Indonesia
5 Chapter M&A
-
-
1 Chapter Basic knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.2 Investment regulation and incentives
3 Chapter Economic Environment
3.2 Economy Aiming for Innovation
3.3 Issues of Indonesian Economy
4 Chapter Establishment
4.1 Characteristics and tendency how to set up the legal entity in Indonensia
5 Chapter M&A
5.1 Trends in M & A in Indonesia
5.2 Laws and Regulations Concerning M & A
6 Chapter Coporate Law
7 Chapter Accounting
8 Chapter Tax
9 Chapter Labor Law
9.1 labor law and related rule article
10 Chapter Q&A
-
-
-
Trends in M & A in Indonesia
Indonesia gains its independent from the Dutch colony in 1950. After being independent, the government was developed by nationalization of major industries. In the 1990s, Indonesia has grown and grown strategically centering on the manufacturing industry. However, as a result of inter-company adhesion and family relation of government officials, family business became a social problem, and together with the Asian currency crisis that occurred at the same time , the administration of President Soeharto closed.Later, due to the privatization of state-owned enterprises and the economic policy undertaken under the Yudoyono administration that was established in 2004, personal consumption has grown steadily. The economic growth rate of Indonesia reached 6.2% as of 2012, and the country kept its high level within the standards in Southeast Asia. In recent years, its market value has been recognized and the number of companies developing business in Indonesia is increasing.
The following graph shows the trends in the number of M & A transactions from M & A conducted in Indonesia between 1990 and 2013.
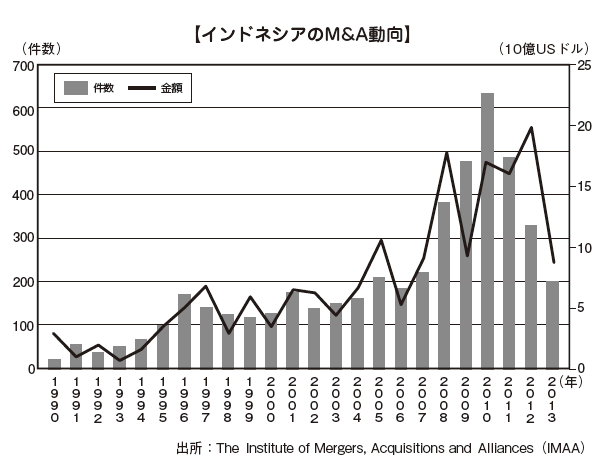
M & A until 2010 is increasing both in number and amount.
Although the number of cases is on a downward trend from 2010 to 2012, it is clear that the amount of money is increasing and that the investment amount per case is large.
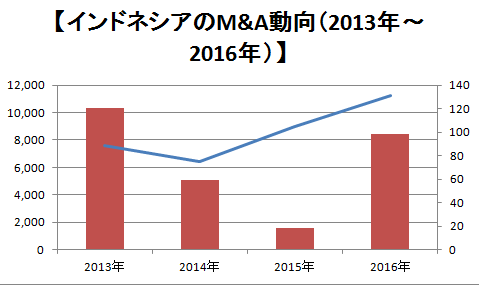
出所:DUFF PHELPS
■ M & A cases of Japanese companies
There are 198 cases of acquisitions of Asian companies by Japanese companies (In-Out) in 2011, 189 in 2012, 202 in 2013, of which 21, 22, and 17 M & A to Indonesia (RECOF examination) respectively. The following table shows examples of M & A from Japan to Indonesia that took place in 2013 and 2015.
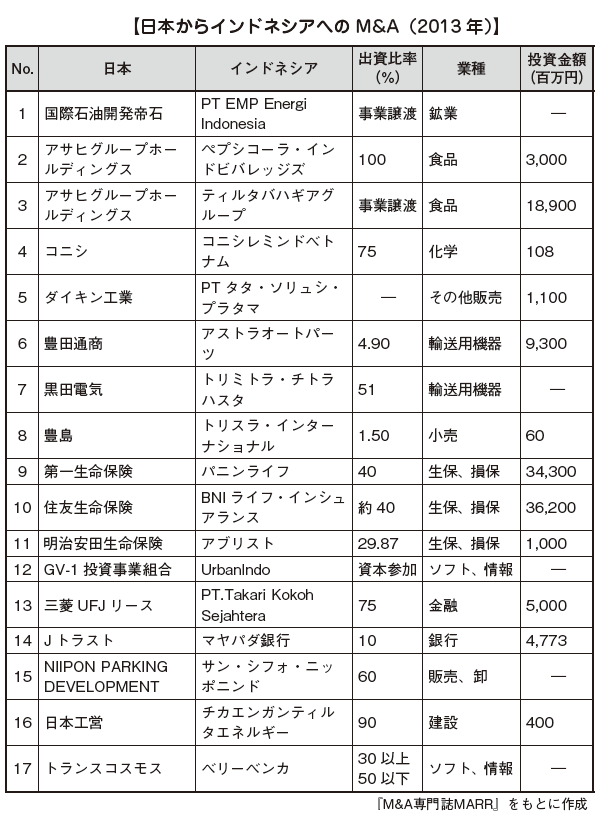
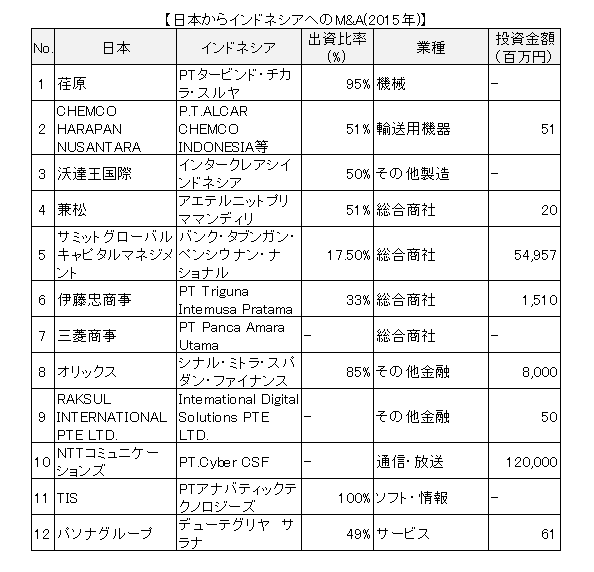 出所:「M&A専門誌MARR」を基に作成
出所:「M&A専門誌MARR」を基に作成 -
Latest News & Updates
【About the revision of the Anti-rust Law in June 2016】
On July 19th, a newspaper expressed the view that there was a suspicion of price agreement between PT. Yamaha Indonesia Motor Manufacturing and PT. Astra Honda Motors by KPPU (Indonesian Fair Trade Commission).
Thus, in Indonesia, the regulation by KPPU has been increasingly strengthened in recent years, and it is no longer necessary to pay attention to the trends not only for large companies but also for small and medium-sized enterprises.
In addition, the Antimonopoly Law was revised in June 2016, and a number of measures introduced in developed countries have also been introduced in Indonesia.
I will outline the trend of Anti-trust Law policy in recent years by example and discuss the Leniency program which is one of the major revised policy.
In Indonesia, strengthening of Anti-trust policy by KPPU has been prioritized more and more in recent years. In particular, price agreements, monopolies and oligopolies are subject to strict seizure.
However, although violating companies were caught by KPPU in seeing the trend by 2010, it is said that it is actually two-thirds that were dismissed by the Supreme Court. However, in order to avoid image deterioration, it is important to know exactly what specific kind of cases were caught.
For example, for conducting M & A that exceeds certain asset amount, notification obligation is imposed within 30 days. On December 11, 2012, PT. Mitra Pinasthika Mustika was fined 4.6 billion rupiah by KPPU on negotiating the notice obligation after the share acquisition.
The Leniency program is a measure that allows a company conducting banned price agreement to take advantage of the penalty's circumstances by voluntarily offering the payment. This system has already been introduced in Japan in 2005. Although it has been discussed for many years in Indonesia, it was finally introduced in June 2016.
However, there are no precedent cases in Indonesia as it has not been introduced. Thus, it can be said that attention is needed to be focused in the future.
-
-
-
Status of Legal Improvement Concerning M & A
Activities and capital market of public companies including M & A activities are regulated and supervised by the Financial Services Authority (OJK: Otoritas Jasa Keuangan), a government agency that constitutes the Ministry of Finance in Indonesia. The laws related to M & A include the following:

Under the Corporate Law there are provisions on general M & A, but OJK Rule and the Capital Market Law take precedence over the Company Law. The company law also applies to issues concerning M & A that are not stipulated in OJK Rule and Capital Market Law.
■ Authorization from Investment Adjustment Agency
The Investment Adjustment Agency (BKPM: Badan Koordinasi Penanaman Modal) is a government agency focusing on investments in Indonesia. Holding foreign shares is under the approval of the Investment Adjustment Agency. In other words, in acquiring companies in Indonesia, if the target company is a foreign company (PMA: Penanaman Modal Asing), for a foreign stockholders to hold majority or control of shares , approval from the Investment Adjustment Agency is required.
-
Investment Regulation
In investing in Indonesia, it is necessary to investigate first whether investment is possible or not and the possible amount of investment needed.
With regard to the contribution amount, capital regulation and investment amount regulation, which had been the window regulation in the past, have been clarified by the Director General of Investment Adjustment Agency No. 5 of 2013 (effective May 27, 2013).
Under the same ordinance, the minimum investment amount is stipulated. It is necessary to set investment amount and capital amount of foreign currency (US dollar) corresponding to the amount of local currency required.
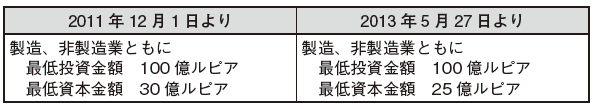
Especially in the case of service business including trading companies, the investment amount of 10 billion rupiah is not realistic. Regarding the investment amount, it is necessary to report the procurement progress to the Investment Adjustment Agency once every half year. However, there will be no penalty due if the investment amount could not be procured and as a result investment was not realized. Regarding the capital amount, in principle, full payment and its certificate are necessary for company registration procedure.
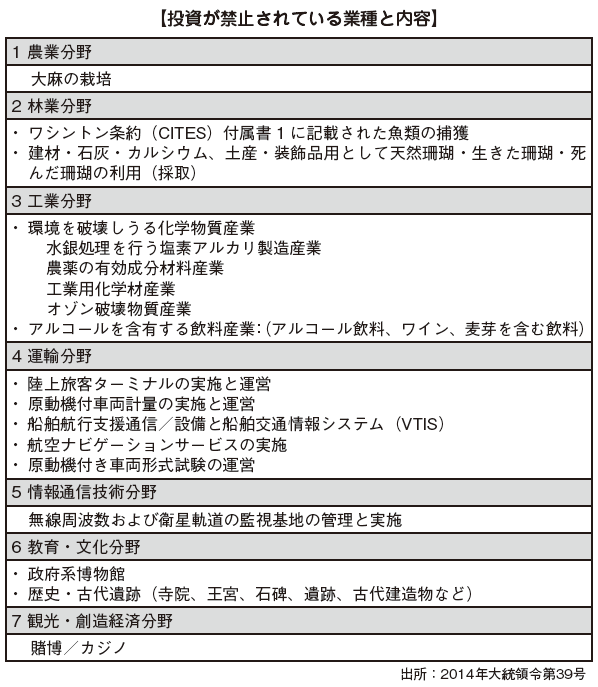
In the case of considering entering Indonesia in a specific business format other than the manufacturing and trading company, there are some prohibited fields for foreign investment, regulation field (negative list type regulation), so we need to confirm its contents.
-
Negative List Revision
On April 24, 2014, Presidential Decree No. 39 (Negative List) 2014, prescribing the foreign investment regulation that was discussed from the previous year was enforced. This regulation will be concentrated in the direction of protection of domestic industry (reinforcement of investment restrictions) and development of special industries such as electric power field (relaxation of investment deregulation) on the premise of forming the ASEAN economic community. This clarified the areas where foreign investment is prohibited and the areas where partial investment will be opened.
As one of easing investment deregulation, up to 51% investment in advertising companies has been approved (only through subsidiaries in ASEAN) to be entered by foreign investors.
Also the wholesale industry was noticed as the biggest issue. In the former negative list, wholesale trade had no particular arrangement, and in principle it was possible to enter 100% foreign capital contribution. However, in revising this time, Mr. Frankie, Secretary General of the Indonesian Management Association (APINDO), told local newspaper that "Since the wholesale business field does not require special skills and large capital amount, I have been trying to encourage them to sets up barriers for the entry of foreign capital . " Since then, the Director of the Mahendra Investment Adjustment Agency said that so far the foreign capital ratio in the distribution (including wholesale business) area will be reduced from 100% to 33%. It is related to strengthen the concern of spreading foreign capital control on wholesale business among people (coverage on December 24, 2013).
However, the Investment Adjustment Agency responded to the fact that importation and exportation and sales through agents are basically no problem even after the revision of the regulation. So investment on the trading company where import / export is substantially the main business style remains unchanged as before. Moreover, the advancement rate of 100% is possible.
■ Regulated industry
Businesses that are conditionally permitted to be invest on are subject to detailed regulatory requirements, such as when the capital contribution ratio of foreign capital is restricted or where special permission is required. Representative ones are listed below, but it is important to check the original contents in detail and decide what kind of restrictions can be invest.

Also, at the Presidential Decree No. 2016 dated May 12, 2016, the Government of Indonesia announced the details of the revised "Business Areas Conditionally Opened". This has came into effect on 18th of May.
Through easing of foreign capital deregulation, the Government of Indonesia aims to accelerate economic growth by attracting foreign investment. Industries with high interest in Japanese affiliated companies are included, such as up to 100% opening for foreign capital investors in the food service industry and raising the cap on foreign capital contribution ratio in trading companies and wholesale business. We will introduce the major foreign investment restraint relaxed industries announced this time.
① Industry relaxing industry
業種
旧外資出資比率上限
新外資出資比率上限
備考
映画
—
100%
電子商業
—
100%
・ 上限100%:現地中小企業との協力を条件
・ 投資額1000億ルピアであれば上限比率49%(電子システムを介した取引)
高速道路
95%
100%
スポーツセンター
49%
100%
病院経営コンサルティング
67%
100%
病院、クリニック67%
倉庫
33%
67%
市場調査
-
70%
通信網事業
65%
67%
ホテル
51%
67%
無害ゴミの処理
95%
100%
医薬品原料産業
85%
100%
既成薬製造業85%
デパート業(400m2-2000m2)
-
67%
私立博物館
51%
67%
陸上旅客輸送
-
49%
レストラン、カフェ
51%
100%
カラオケ、ボーリング場
49%
67%
仕出し業
51%
67%
販売代理店(特定地域)
33%
67%
建設コンサルティング
55%
67%
再生ゴム
-
100%
工業長官の特別許可が必要
冷凍倉庫業
33%
100%
高圧電力設備の設置
49%
② Industry with Strong Regulation
In the construction industry, the investment ratio of foreign capital remains unchanged at 67%, but the minimum construction cost has been raised from 1 billion Rupiah to 50 billion Rupiah.
■ Utilize nominee
In Indonesia, a negative list exists as foreign investment regulation. Therefore, no matter how Indonesia sets an attractive market, by this foreign capital regulation it may be impossible to establish or acquire a foreign company. To avoid this situation, a technique called nominee was established.
For example, in areas where the foreign capital contribution ratio is regulated to be less than 40%, Japanese companies contribute up to 40% and the remaining 11% capital contribution necessary to reach 51% is invested by local companies whose a so-called friend of the investing Japanese companies.. It is virtually a way to acquire the management rights of the investee company.
However, it is necessary to develop a legal agreement concerning the transfer of management rights. Please pay attention to actual utilization of the nominee, since there is no doubt of the possibility of being denied of substantial management rights in the case of a legal conflict or being subject to penalties as it actually circumvents foreign investment regulation..
■ Regulations concerning capital
In Article 32 of Indonesia Company Law (Law No. 40 of 2007), the minimum authorized capital is set at Rp. 50 million. However, attention should be paid because the Investment Adjustment Agency may require additional capital in practice in order to determine the investment amount and capital from the contents of the investment project.
■ Regulations on the Use of Land of Foreign Companies
In Indonesia, foreigners and foreign companies are forbidden to possess land. Foreign companies are only permitted to use the land according to law. Permission to use this land can only be exercised restrictly on the surface of the land, not including the use of natural resources such as the air and underground. The rights to use of land obtainable by foreign companies are classified into development rights, construction rights, and usage rights due to differences in their uses.
Even in Indonesia, there is a real estate registry system just like in Japan, and the above three rights are issued right from the time of registration at the Indonesian National Land Bureau. If you acquire land use rights, 5% of the acquisition amount is imposed as real estate acquisition tax.
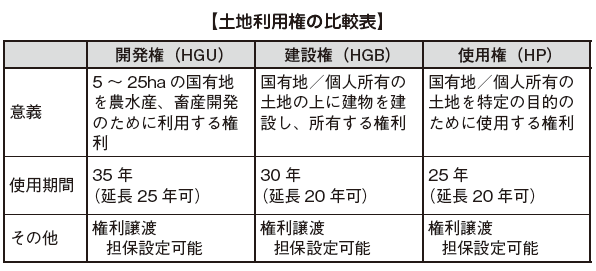 In the case of building a factory in Indonesia, in addition to the construction right (HGB: Hak Guna Bangunan) the investor needs to ontain the site permission (IL: Izin Lokasi) from the land office and the building permission (IMB: Izin Mendiri kan Bangunan) from the Public Works Bureau.
In the case of building a factory in Indonesia, in addition to the construction right (HGB: Hak Guna Bangunan) the investor needs to ontain the site permission (IL: Izin Lokasi) from the land office and the building permission (IMB: Izin Mendiri kan Bangunan) from the Public Works Bureau. -
Public Company Purchase Regulation
■ Optional Tender Offer
Acquisition of the shares of the public company can be done by the method of voluntary public tender offer (VTO).
Optional Tender Offer is the method prescribed by Rule 9, Paragraph 1 (OJK Rule No. IX.F.1) on voluntary tender offer.
An arbitrary tender offer can be exchanged with another securities to acquire shares through mass media. (or securities that can be exchanged for other stocks or securities with stock acquisition rights) to individuals, companies, organizations or groups. It is to bid by purchase. Mass media refers to newspapers, magazines, images, television, radio, other electronic media, documents, booklets, printed matter published to more than 100 people. VTO transactions are carried out both within the stock exchanges and outside the exchange. The obligation owed for mandatory tender offer as described below (see page 339) is not subject to a voluntary public tender offer.
[Disclosure obligation]
Businesses who desire voluntary tender offer will submit the following declaration to OJK.
· Stocks listed on stock exchanges
· Target company
· If it is also valid during the offer period, other companies that have submitted a voluntary public offer for the same shares issued by the same target company
On the same day as a voluntary tender offer statement was submitted to OJK, this information will be published in Indonesian language newspapers (circulated all over the country) for at least two days.
An arbitrary tender offer statement is valid if the following requirements are satisfied.
· 15 days from the date on which OJK accepted the tender offer representation, or 15 days after the date of the final change made by the OJK request or the creation of a voluntary tender offer representation by the business operator and submitted Case
· When OJK does not request change or additional information
[Prohibited matter]
Any party applying for a voluntary tender offer is forbidden to buy and sell between 15 days after the announcement of the VTO and the expiration date.
The parties to the voluntary tender offer application will not be subject to other regulations or requirements depending on the type and position of the shares to be acquired (unless there is a discrepancy in the interests or rights of the stock). The target company must not act to prevent the change of the controlling right which is the validity of the voluntary tender offer from the day when the tender offer is announced to the expiration of the optional tender offer effective period.
[Timetable]
The effective period of the Optional Tender Offer will commence within two business days from the date of execution of the voluntary public announcement. The validity period is at least 30 days, and if approved by OJK it can be extended up to 90 days.
The Optional Tender Offer Period is extended for at least 15 days and will be announced for at least two days in the Indonesian newspaper circulated nationwide.
The voluntary tender offer transaction (VTO Transaction) must be completed within twelve days from the expiration of the Optional Tender Offer Effectiveness Period by payment of lump sum or delivery of securities.
As long as there are no special conditions, in the case that the voluntary tender offer is canceled, the securities (Offered Securities) must be returned within 12 days from the expiration of the Optional Tender Offer Effective Period.
[Preparation Fund]
For voluntary tender offer, preparation fund is required. Among the information disclosed in the voluntary tender offer statement are a statement that "companies that conduct voluntary tender offers have enough funds to conclude transactions", along with opinions of accountants, banks and securities companies included. OJK RuleIX.H.1, stipulating mandatory tender offer as described below does not have the above-mentioned provision.
■ Mandatory tender offer system
Mandatory tender offer is a system to secure appropriate disclosure of information and securing equal equitable selling opportunity among shareholders when acquiring a company. Also, it is an obligatory system that have the same purpose as above when a change occurs in the control of a public company. When a mandatory tender offer is applied, OJK Rule IX.F.1 which regulates a voluntary tender offer shall not apply, as it must comply with the framework defined by OJK Rule IX.H.1.
Control by a public company is defined as "if you own 50% or more of the company's stock or you can directly or indirectly determine the management and policy of the company in any way".
However, in the following cases, we will not be obliged to make a tender offer.
· When the shareholder and the new controller acquire shares
· Shares owned by the third party and receiving offers under the same terms from new contollers
· A third party owns shares and simultaneously makes mandatory public tender offers and public tender offers for shares of the company
· Shareholdings owned by major shareholders (more than 20% directly and indirectly)
· Shares owned by other controller
[Overview]
Shareholders who have newly acquired control must publish the following information within two days after the acquisition of control and notify the capital market / financial institution supervising agency about the following matters.
· Number of shares acquired and number of shares held
· Information of the Purchaser (name, address, telephone number, business contents, etc.)
· Purpose after acquisition of control
In principle, the acquirer must also make a tender offer in order to acquire shares that have not yet been acquired.
As a result of the tender offer, if the controlling shareholder acquires 80% or more of the stated capital of the public company, it is obliged to return at least 20% to the market, and within 2 years after the end of the tender offer the shares must be held by a minimum of 300 shareholders.
■ Information Disclosure
In OJK Rule I X.H.1 which regulates the mandatory tender offer, the acquirer is permitting the seller shareholder information related to the acquisition and the confidential information to be released during the negotiation.
If the acquirer chooses disclosure, it will be published in Indonesian newspaper for at least one day and will be submitted to the stock exchange where the target company or target companies are listed. After that, the acquirer must fulfill the obligation to disclose the progress including extension and termination of acquisition within 2 days from the execution.
Information that is obligated to disclose is as follows:
· Amount of shares to be acquired
· Personal information of the acquirer (name, address, telephone number, business type, purpose of acquisition)
· Amount of securities already acquired by acquirer (if any)
· Plan for achieving the purpose of acquisition
· Method and process of negotiation
· Contents of negotiation
However, if the acquirer chooses not to disclose, the information confidentiality of all negotiations will be maintained until the transaction is completed.
After completing acquisition, the offeror have the obligation to disclose the following information.
· Amount of shares acquired, tenure of shares
· Personal information of the parties (name, address, phone number, business type, purpose of acquisition)
· A statement that the acquirer is an organization (only when applicable)
-
Company Law
■ Classification of M & A
M & A in Indonesia is classified into five main types: mergers, absorption mergers, direct acquisitions, indirect acquisitions and divestitures. However, since the merger cannot be used unless it is a domestic corporation in Indonesia, the method used by foreign companies including Japan is mainly acquisition.
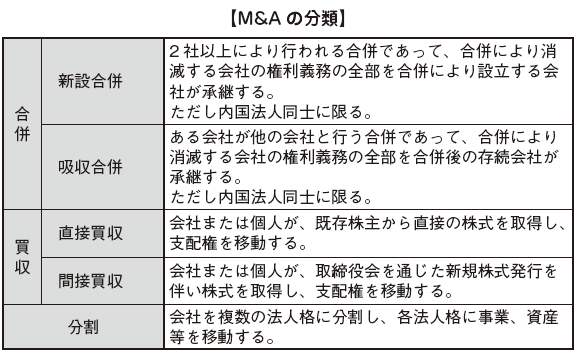
Legal provisions on M & A are stated in Chapter 8 of the Companies Act. In this section, we will explain only matters that we should pay attention to when making M & A.
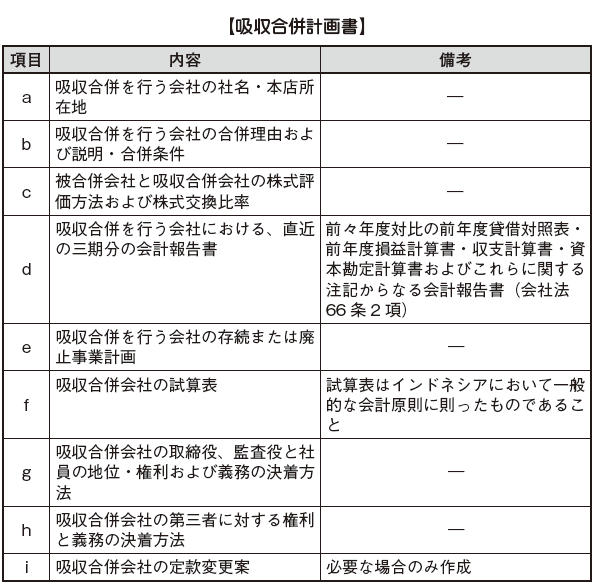
■ Preparation of Absorption-type Merger Plan
The Board of Directors of the Absorbed Merger Company and the Absorbing Company in an Absorption - Type Merger shall prepare an Absorbing Joint Venture Plan. Matters listed in the following table shall be included in the absorption-type merger plan.
After preparing the absorption merger plan, proposal will be made to the general meeting of shareholders after approval of the Board of Corporate Auditors. The point to keep in mind here is that a specific company needs to obtain approval from the relevant government agencies in advance in accordance with the Cabinet Order in addition to the matters of this law.
"Specific company" refers to the financial industry such as banks and other financial companies.
In addition, these provisions are also effective for public companies if there is no provision in capital market related laws and regulations. It is unnecessary to consider the share exchange ratio to be stated in the Absorption Joint Venture Plan. Like general M & A in Japan, stock prices are judged by market value.
Acquisition by Shares Acquisition
In shares acquisitions, we will acquire outstanding shares and plans to be issued directly from the Board of Directors or shareholders. At that time, it will be based on the resolution of the general meeting of shareholders meeting quorum and resolution method prescribed in Article 89 of the Companies Act. The resolution scheme at the shareholders meeting is as follows.

In addition, when acquiring through the board of directors, the acquiring party is required to submit the purpose of acquiring shares to the board of directors of the acquirer and to prepare an acquisition plan. The items described in the acquisition plan are as follows.
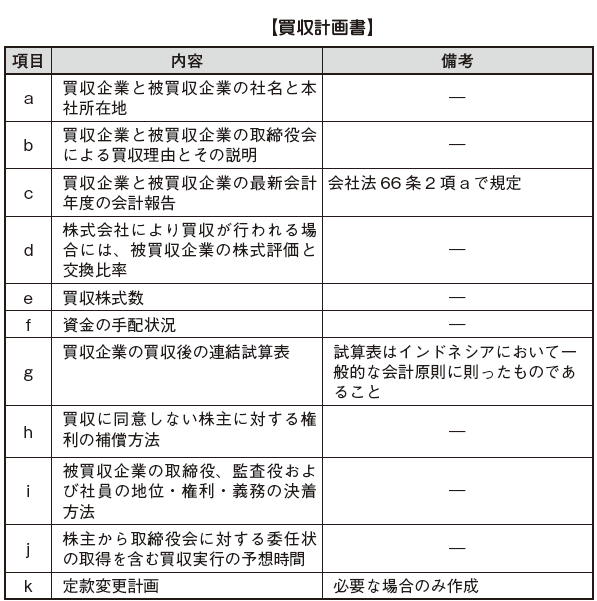
On the contrary, when acquiring shares directly from shareholders, it is not necessary to prepare an acquisition plan. However, attention must be paid to the stock transfer rules prescribed in the articles of incorporation of the acquired company and the contracts the company has made with third parties.
■ Advance notice of shareholders meeting resolution
In conducting mergers and acquisitions as described above, the Board of Directors must make prior notice of the resolution of the general meeting of shareholders. This is to give opportunities for opposition to concerned parties who feel that their profits are damaged. The details and deadlines of various advance notifications are shown below.
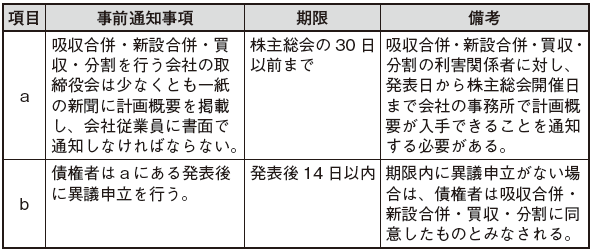 If there is an objection from the creditor and cannot be resolved, the Board of Directors is obliged to report the opposition so that it can be resolved at the shareholders meeting. Also, it is forbidden to conduct mergers, acquisitions, or divesting acts until the opposition is resolved.
If there is an objection from the creditor and cannot be resolved, the Board of Directors is obliged to report the opposition so that it can be resolved at the shareholders meeting. Also, it is forbidden to conduct mergers, acquisitions, or divesting acts until the opposition is resolved. -
Business Transfer
In addition to the methods of acquiring business mentioned above, business transfer may be adopted. Basically, the business transfer scheme is the same as the company law in Japan in terms of contracts for sale and purchase of assets etc. to counterparties. However, there is no provision in the article under Indonesian corporate law. Therefore, I will describe the points of business transfer in Indonesia below.
○ For the transfer of assets exceeding 50%, special resolution of the general meeting of shareholders is necessary.
○ Shareholders who cannot agree on business transfer can request buying at reasonable price.
○ It is necessary to transfer assets, obligations, contracts, employment relationship one by one individually.
○ Transfer of rights relating to real estate needs to be transferred and registered based on assignment certificate (Deed).
○ For the assignment of contract relationship, consent of all parties to the contract is necessary.
○ It is not allowed to force an employee to transfer to a transfer company, and it is necessary to pay a retirement allowance for an employee who will undergo a normal dismissal such as contribution fee (cf. If it is self-convened retirement, payment is unnecessary).
■ Shareholder rights
Shareholders' rights concerning M & A is stipulated in Article 126 of the Companies Act. According to the said Article, if we do not agree with the shareholders' general meeting resolution concerning the Consolidation - type Merger, Absorption - type Merger, Direct Acquisition, Indirect Acquisition, Split (Shareholders cannot agree with the resolution if an specific action taken will a damages the shareholders or the Company itself), shareholders can exercise their rights.
The acts that give damages here are as follows.
· Change of articles of incorporation
· Transfer of assets worth 50% or more of the company's net assets or security deposits
· Consolidation-type merger, absorption-type merger, direct acquisition, indirect acquisition, division
If the actions of the company fall under the above items, shareholders can have the company repurchase the shares at a reasonable price. Provided, however, that this exercise of rights shall not preclude the processes of consolidation merger, absorption merger, direct acquisition, indirect acquisition and division.
■ Application to the authorities
The new consolidation merger, absorption merger, acquisition or division approved at the general shareholders' meeting was prepared as a notarial deed in Indonesian language and a copy thereof must be notified to the Minister of Law and Human Rights. If these restructuring involves elements of foreign investment, further approval by the Investment Adjustment Agency is required.
-
Competition Law
■ Prohibited items in M & A
The following actions are prohibited items related to M & A.
Concurrent Posts
The same person belongs to several companies with competitive relationship etc. (Competition Law Article 26).
Stock Ownership
The business owning majority of the shares of the competitor brings the market structure corresponding to the market dominant position (Article 27).
Merger etc.
Mergers or affiliations with other companies, or acquiring shares of other companies, will result in monopolistic acts or unfair business competition (Article 28).
With regard to mergers, etc., if the total assets amount exceeds Rp.2.5 trillion Rupiah or the total sales amount exceeds 5 trillion rupiah (total assets amount of 20 trillion rupiah for banking industry), within 30 business days from the effective date of the merger, we must notify the Competition Monitoring Committee (KPPU, hereinafter the Committee). Businesses can consult with the committee in advance about the plan of merger etc. (Article 29 and Decree No. 57 of 2010). The company must report all acquisitions that will cause monopoly and inequality competition to the committee (Mergers and acquisitions of legitimate companies and monopolies and inequality competition shown in Decree No. 57 of 2010 Acquisition of corporate stock to cause).
In Cabinet Order No. 57 of 2010 it is stipulated that any merger, integration, or acquisition that outweighs asset value or certain sales must be reported to the committee within thirty days when it occurred. This is to prohibit private and corporate monopolies and inequality competition.
Regarding whether mergers, consolidations and acquisitions will lead to monopoly or inequality competition, you have the right to evaluate the transaction (Article 3, Paragraph 1 of the Business Competition Monitoring Committee, Cabinet Order No. 57 of 2010).
According to Article 9, Paragraph 4 of the Cabinet Order, if the Committee suspects of monopoly and inequality competition, after receiving a letter of notice, the Committee will stop mergers, consolidations, acquisitions and the companies will pay damages or fines (25 billion to 100 billion Rupiah) and even an imprisonment (up to six months).
■ Consultation before the acquisition to the business competition monitoring committee
It is possible to consult the committee before the transaction, but there is no exemption from the duty of the notice.
When a company thinking of mergers, consolidations, or acquisitions consults the committee, guidance and advice will be given in writing. However, not every company can consult with the committee. Companies that are considering mergers, consolidations, or acquisitions can request consultation either orally or in writing only when the business assets or sales exceed the limit.
The committee will evaluate based on the submitted document. They will give guidance and advice in writing within 90 business days after receiving all documents concerning mergers and acquisitions. According to Cabinet Order No. 57, Article 11, Paragraph 4, 2010 Rule 7, the Committee's evaluation will not affect the approval and dismissal of the merger, integration and acquisition plan document. In addition, it does not impede the authority of the committee's evaluation to conduct after the transaction is completed.
The written assessment is a view of monopolistic practices or cases where there is an indication that inequality competition will occur. Corporate groups who consulted the committee are not affected by the evaluation, so you can continue to the plan regardless of the evaluation. However, at the next stage, the transaction can be terminated when it is determined that the committee is a merger, integration or acquisition likely to cause monopoly or inequality competition.
-
Latest News & Updates
* About deregulation of foreign capital investment
At the Presidential Decree No. 2016 of May 12, 2016, the Government of Indonesia announced the details of the "Released Business Areas with Conditions" list, and came into force on May 18th.
Through easing of foreign capital deregulation, the Government of Indonesia aims to accelerate economic growth by attracting foreign investment. Industries with high interest in Japanese affiliated companies are included, such as 100% opening up to the foreign capital of the food service industry, raising the cap on foreign capital contribution ratio in trading companies and wholesale business. We will introduce the major foreign investment restraint relaxed industries announced this time.
業種
旧外資出資比率上限
新外資出資比率上限
備考
映画
—
100%
電子商業
—
100%
・ 上限100%:現地中小企業との協力を条件
・ 投資額1000億ルピアであれば上限比率49%(電子システムを介した取引)
高速道路
95%
100%
スポーツセンター
49%
100%
病院経営コンサルティング
67%
100%
病院、クリニック67%
倉庫
33%
67%
市場調査
-
70%
通信網事業
65%
67%
ホテル
51%
67%
無害ゴミの処理
95%
100%
医薬品原料産業
85%
100%
既成薬製造業85%
デパート業(400m2-2000m2)
-
67%
私立博物館
51%
67%
陸上旅客輸送
-
49%
レストラン、カフェ
51%
100%
カラオケ、ボーリング場
49%
67%
仕出し業
51%
67%
販売代理店(特定地域)
33%
67%
建設コンサルティング
55%
67%
再生ゴム
-
100%
工業長官の特別許可が必要
冷凍倉庫業
33%
100%
高圧電力設備の設置
49%
② Industry with strong regulation
In the construction industry, the investment ratio of foreign capital remains unchanged at 67%, but the minimum construction cost has been raised from 1 billion Rupiah to 50 billion Rp.
Details will be updated soon.
-
-
-
Tax on M & A
■ Asset transaction
Acquisitions will be made through existing subsidiaries or newly established legal entities in Indonesia. Acquisition and transfer of assets requires the approval of various government agencies.
In Indonesia, it is difficult to determine undisclosed liabilities of the acquisition target companies, so the method of asset acquisition is often taken. However, the seller has ordinary shares and equity transactions for various reasons, resulting in a small number of asset transactions in Indonesia.
As a tax relating to property acquisition, corporate tax of 25% is imposed on gains on sale of assets of the seller side. Also, in asset transactions, tax liabilities are not transferred and remain on the seller side.
For assets and business transactions, the seller will bear a 5% income tax and the buyer will bear a 5% real estate transfer tax, respectively. However, in approved acquisitions, you can receive exemption from real estate transfer tax.
Acquisition price
If you acquire multiple assets and businesses, the buyer must appropriately distribute the acquisition price. There are currently no special rules in Indonesia, but we need to be careful not to receive any indication from tax authorities.
Business Transfer of assets by merger, combination, expansion is accounted for by the market price. If certain eligibility requirements are met, no profit or loss will be incurred as the transfer of assets by book value is allowed. However, approval by the DGT is required.
[Goodwill]
When acquiring assets and liabilities, as with the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS),in the Indonesian accounting standards, assets or liabilities are valued at the fair value of the acquisition date. Against the acquisition price of the assets and liabilities, the portion that exceeds its fair value is goodwill.
Goodwill is generally amortized over a useful life of less than 5 years using the straight-line or declining balance method. However, if judged to be legitimate under special circumstances, extension is allowed up to 20 years. Goodwill for both assets and liabilities will be subject to impairment from the balance sheet creation date.
[Depreciation]
Depreciation expenses are deducted from taxable income. An asset that can be depreciated is a tangible asset used in business or owned as a product and has a useful life of 1 year or more. Land cannot be subject to depreciation except for certain projects.
Buildings are classified as permanent or non-permanent. In practice, the tax law determines the useful life, but assets that do not fit into the asset category of the tax law are depreciated according to the useful life. Buildings and other real estate can only be depreciated by the straight-line method while other assets can be depreciated by choosing either the straight-line method or the declining-balance method.
Also, if you pass the business purpose test, you can transfer the asset at book value, but in that case you need permission from DGT.
[Value-added tax]
Mergers and consolidation approved under VAT regulations revised on April 1, 2010 will not be subject to Indonesian VAT. On the other hand, for approved mergers and assets and business transactions other than integration, 10% will be taxed as usual. Regarding VAT, it is desirable to consult local experts.
[Transfer tax · stamp duty]
Uncollectable right transfer tax (5%) is imposed on transfer of land and building rights. However, if it is an approved merger or integration, 50% taxation will be exempted.
Also, for certain legal documents such as receipts, agreements, proxy statements, stamp duties of $ 0.6 USD (6000 Rupiah) are usually charged.
Stock trading
Although it is preferable for the seller because the tax burden on the transferred profit is only once, in many cases offshore capital is often used for stock trading so as to further limit the taxation in Indonesia at the time of transfer.
Most stock acquisitions are made by domestic direct investment from Indonesia. In order to minimize withholding tax and capital / gain taxation on dividends, the buyer intends to acquire a target company in Indonesia through a corporation located in a country that has a tax treaty with Indonesiawhether the optimal acquisition structure or not is influenced by the taxation relationship of the buyer.
[Tax provision and guarantee]
In stock trading, buyers are asked for a broader guarantee because they will assume all related liabilities and accrued taxes of the target company.
The tax authorities will conduct a tax audit within five years from the date the tax return was filed. According to world standards, the tax audit of the Indonesian tax authorities is said to be tough, so we should receive advice from experts to reduce tax risks. When conducting M & A in Indonesia, it is prudent to conduct tax due diligence to identify existing tax risks and to avoid future tax risks.
[Tax loss carryforward]
The tax loss carryforwards can be deferred basically for 5 years, and 10 years for certain business areas. However, under the new law on mergers and integration, the target company's carryforward loss cannot be assumed with the acquiring company and will expire on the acquisition date.
[Dividend before selling stock]
Dividends to shareholders who hold more than 25% of the company's issued shares will be tax exempt and dividends to individuals will be subject to 10% income tax.
As all corporate income tax is imposed on profits on sale, there is the possibility of establishing a scheme that can enjoy tax benefits by utilizing the dividend before selling the shares.
[Transfer tax]
No other stamp duty will be incurred in Indonesia, except for US $ 0.6 (6,000 rupiah) for certain documents that arise at the time of transfer of rights. However, income tax of 0.1% is imposed on gains on the sale of shares of companies listed on the Indonesian securities trading market (additional 0.5% is added to the founders’ shares). Under certain circumstances, certain types of venture capital companies have tax exemptions on capital gains. In addition, 5% income tax is imposed on gains on the sale of shares of private companies owned by foreign companies unless they are protected by the double tax treaty.
[Tax Permission]
In acquisitions, in order to transfer assets at book value, it is necessary to obtain a tax permission. Also, in order to receive an exemption from 5% rights transfer tax on land and buildings for approved mergers and consolidations, it is necessary to acquire a tax permission.
-
-
-
Babiliography
[1] Keiko Kaneko, Taku Matsumoto "M & A in Indonesia" JOI 2012 May issue
[2] "M & A magazine MARR" Recoff data, February 2014 extraordinary issue
[3] Supervised by Yasunari Kuno "Investment / M & A in Indonesia · Company law · accounting taxation · labor" TCG publication, 2014
[4] Kuroda Law Firm edited "Complete Guide to Advancement in Indonesia" Canary Shobo, 2009
[5] PricewaterhouseCoopers Co., Ltd., PricewaterhouseCoopers Corporation "Asia M & A Guidebook" Chuo Nozaka, 2010
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya