compensation Committee. In addition to these three committees, it is possible to establish committees in specific fields, if necessary. More than two-thirds (2/3) of the members of each committee must be outside directors (Article 81 paragraph 2 of the Companies Act).
[Audit Committee]
The chairman of the Audit Committee (Audit Committee) must be an independent director (Independent Member of the Board of Directors).
The chairman of the Audit Committee must carry out the following matters and report it to the directors; (Article 81 paragraph 4 of the Companies Act).
· The company's accounting standards are monitored for compliance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), the work of the internal audit and risk management department, financial statements, financials • the accuracy of economic and other information
· Appointment of internal auditors, salary · Proposal for determining bonuses
· Selection of auditing corporation, Proposal on cost
· Monitor important company transactions, conflicting transactions
· Articles of association and other matters required by the Board of Directors
[Nominating Committee]
The authority of the Nominating Committee is as follows; (Article 81 paragraph 5 of the Companies Act).
· Establishment of criteria setting for criteria of executive officers and business executives of the company's board of directors and evaluation criteria for skills, knowledge and work experience
· Determining whether the outside director meets the requirements specified in Article 79, paragraph 1 of the Companies Act
· Register candidates for officers of the Board of Directors · Select and appoint candidate at shareholders meeting
· Business of the Board of Directors and Executives · Decision on Activities
· Create contract terms with business executor
· Judgment of evaluations by executives on activities of officers of other companies excluding Board of Directors
· If the authority of the Board of Directors is invalid due to not having held a general meeting of shareholders within four months after the end of the fiscal year, refusal to reappoint the reappointment of a person who was an officer of the board of directors for three years
[Remuneration Committee]
The Compensation Committee (Committee on Salary and Bonuses) must carry out the following matters and report it to the Board of Directors (Article 81 paragraph 6 of the Companies Act).
· Salaries of officers, business executives and other officers of the board of directors of the company • Approval and monitoring of bonus policies
· Salaries of the Board of Directors, executives and other officers · Set the upper limit of bonus · Create sentences to propose granting
· Bonus system for the results of operations applied in the company Determining the purpose of the system and evaluating the results
■ Secretary of the Board of Directors
If the chairperson of the Board of Directors is required, it is possible to appoint a secretary (Secretary of the Board of Directors) of the Board of Directors (Article 82 (1) of the Companies Act).
The obligation of the secretary of the Board of Directors is as follows; (Article 82 (2)).
· Book keeping, maintenance, management of shareholders meetings and documents of the Board of Directors, providing information to shareholders
· Preparation of general shareholders' meeting and board of directors, report of general meeting, plan concerning matters, preparation of other documents, management of sending
· Records of general meeting of shareholders and board of directors, approval of decision items, management of implementation
· Operation management between general shareholders meetings, board of directors and executives
· Management of internal activities of the Board of Directors
The director of the company and the secretary of the board of directors must receive a lecture on corporate governance and obtain a certificate (Article 75 (8)). This certificate can be obtained by receiving a lecture of a company recognized by the Mongolian Finance Regulatory Commission for 4 days and passing the examination. Because lecture can choose either Mongolian or English, certificate can be obtained even by foreigner. -
Business Executor
Business executor will execute the business of the company within the authority based on the articles of incorporation and the contract with the board of directors. If the executive is an individual, that person becomes the representative of the company (Article 83, paragraph 3 of the Companies Act). The executive officer may be a director of the company, but the chairperson of the board of directors cannot become a business executor (Article 83 (4)).
-
Accounting Auditor
Under the Corporate Law, it is mandatory to establish an accounting auditor for the Corporation (Article 94, paragraph 2 of the Companies Act). The requirements and appointment / dismissal of the accounting auditor are the same as those of a limited liability company.
Please note that since the provision on the accounting auditor of the corporation was changed to an audit corporation from Article 94 paragraph 2 of the Corporate Law, and it was decided to follow this from January 2016, it is necessary to be careful.
-
-
-
Type of stock
According to the Mongolian Company Law, issuance of two types of shares, common stock and preferred stock, is permitted (Article 32, paragraph 2 of the Companies Act). Although the company is obliged to issue ordinary shares without fail, it is possible to arbitrarily issue the preferred stock (Article 32 (3)). The par value of the shares is stipulated in the articles of incorporation, and all the same type of shares are the same face value (Article 32 (4)).The rights of shareholders holding common shares are as follows (Article 34 (1)).
· Attendance at shareholders meetings, right to participate in resolutions· Right to receive dividends· Right to receive distribution of residual assets -
Change of Capital
When changing capital through capital increase or capital reduction, it is necessary to change the articles of incorporation without fail (Article 31 paragraph 1 of the Companies Act). However, the provision will be invalid from January 2016. In order to change the articles of incorporation, a resolution of the shareholders meeting is required (Article 31 paragraph 2).
Also, if performance deteriorates and capital (Total Equity) in the accounts statement falls below the capital (Charter Capital), the Board of Directors (business executor if not established) must meet the general meeting of shareholders within 10 business days after the reporting of the settlement It is necessary to convoke and resolve about capital increase or dissolution, etc. (Article 31 paragraph 3). When the above problem arises, the business executor must report to the creditors of the company within 30 days after the resolution (Article 31 (4)). -
Dividend
If there is no other provision in the articles of incorporation, the dividend will be decided by resolution of the Board of Directors (if not established, shareholders meeting) (dividends: Article 46 paragraph 1 of the Companies Act).
Directors need to decide on dividends within 50 days after the end of the fiscal year (Article 46 (5)). Directors must always report on dividends at the ordinary general meeting of shareholders. Even if we resolve not to pay dividends, we must announce the resolution at the ordinary general meeting of shareholders (Article 46 (6)). It is also possible to distribute not only cash but also physical distribution of assets, securities etc. (Article 46 (7)).
Dividends can be distributed only from the company's after-tax net profit (Article 46 (8)). In the event that the net asset value decreases by more than 25% as a result of payment of dividends, the company must report the net asset value to all shareholders in writing within 15 business days from the date of dividend payment in writing (Article 47 (4)).
-
-
-
Reference
・Company Law(Revised),2011
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya