Laos
2 Chapter Investment Environment
-
-
1 Chapter Basic Knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.3 Investment regulation and incentives
2.4 Industrial park information
3 Chapter Establishment
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.2 Establishment of business base
3.3 Company liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter Corporate Laws
4.4 Regulatory Body/Bodies And Affiliated Institutions
5 Chapter Accounting
6 Chapter Tax
7 Chapter Labor
-
-
-
Economic trend
Laos overcomes the disadvantage as an inland country so that it has developed a social capital such as roads, irrigation, and irrigation dam is promoted. It is said that Laos can obtain economic levitation effect from three neighboring countries (Thailand, Vietnam, and China) with remarkable economic development, which means Laos is the country that shares the prosperity and fate with Southeast Asia other regions. In that sense, it can be said that it is one of the countries with the highest affinity with the framework of ASEAN that Laos became the first president country in 2004. In the past 20 years since taking the economic liberalization policy, the real GDP growth rate has been at a high level of 6-8%.
Speaking of domestic industries, however, it has become a receiver of industrial import from Thailand due to self-consumption agricultural and livestock industry, energy industry such as hydraulic dam to collect foreign capitals, mining such as gold and copper, and low personnel expenses in the growing sewing industry. But after all, the industry range of its own nation is not wide. The high growth rate is also the composition driven and led by the mining and construction industry, the development situation of Laos is similar to the certain period of process of Japanese high and rapid economic growth supported by engineering and construction work because tons of hydroelectric power plants faced with the Mekong River have been built randomly with the inflow of foreign capital including Japan's ODA’s aid.
【Real GDP Total and Economic Growth Rate】
.png)
出所:世界の経済・統計よりTCF作成
The national finance is a chronic issue that the tax revenue is limited. Also, in addition to the fact that the financial base is originally weak, they strongly promote public works projects with foreign capital, so expenditures are far much more than revenues with a deficit constitution. However, while holding a budget deficit, the economy in the process of growth is not confronted by volatility and the inflation rate has fallen below 10% since 2004. With such hydropower development and electricity export mainly to Thailand as a power transmission destination, Laos is now called "Southeast Asian battery". Although there are issues such as assessment of dam construction, compatibility with the environment, and elimination of business corruption and others, in such development type public works, it is considerable that these greatly contribute to the leap of Laotian economy.
【Changes in Consumer Price Index and Inflation Rate】
.png)
Note: Consumer price index should be base year average = 100. Source: created by TCF from global economics and statistics
-
Trade
Mining products such as gold and copper account for more than half of total national export value. Despite the large-scale development by foreign capita such as Sebon mine invested with much Chinese capital has initiated since 2003, , in only five years the profitable amount accounts for nearly 60% of the total export value of Laos by a economic tailwind such as the rise in resource prices. Afterward Lehman Brothers’ shock and other factors stopped the high cost of resource, and Laos' quantity of mineral exports are not as much as the previous thriving period, but still accounts for the largest proportion of the country's exports. In this way, mineral exports can be said to be so-called national policy projects by minority oligopolistic companies authorized by the government. In Laos export items following after minerals, there are electricity, garment products, agricultural forest products, wood products, and coffee.. As a major change in export items, timber exports accounts with more than 50% up to six years ago, but the proportion of mineral resources increases year by year due to logging and export prohibition of timber.
【Major export items】 (2013)
.png) Source: Created by TCF from Central Bank of Laos
Source: Created by TCF from Central Bank of LaosMajor partner countries of export are neighboring countries such as Thailand and China, and more than 60% of the total is accounted with these two countries. Regarding exports of mineral resources, Thailand, Vietnam, Switzerland, and China account for 90% of exports of mineral resources. Sewing products are mainly exported for Europe and more than 60% are exported to the UK and Germany. It is certain that Thailand's influence is very large, as the export of electricity is done to neighboring countries including Thailand, but in recent years has increased toward China, Vietnam and other countries with multilateral trade. Also, in major export items to Japan, there are clothing and wood products, but in proportion to the total import value of Japan, the animal's skin accounts for 39.2%.
【Major export partner countries】 (2012)
.png) Source: TCF created from the Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos"
Source: TCF created from the Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos"Meanwhile, in imported goods, basic consumer goods, that is, domestic industries that produce industrial products are not developed, so vehicles carrying vehicles and trucks, machinery, chemical products, etc. are targeted. Also, even though it is a resource-producing country, it does not produce fossil fuels, so it imports fuels. Along with economic expansion in recent years, imports of such industrial materials are also increasing, so it would happen that rising import prices will lead to a decline in foreign exchange reserves.
【Major Import Items】 (2012)
.png) Source: TCF created from the Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos"
Source: TCF created from the Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos"Looking at the country of import, Thailand alone accounts about 60% of the share. Regarding trade with Japan, imports from Japan have been in excess for many years, while imports from Japan are about 11 billion yen in 2012, while exports to Japan are about 9.9 billion yen in 2012, Japan We mainly import passenger cars, bus and truck, construction machinery etc.
【Major importing partners】 (2012)
.png)
Source: TCF created from the Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos" -
Industry trends
【GDP composition ratio】 (Unit:%).png) Source: TCF created by JBIC
Source: TCF created by JBIC■ Sewing industry
A while ago, the Chinese handicraft industry is representative, but now the average labor cost in China soared and foreign investment spreads out to India, Vietnam and their surrounding countries. In the manufacturing industry as a whole, personnel expenses in Laos are lower than Vietnam, but in terms of the number of personnel supplies it’s limited. As a result, the manufacturing industries which already have their production bases in Thailand transferred only the labor intensive tasks in the process to Laos where Thai language is spoken, and the completed product is received by the Thai side through the improved land transport as a limited pattern of foreign investment. However you can’t overlook that In Laos, while some of these large garment factories obtains beneficiary of the preferential tariff system and are established as export industries, high-quality fabric products are woven from domestic handicraft including the craftsmanship of ethnic minorities. For instance, silk fabrics known as Laos Silk are also used with these production methods.
■ Agriculture, agricultural products
Laos is an agricultural country mainly producing rice as a prior, corn, potatoes, vegetables and others for self-consumption, but as crops produces mung bean, soybean, peanut, tobacco, cotton, sugar cane, coffee, tea, etc. Especially cabbage, coffee, and potatoes are cultivated on a large scale in the Bolaven Plateau in the southern area of province of Champasak. In vegetables such as cabbage an organic cultivation of Laos has added its value to the sale price sold as a premium price to neighboring around Thailand. As to coffee, it was introduced by France as a former ruler country about 100 years ago and has been succeeded continuously to small farmers with depending on the climate and now exported to the world as "high quality coffee” as Laos coffee.. Because a transfer of coffee takes long time to reach a place of final consumers like customers of coffee shop and only can gain a few potions of the final price, this field is expected to return a large amount of profit to more agricultural families by fair trade demonstration.
-
-
-
Financial (stock) market
Laos opened a stock exchange under the full cooperation of Korea Stock Exchange (KRX) on October 10, 2010 (a capital structure of 51% shares of the Lao government and 49% of KRX) earlier than Cambodia on October 10, 2010. In the first trade on 11th January 2011. There were only three listed companies, Laos’s power generation (EDL-Gen) which performed a hydroelectric power development, two nation-owned enterprises of Laos’s foreign bank (BCEL) and LAO WORLD PUBLIC COMPANY listed nowadays.
【Transition of LXS index (major stock price index)】
.png)
Source: lsx.com
As mentioned above, the opening of securities exchanges has not yet reached the stage influencing the actual economy of Laos, but it’s not a trifle matter that Laos caught pace up with the financial advance internationally to assume for common market of ASEAN. Nevertheless it seems that it will take more time for foreign individual investors to make an investment to Laos. -
Exchange rate
Laos' currency, kip has steadily become a little high in compassion to US dollar, reflecting on its economic growth over the past decade. Compared with Thai currency baht in the same period, there are a rate certainty to keep its strength although it’s woven and a foreseen connection in the mid to long term to keep a track of the price movements of baht.
The exchange rate, as of June 8, 2015, is 1 keep = 0.01526 yen.
【Keep exchange rate】
.png)
Source: Laos · Kip (LAK) Japanese Yen (JPY)
-
The Amount of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Foreign direct investment in Laos has expanded year by year and the amount of FDI has reached 10% of GDP in 2010 and accounts for a large proportion. The cumulative amount of Foreign direct investment to Laos from 2000 to 2010 is $ 13.2 billion of which only 4% of the total investment is 440 million dollars, resulting in only 3% of the total.
However, in the case of Laos, it is said that the role of between governments of ODA is larger than or equal to that of FDI, Japan to achieve an economic development and Japan contributes to assist a large amount of ODA to infrastructure development.
The majority of foreign direct investment is mainly focused on a large project such as hydroelectric power and mineral resource development from neighboring countries such as China, Vietnam, and Thailand. Among them, investment from Japan is on the rise, mainly in the manufacturing industry. Although there are still a plenty of issues in the field of infrastructure and finance, an improvement of the transport network connecting with neighboring countries is also progressed, thus an improvement of further investment environment of Laos is expected.
【Inward Direct Investment by Industry (Authorized Base)】 (Unit: $ 1 million)
.png)
Source: JETRO【Trends in Lao PDR's Direct Investment Amount (International Balance of Payments)】
.png)
Source: Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos"
【Foreign Direct Investment Fund to Laos】 (1989 ~ end of 2012)
.png)
Source TCF prepared by JBIC "Investment Environment of Laos"
-
Infrastructure
■ Roads, railways, water transport
Although "East-West economic corridor" is not included in a concept of formal Asian highway concept route, (total length 1,450 km) this route as crossing of Southeast Asia has already been opened except Myanmar's the most west section. This final construction was the 2nd tie-Lao Friendship Bridge bridged between Thailand’s Mukdahan and Laos’ Savannakhet with Japan's ODA loan. It completed in 2006, and its service started in 2007. Currently, East-West economic corridor has been conducted with an operational adjustment among the countries and make it to export the products of Thailand and Laos from Dannan port in Vietnam although has not yet reached the stage of achieving mass transit yet. Meanwhile, the "North-South Economic Corridor" (total length 2,000 km) connects from Kunming, China, to Bangkok, Thailand and plan to longitudinally concentrate Laos in the north and south. There are the rest sections where the full highway has not yet been made.
【East-West Corridor and North-South Corridor】
.png)
【Major road of Laos】.png)
Source: Mitsubishi UFJ Morgan Stanley Japan Securities Co., Ltd. "FY2010 CDM / JI Project Survey, Laos · Traffic NAMA Feasibility Study" in similar to the North-South Corridor,
Laos' railroad development plan also has an aspect of infrastructure plan that strongly reflects on Chinese resource diplomacy. As a railway opened for the first time in Laos in recent years, there is a route to Laos Tanareen opened in 2009 by extending the existing line of Thailand. Thailand planned to extend it to Vientiane using ODA’s aid, but this time it is currently in the middle of be stuck in temporary stop because Thailand announced this railroad is supposed to link with the two countries through crossing of Laos in cooperation with China.
The plan of railway construction led by China doesn’t maintain its achievement mind of the end of 2010 when they announced, but it doesn’t seem to come true that the construction schedule of completion of 2015 ends from 2011 and also its rapidity called as highway railway..In some cases, it is pointed out that for Laos’s people with a population of 6 millions, the burden of construction project costs exceeds Laos’s GDP, only imposes on them as a burden of national finance and doesn’t result in the economic high boosting effect. The stakeholders watch over this development of railroad plan, while they are cautious against the economic entire situation of Laos, China and other Southeast Asian countries as a whole, the domestic politics of Laos, and the Chinese resource diplomacy. Domestic water transport is done through Mekong River on the west of Laos from the north to south, but because of a bunch of waterfalls called Corn Papen Falls in the middle area near the river Cambodia border, it is impossible for ships of Laos can to pass to the ocean This is one of the reasons why Laos needs to invest a huge amount to the land transport for the fame of a country of land transport.
■Power
Although Laos is called "Battery of Southeast Asia" and transmit electricity from hydropower dam constructed nearby Mekong River to Thailand and other countries but because the domestic general transmission facilities are not sufficiently installed, they quite often cause a black out even in the area where the electricity is supplied. Also, in some areas of the country, there is a cynical situation that Laos imports the exported electricity to Thai again with high price. In order to respond to the increasing demands for electricity, the government of Laos has requested a cooperation with foreign countries to resolve this situation. The research team of electric power filed also is head for Laos from Japanese electricity companies. Although the proportion of total electric power is still small, various attempts to utilize solar power are proceeded. This is because the hydroelectric power is weak in the dry season, so the utilization of sunlight complements it and in many cases the profit margin of setting the transmission line to rural areas with low population density is not suitable the beneficial reason of utilization of solar power is that the large electric grid is unnecessary.
■Communication
As a communication method in urban areas mobile phone is popular and dominated equipment. The scenery of Internet cafes occupied with a plenty of users is the same as the other developing countries. There are places where high-speed Wi-Fi lines are available in the industrial areas where maintenance has been recently progressed. Laos, with its a one-party dictatorship system, also has moderate speech control, but it is not a big issue that interferes with communication in general business activities, as long as you stepped into information of deep political matters, the content of output information is not restricted.
-
Human resources
Laos is a country classified as least developed country (LDC), and by a consideration of the reward level from the average annual income level of the people is from one third to one fifth of one of Thailand or sometimes lower level on the data. However, in reality, it doesn’t seem easy to hire the appropriate personnel with this compensation level, and its low population.
While the majority of citizens operate self-sufficient farming, the proportion of workers in industrial and service industries is lower. Moreover, the proportion of workers in these filed is much lower, therefore a wage for talented workers, tends to stay high. If foreign investment becomes active more in the future, it is expected to bring a competition for employing more talented workers intensively.
Chart 1: Wage levels in Asian countries (2011, monthly basic salary)
.png)
Source: Nippon Research Institute's method of selecting overseas production bases (wage level) http://www.jri.co.jp/page.jsp?id=22573
Likewise Laos’ neighboring country, Laos is a country with a high proportion of children, as a country that the average age is younger. However, due to absence of intensive industries and delay of education, the literacy rate is low, and there is a challenge how to raise a quality of education in urban and rural areas. Just because Lao people are generally serious, industrious and kind, they have enough potential to work together and develop themselves through training even though they have not yet had a practical and experienced ability. It would be great to take a consideration of advance to this country.
【Population pyramid (2010)】 (Unit: 1,000 people)
.png)
Source: Lao Statistics Bureau 【Population Trend of Laos】
.png)
Source: created by TCF from global economics and statistics
-
Other Investment Advantage and Disadvantages
Vientiane, the capital of Laos, is so small entity of city that it is unlikely to gather the government functions. Moreover, there are no any unsafe areas unlike the other cities in other Southeast Asian countries. Under the rule of Lao People Republic Party (communist party), its politics is stable and many citizens operate self-sufficiency agriculture despite its poor economic income. Also, Laos has plenty of hydraulic resources along with Mekong River and underground resources that secure their future life. Most of the land is covered with forests, which show you a contentious idyllic landscape with the unimproved roads even on flatlands and highlands. If you don’t regard economical success and wealth as richness and satisfaction of your life, Laos is a so joyful nation that you can feel and obtain them in different way apart from the aspect of growth of GDP of the consecutive 10 years.
For Japanese companies entering Laos, it would be required to devote themselves to make an effort to engage in cooperation with the society of local area in the long time by leaving the general viewpoint of low-cost labor. When Japanese companies establish a base in Laos, most of them already have the existed business bases in Thailand and seem the entity form which achieves to fulfill a supplemental tasks and roles. It is also effective for Japanese expatriates to raise their insights about Laos including languages by experience and training in Thailand.
-
-
-
Investment regulation
The investment in Laos must be take a consideration based on the Investment Promotion Act of 2009 and the Ordinance of prime minister concerning Special and Specific Economic districts promulgated in 2010. The new Investment Promotion Act enacted in 2009 is a substitute of the Internal Investment Encouragement Act and the Foreign Investment Encouragement Act enacted in 2004 to change into removing the barriers between domestic and foreign investment and actively attracting foreign investment. However, its detailed rules have not been publicized even as of May 2012, making it difficult to obtain information. Here, this is not the latest information because of the information based on the Investment Encouragement Act Bylaw of 2005 in the following descriptions. Please note that it is necessary to confirm with the administration organizations for each individual case when you actually make an investment.
■ Prohibited business and regulated industry
In the list of industries regulated by the country, so-called negative list, there are some listed industries that have a great influence on national security, social order, national traditions and its environment. For Laos, business sectors listed on the negative list must receive permission and inspection by the relevant authorities prior to corporate registration (Article 2 of Corporate Law). In foreign investment you are able to advance for all businesses unless your business is harmful to national security, social order, national traditions and its environment. Because the content of the negative list prescribes 12 industries as below, you cannot be approved in regard with the entry of private enterprises for these projects.
1. Manufacture of all kinds of weapons and ammunitions
2. Manufacture and procedure of drugs
3. Manufacture of cultural products destroying cultures and traditions of Laos
4. Emissions of chemical substances and industrial wastes harmful to human life and the environment
5. Central banking operations
6. Survey and security services
7. Foreign Affairs
8. Defense
9. Public Order and Safety Business
10. Political organization activity
11. Funeral services and related business activities
12. Teacher training, religious education other than Buddhism, training of defense and social security maintainers Regulated industries are divided into conditions and business fields as follows.
【Regulated industry】
■ Regulations concerning capital and investment rate.png)
General business requires you capital of more than 1 billion kips which is equal to (Article 17 of Investment Promotion Act), but when you purchase the usage right of land you must have capital of 500 thousand dollars or more (Article 58 of Investment Promotion Act). In principle, foreign companies are permitted to make an investment of full amount, but in the case of joint venture, investment of 10% or more of total capital is required (Article 10 of Investment Promotion Act).
■ Regulations on land ownership
Until now, it was prohibited for foreigners to possess the usage right of land, but since September 2011, by an investment with registered capital of more than 500 thousand dollars you may grant the usage right of land (Article 58 of Investment Promotion Act). Foreign investors are now able to purchase a private and government usage right when they purchase a land to build residential or business facilities. The land can be invested on the real estate sector and you can perform sales.
■ Employment of foreigners
Foreigners may be employed as long as a company may not hire appropriate personnel in Laos. Except for international aid, foreign employment must obtain a prior approval from the Ministry of Labor in both short and long term. In addition, because the number of employees and labor period are limited, it is necessary to conduct a technical transfer to Laotian workers (Article 7 of Labor Law). Please view to Chapter 7 Labor.
■ Regulations of foreign exchange
[Regulation on loan]
Companies may borrow an unsecured loan of short-term from Bank of Lao PDR (Article 38 of Lao PDR act) as long as a company may meet certain financial requirements.
[Overseas remittance regulation]
Foreign companies are legally permitted to remit capitals, assets and profits internationally. However, in case of international remittance, it must be done after they clarify the remittance by a proof that taxes and legal commissions have been properly paid (Article 68 of Investment Promotion Act).
[Taking out cash]
Foreign currency may be freely taken out as far as the amount is within $2,000 dollars, but once you notify this matter to custom clearance in advance you may bring the amount over $2,000 dollars. However, you must be aware that you may neither take nor bring cash of local currency over $2,000 dollars (Article 12 of Bank of the Laos PDR law).
-
Investment incentives
In Laos, the government prepare for various incentives such as corporate tax exemption of 10 years at the longest to invite foreign capital. In Laos, the distinct of investment incentives are separated into two; regional incentive and economic special incentive. In addition, regional incentives are divided into zones from No.1 to No.3 and economic special incentives are divided into special economic zone and specific economic zone..These zones are categorized according to the degree of infrastructure improvement. Less and less an installation of infrastructure is done, the degree of incentive is higher. But for special economic zones, incentives is finely different depending on the kind of industry and condition.
[Destination of application]
In order to receive investment incentives based on the Investment Promotion Act, the destination of application is different for each type of investment. Regarding general business, you shall apply to the one-stop service office of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry or the local commerce and industry office (Article 17 of the Investment Promotion Act). And, for investment of concession business, you shall be required to apply to the Ministry of Planning and Investment or one-stop office (Article 21 of Investment Promotion Act). Regarding investment in projects described in the investment request list, you shall apply to the national government or local government (Article 29 of Investment Promotion Act). Also, an investment on special economic zone or specific economic zone shall be applied to the one-stop service office of the administrative committee of either of zones (Article 33 of Investment Promotion Act).
.png)
One stop service office
The one-stop service committee is composed of representatives of each sector and local government and has a mandatory to provide investors with various kinds of services such as investment information, examination of investment application, issue of incorporation registration certificate or concession certificate (Article 44 of Investment Promotion Act).These services bring investors to perform prompt and simple invest procedures. The one-stop service office is located in the following location.
· Ministry of Planning Investment and Regional Planning and Investment Bureau
...administrating concession business and investment for special economic zone and specific economic zone
· Ministry of Commerce and Industry and Regional Commerce and Industry Bureau
...administrating investment on general business
· Special economic zone and specific economic zone
...administrating investment on special economic zones and specific economic zones
■ Regional Incentives
In Laos, the whole country is divided into three zones. Farther and farther you leave from the city, the more benefits are granted (Article 50 of Investment Promotion Act). For example, the period of corporate tax exemption is the longest 4 years in the third zone within the capital area, while in the first zone away from the capital the period is 10 years at the longest. It is aimed to diversify industries and suppress the gap between rich and poor in rural and urban areas, with imitating Thailand of neighboring country.
Zone 1: Remote regions in mountainous where you can take the best and most investment incentive measures. Because infrastructure is economically underdeveloped as a main
Zone 2: Areas where socioeconomic infrastructure has been developed to some extent than the first zone. Because geographical conditions are convenient, you can obtain incentives of middle level.
Zone 3: Areas where infrastructure is economically developed. The treatment of investment is lower than other areas.
【Investment promotion zone】
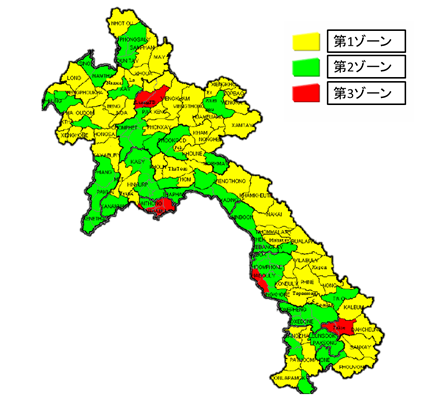
Source: created by TCF from Investment Promotion Division of Ministry of Planning and Investment 【Regional division list】
.png)
Source: created by TCF from Investment Promotion Division of Ministry of Planned Investment [Target Industry].png)
By the provisions of the amendment of Investment Promotion Act in 2009, the recommended fields are determined and defined, but the details are unknown because they have not been announced so far. However, since these fields should be created to some extent based on the recommended fields before the revision, for the sake of reference, we will describe the incentive businesses from Foreign Investment Promotion Act in 2004. Three levels are classified according to the details of activities, but this detail is also prescribed on provisions (Article 49 of Investment Promotion Act).
【Details of Investment Recommended Field by Foreign Investment Promotion Act in 2004】 [Content of incentive measures]
① Corporate tax exemption
As a principal, the following periods of corporate tax exemption are adopted for each zone. The period of tax exemption is different for each zone and the treatment of corporate tax exemption is adopted for a certain term from the first date of operating commerce. Besides, in the manufacturing industry corporate tax exemption is applied from the year of obtaing profits (Article 51 of Investment Promotion Act).
【The period of Corporate tax exemption】.png)
Source: created by TCF from Investment Promotion Act 2009
However, in addition to the above periods of tax exemption, the incentive industries complied with Foreign Investment Promotion Act in 2004 can extend another five years (Article 54 of Investment Promotion Act).
① Exemption of lease fee or concession fee for specific industries
Hospitals, schools, vocational training schools, research laboratories, and public utilities can take an exemption from either lease fee or concession fee of the government-owned land (Article 54 of Investment Promotion Act).
1st zone: 15 years
2nd zone: 10 years
3rd zone: 3years
■ Incentives for special economic zones
The Special Economic Zone is the area defined by the government which has location conditions and economic environment that it can provide corporations facilities and self-governing authority better than other domestic areas for their activities. The government can achieve an economic development through industrial development and employment promotion to invite foreign capital and construct comprehensively socioeconomic infrastructures and facilities with the vision to strengthen the competitiveness of corporate activities,
Even in Laos, this system is used. The following nine special economic zones are arranged so far. Unless the following items with numbers are specified, these would be complied with the provision of the Prime Ministerial Ordinance concerning the Special Economic Zone and the Specific Economic Zone.
According to the above ordinance, the fields and projects for promoted investment to special economic zone are as follows (Article 23).
1. Electronic Industry
2. Research on industrial technology
3. Manufacturing of the updated architectural materials
4. Tourism infrastructure development
5. Clean agriculture and the related agricultural processing product
6. Organic agricultural products
7. Production for export
8. Afforestation
9. School
10. Disease
11. Park
12. Other activities considered as having aptitude and potential for other special economic zones
[Content of incentive measures]
Developers and investors in special economic zones can take a preferential treatments; incentives as follows (Article 37).
-Duty free of importing fuel
-Exemption of custom fees and taxes on the import of fuel during the construction period of developers of special economic zones located in remote districts or geographical dangerous districts (you must obtain an approval of annual importing plan of national economic special committee).
Exemption of custom fees
Because raw materials transferred from Laos and used in special economic zones are treated as exports to special economic zones you can take preferential treatment of custom fees and taxes according to bylaw
Leased land
In the case investors plan to borrow a land of special economic zone for a long term, they may take the privileged treatment in regard with leaded lands by methods of the Special Economic Zone Administrative Committee or Economic Executive Committee and leasing fees (Article 39).
Collecting funds
Investors may collect fund by commercial banks and other financial institutions both their domestic country and foreign countries (Article 40).
Deduction of expense
Developers and investors of special economic zone may deduct training expenses from annual taxable profits (Article 41).
-
-
-
Industrial park of Laos
An industrial park is the land arranged with well-balance and sold separately for industrial factories. In addition to the factorial areas, there are public facilities and infrastructures such as road, drainage canal, central wastewater treatment facility, flood prevention facilities, electricity, water supply, telephone but also indispensable services arranged systematically for the efficient operation such as post offices, banks, shopping centers, gas stations, and even workers' apartments. The development of Special Economic Zones (SEZ) in Laos accelerates and the existing SEZ and the development ones are as follows.
.png)
Source: created by TCF from the Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos"[Savan Seno Special Economic Zone]
The representative SEZ is Savan Seno special economic zones located in Savannakhet Province located in central Laos. This is located on the intersection of Route 9 which forms a part of the East-West Corridor connecting from Myanmar to Vietnam and in the cross of National Route 13 cutting across the whole Laos with the geometrical condition of the distance of approximately 460 km to Ho Chi Minh Airport in Vietnam.
This industrial park has been released with the issue of Prime Minister Ordinance No. 177 concerning administrative rules and incentives for the Savan Seno Special Economic Zone on 13 November 2003 by the Government of Laos. You can see the government would be zeal to invite the labor intensive agriculture related industries and request for assist funds from government of foreign countries. Logistic System Corp, O-M Ltd.and others have already advanced into this zone among Japanese corporations. The incentives of companies entering into the Savan Seno economic zones are described as below.
1) Corporate tax exemption for up to 10 years
2) Income tax exemption
3) Exemption of custom fees of import of raw materials
4) Leasing of land for up to 75 years (50 years in common)
On September 19 2013, there are 33 authorized companies, whose contents are 11 Laotian companies, four Malaysian companies, four Thai companies, three Japanese companies, three France companies, two Netherland companies and others are Australia, Belgium, Hong Kong, Korea, and Malaysia.
[Development of Economic Special Zone Proceeded in Vientiane]
The development of three new specific economic zones specializing in commercial service in Vientiane has started. The Laotian government plans to the establishment of 25 SEZ by 2020, but by the aid of donor countries including Japan, the plan of maintenance of roads and construction of hydroelectric power plants is advanced as well. New urban development is also conducted by cooperation of the Chinese government. It is a development plan of complex city in the Pha That Luang of Vientiane with 1,600 ha. In December 2013, in the first phase there are the undeveloped places yet but the construction of road in the development zone and custom clearance building were completed. The other facilities including transformer substation are under construction.
-
-
-
Websites
[1] ビエンチャン日本人商工会議所
[2] ラオス中央銀行
[3] 外務省
[4] 日本貿易振興機構
[5] 日本アセアンセンター
[6] ジェトロ世界貿易投資報告
[7] 国際協力銀行 ラオスの投資環境
[8] ラオス株ドットコム
[9] アジア開発銀行
[10] ラオス証券取引所
[11] 公益財団法人 地球環境センター
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya