Laos
7 Chapter Labor
-
-
1 Chapter Basic Knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.3 Investment regulation and incentives
2.4 Industrial park information
3 Chapter Establishment
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.2 Establishment of business base
3.3 Company liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter Corporate Laws
4.4 Regulatory Body/Bodies And Affiliated Institutions
5 Chapter Accounting
6 Chapter Tax
7 Chapter Labor
-
-
-
Working environment
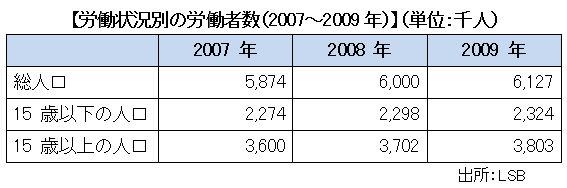
■ Labor force population
The population of Laos is the least among the Mekong River basin areas including Cambodia, China, Myanmar and Thailand, about 650,000 people (2012 / Ministry of Foreign Affairs). Among them, the labor force population (over 15 years old) is about 3.8 million. It is said that by the year 2015 the labor force population will increase to 4.15 million people. It is said that Laos is divided into more than 60 ethnic groups, but the Lao family is the most frequented, accounting for about 60%. Buddhist religious beliefs are the most frequented, about 60% religious.
■ Working Population by Industry
According to the Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare (MoLSW) survey, manufacturing, construction, transportation and telecommunications are the main sectors of employment in the entire industry, especially the clothing industry is domestic I am growing with receiving a lot of investment from outside. About 60% of companies employing more than 100 people are manufacturing industries. Successively there are many, the electricity and water department. On the other hand, in companies with fewer than 100 employees, the major sector of employment is the construction industry sector.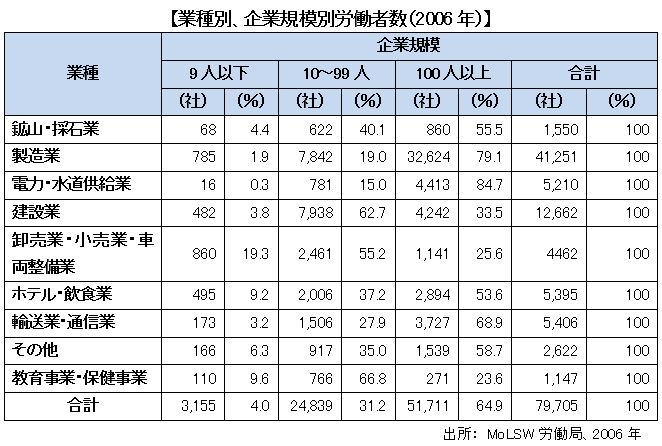
Looking at the employment structure of general workers by industry, about 75% are engaged in agriculture. Therefore, when establishing a factory in the area where agriculture is the foundation of living, there are also many workers who engage in agriculture and work at the factory, and there are cases where absenteeism occurs frequently during the busy season of agriculture.
In addition, the educational level of Laos is not high and the rate of advancement to junior high school is about 50%, and some enterprises take measures such as incorporating primary education level training as a post-employment training. The minimum working age of Laos is 14 years old according to graduation of junior high school.
■ Unemployment rate
The unemployment rate of Laos has decreased to 1.4%, about 38,000 people. The reason for this is that many of the working population is engaged in agriculture and it is difficult to become unemployed. In fact, it is true that workers who are engaged in agriculture and only work in real low hours are also included as employees.In Vientiane city there are many choices of workers and it is said that there are many cases where you go to another factory in search of high wages and go to illegal migrant work in the northeastern part of Thailand that border with Laos across the Mekong River.
■ Wage level and wage increase rate
Wages of Laos workers are said to be about one fifth of Thailand's wages. Therefore, in order to make use of cheap labor, mainly seeking factory workers, entry of foreign capital is proceeding.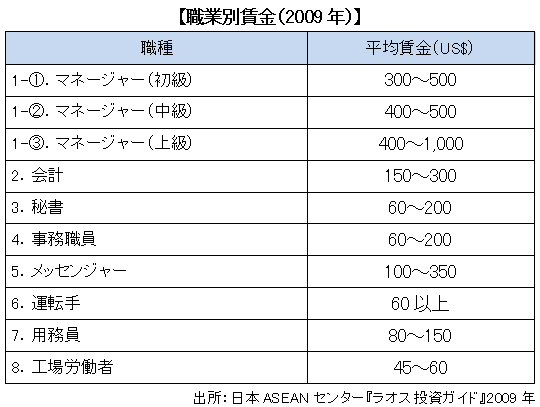
The salary system is determined by organization or department, by skill level, background and academic background of job title and worker. Salaries for Lao workers are 45 to 60 dollars for factory workers, 60 to 200 dollars for clerical staff and 400 to 1,000 dollars for managerial positions.
-
Labor disputes with labor unions
■ Outline of labor union
The Lao National Center (the national central organization of trade unions) is the Lao Federation of Trade Unions (LFTU). As of 2010, the number of affiliated organizations is approximately 3,000 and the total number of members is approximately 155,000.
In Laos, all offices with labor unions must provide the necessary funds and facilities for trade union movement within the extent possible. Also, if labor unions do not exist, it is necessary to put worker representatives. In case of dispute resolution in Laos, we must use Laos language. Therefore, when you leave a record to conflict in writing, it is necessary to record it in Laos language.Issues and occurrence status of labor dispute
In Laos, 75 labor disputes were reported in 2004-2005, 60% of which were settled internally by companies, etc. rather than mediation and mediation by external institutions. Nine cases were requested by the labor union to intervene directly, and three cases were resolved through the Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare.
In the event of a labor dispute, both parties, employers and labor, must resolve by settlement, mediation or litigation based on the general principles of Article 25 of the revised Foreign Labor-Management Incentive Act. In cases where it can not be resolved with a settlement between the parties, we propose a resolution to the Investment Promotion Management Committee that received permission and resolve by mediation. Also, if the Investment Promotion Management Committee can not solve it, it will file a complaint with the Economic Dispute Arbitration Commission.
Labor disputes can be classified into the following two according to the point of issue.
① "Disputes concerning rights": labor laws, labor regulations, employment contracts, disputes related to employment rules and other regulations
② "Disputes concerning interests": Disputes arising from advocating users to expand or improve right, welfare benefits, etc. -
Employment Practices and Labor Management
■ Employment Practices in Laos
In Laos' s large and medium enterprises, there are many cases where bonuses are offered called "13th month salary". Bonuses are normally paid according to outcomes, but there is no provision in the law regarding the presence or absence of payment or the amount of money, and the company can arbitrarily specify it.
Foreign-invested enterprises including Japanese companies often receive travel expenses for homecoming including families, and payments are usually made at the end of the year.In the factory, there are cases where workers are preparing free dormitories. However, in reality it is sometimes seen as problematic concerning the living environment and sanitation condition of the dormitory. The Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare does not consider treatment of the living environment of such facilities, but regulations concerning occupational safety and health of workers are established.
Benefits
One of the characteristics of Lao's labor law is the manifestation of worker skill acquisition (Article 10). Companies must accumulate 1% of annual labor costs in order to acquire skills of workers. Also, if it is difficult to acquire skills at your company, you need to pay the above amount to the National Skills Development Fund.
-
-
-
Labor Standards Related Laws
■ Regulations related to labor standards
Lao PDR provides the framework of employment and labor laws aiming to create a framework for socio-economic development under the Constitution of the People's Democratic Republic of Laos and provides the following laws and regulations.
· Labor law No.06 / NA (promulgated on 27th December 2007)
· Foreign Investment Promotion Act No. 11 / NA (promulgated on October 22, 2004)
· Economic dispute resolution method No.02 / NA (promulgated on May 19, 2005)
· Laos Trade Union Act No. 12 / NA (promulgated on December 25, 2007)
· Improvement of women's status and protection related law No.08 / NA (promulgated on October 22, 2004)
· Domestic Investment Promotion Act No. 10 / NA (promulgated on October 22, 2004)
· Child rights and interests protection law related law No. 05 / NA (promulgated December 27, 2006 -
Legal system on wages
■ About wage payment
Currently, Lao PDR does not prescribe rules to determine salaries and wage levels for specific industries. Companies can set internal regulations, but labor laws and statutory minimum wages must be complied with.
In principle, users are not supposed to deduct from wages, but Labor Law No. 06 / NA promulgated on December 27, 2006 stipulates concerning deductions such as salaries and individual income taxes . Based on the following provisions, it is permitted to determine wages or deduct from wages.
· Article 44: salary, wage
· Article 45: Right of equality compensation
· Article 46: Determination of remuneration level
· Article 47: Method and rule of salary, wage payment
· Article 48: Calculation of overtime
· Article 49: Deciding to pay salary, wage payment
· Article 50: Payment of wages at temporary leave
· Article 51: Priority for salary and wage receipt
· Article 52: Salaries to compensate for damages, deduction from wages
· Article 53: Personal income tax salary, deduction from wages
Regarding the payment of wages, at least the minimum monthly payment must be paid on a fixed date, and in case of payment or hourly workers, payment must be made twice a month or a period not exceeding 16 days It has been.
■ Minimum wage
Decisions on workers' wages are determined by the content of the work, the conditions and the position of the workers. From January 2012, it is said that the minimum wage of 626,000 Keeps per month is prescribed by the government, and the amount of basic salary must not fall below the minimum wage.
【Minimum wage for 1991 ~ 2012】 Source: Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos"
Source: Japan Bank for International Cooperation "Investment Environment in Laos"
Apart from the minimum wage above, the user must pay a living subsidy of 8,500 keeps per day or 221,000 keeps per month. For example, users need to pay 569,000 keeps (348,000 + 221,000: minimum wage and subsidy sum) for employees working 8 hours a day, 26 days a month. -
Employment contracts and employment rules
■ Creation of employment contract
When hiring workers, the employer must prepare an employment contract in writing, except for short-term work such as day labor. Employment contracts include fixed-term employment contracts (employment contracts with fixed periods) and indebted employment contracts (employment contracts without a fixed period), but when specifying the term of employment contract, the employer unilaterally It is not decided but decided by agreement with the worker himself.
Trial period
The user has the right to set a trial period when hiring workers in order to confirm the abilities of workers' ability to carry out skills. The period of trial is stipulated as follows according to occupation.
· Physical labor jobs (labor that does not require experience or technical expertise like physical labor) ... within 30 days
· Professional technical work (labor with expertise) ... within 60 days
However, even during the trial period, you must pay more than 90% of the salary at the time of this adoption.
Upon expiration of the trial period, the employer must notify in writing by 7 days in advance about the subsequent adoption of this hiring. If the worker lacks the necessary skills and abilities, the trial period can be extended or can not be accepted. Also, if you extend the trial period, you have to set it within 30 days.
In addition, if a worker is absent for reasons of illness or for other unavoidable reasons during the trial period, do not include that period in the trial period.
■ Termination of employment contract
In case of terminating the employment contract by notice from either the employer or the worker, we have to notify in advance by the following deadline according to whether there is a fixed period of employment contract and occupation respectively.
· Physical labor jobs (labor that does not require experience or technical expertise like physical labor) ... up to 15 days ago
· Professional technical work (labor with expertise) ... up to 45 days ago
Regardless of occupation, up to 15 days in advance
In the case of a fixed-term employment contract, even if you extend the employment contract, you must notify you 15 days in advance and sign a new employment contract.■ Obligation to create employment rules and items to be created
In Laos, users who constantly hire more than 10 workers, as in Japan, must establish work rules and be thoroughly disseminated to workers. When creating work rules, you must comply with Laos labor-related laws and regulations. Also, when creating work rules at business establishments, it is necessary to receive approval from the labor regulatory agency in advance.
Items that must be stated in the employment rules are as follows.
· Working hours, break time, lunch time
· Week holiday, paid vacation
· Use of personal protective equipment
· Bringing in work · taking out from the workplace
· Overtime work, payment overtime fee
Sick leave
· Vacation by personal reason
· Complaints
· Solving the labor dispute
· Penalties for violating employment rules
■ Dismissal
If the employer is short of workers' technical expertise or when dismissing workers due to reasons of health, it is necessary to notify advance notice and pay dismissal allowance to the workers. When dismissing, you have to give notice in advance by the following deadline according to job type.
· Physical labor job (labor requiring neither experience nor technical expertise like physical labor) ... 15 days ago
· Professional technical work (labor with expertise) ... 45 days ago
Before terminating the employment contract, the user must consider appropriate placement change according to the capability and health of the worker. However, in the absence of proper work, you can terminate your employment contract. Also, for reasons such as deterioration of the business environment, when dismissing workers, we have to notify labor regulatory agencies and workers 45 days in advance.
In addition, when dismissing due to lack of specialized skills of workers, reasons of health condition, deterioration of business environment, etc., it is necessary to pay the following dismissal allowance to workers according to the number of years of service and salary form .
【Fired allowance】
· When the length of service is less than 3 years ... 10% of monthly salary
· If the number of years of service exceeds 3 years ... 15%
· Volume wage system workers ... retirement calculation based on the average of salary for the last three months
Also, in case of dismissal due to unfair reasons, the employer pays compensation of 15% of monthly salary if the length of service is less than 3 years, 20% of monthly salary if the length of service is over 3 years You must do it.
In addition, in case of dismissal due to the following reasons, it is not necessary to pay dismissal allowance.
· When you take dishonest behavior or deliberately cause huge damage to the property of the user (however, evidence for such illegal act is necessary)
· In case of violation of employment rules despite repeated warning from users
· In case of absenteeism for more than 4 consecutive days without legitimate reason
· When imprisonment is imprisoned by a court's ruling
However, even if you do not pay the dismissal allowance, the employer must notify the employee 3 days in advance. Therefore, if you decide to dismiss in accordance with the above matters, you have to treat it as a retirement date after 3 days after notice of dismissal.
-
-
-
Social insurance law
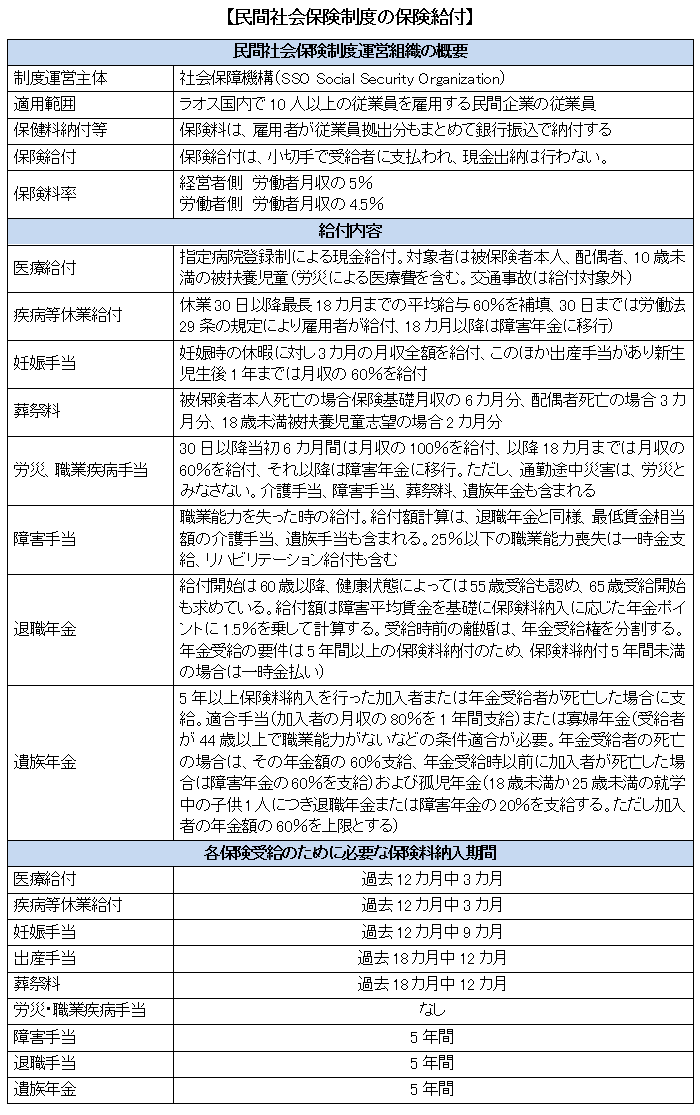
■ Overview
Based on the Prime Ministerial Ordinance No. 207 on Social Security System in Laos (enforced on 1st June 2001), establishments hiring 10 or more workers are obliged to apply the social security system.
The benefits of the social security system are ten types of workers 'health, illness, childbirth, death, occupational accidents, pensions, sequelae, etc., outside the workers' work. The social security system is roughly divided into four categories: the Social Health Insurance (SHI) system, the Civil Servants' Scheme (CSS), the social security system such as farmers (CBHI: Community Based Health Insurance ), And the poorest social security system (HEF: Health Equity Fund).
■ Private social insurance system (SHI: Social Health Insurance)
(1) Scope
Private offices that employ more than 10 workers are obliged to join the private social insurance system. However, excluding workers working at embassies, international organizations, etc. In addition, although business establishments with less than 10 people are not compulsory participation, they can be voluntarily joined.(2) Insurance premium
The private social insurance system takes a social insurance system, and according to the monthly wages of workers, 5% of employers and 4.5% of workers pay insurance premiums. The employer deducts the premium of the worker's share from the monthly salary and pays it to the Social Security Organization by 15th of the following month together with the user's share. As for the premium equivalent of occupational accidents and occupational disease benefits, only the user is burdened, so the burden rate of users is 0.5% higher.
The upper limit of monthly salary subject to insurance premium calculation is 1,500,000 keeps. For that reason, it is 142,500 Keeps (about 1,425 yen) per month combined with the burden on the user and the workers' burden at most. Because Japan and Laos have not concluded a social security agreement, Japanese expatriates working in Laos will join social insurance both in Japan and Laos, but due to the upper limit there are Japanese companies and Japan It will not be such a big additional cost for people.(3) Insurance benefits
The benefits of health insurance are cash benefits based on designated hospital registration system. Insurance is applied only at designated hospitals of the Social Security Organization (SSO) that operates the private social insurance system. Therefore, when you receive medical treatment, you need to confirm whether it is a designated hospital in advance or not.
The health insurance benefit subjects are insured persons, spouses, dependent children under 10 years old. Including medical expenses due to workers' injuries, medical expenses due to traffic accidents are not eligible for benefits.
Compensation for workers compensation will be paid according to disability against injury owed to work. However, injuries or other injuries owed by acts done for personal purposes, not under the command of the user etc. are not considered "occupational accidents".
As wage compensation in the event of a disability, 100% of the monthly salary will be paid up to six months after the 30th day, 60% of the monthly salary will be paid up to 18 months from the 6th month and will shift to the disability pension after 18 months. Please note that disasters in the middle of commuting are not considered as workers' accidents, unlike in Japan. As compensation for other workers compensation, there are nursing allowance, disability allowance, funeral expenses fee, survivor pension.
In principle, payment for old-age benefits begins after 60 years old, and depending on the health condition, 55 years old payment may be provided. The benefit amount is calculated by multiplying the pension point according to the insurance premium paid based on lifetime average wage by 1.5%. The requirement of pension receipt is a lump sum in the case where the insurance premium payment period is over 5 years and the insurance premium payment period is less than 5 years. If you divorce before receiving pension, we divide pension entitlement.
The death protection guarantees the survivor a fixed amount of burial expenses and consolation money at the time of death of the workers.
■ Civil Service Social Security System (CSS: Civil Servants' Scheme)
The subjects of the Government officials social security system are government officials, military personnel, policemen, etc. Insurance premiums collected from government officials, etc. are 6% of monthly salaries, and part of the insurance benefits are borne by the government. Contents of insurance benefits are medical expenses, injury and disease allowance, funeral expenses fee, retirement pension, survivor pension.

■ Farmer and others Social insurance system (CBHI: Community Based Health Insurance)
Social insurance system such as farmer is a social security system dealing with informal sector. This system came into effect on 13th April 2005 and is operated at the local, regional and national level. Items eligible for benefits are medical benefits only. However, as with the private social insurance system, traffic accidents are not covered.
■ The poorest social insurance system (HEF: Health Equity Fund)
The World Bank, the Asian Development Bank, etc. are the center of the poorest social insurance system, and the institution is being launched. Currently it is managed by Ministry of Health.
-
-
-
Immigration and visa
■ Work permit and visa obligation
If a foreigner enters into Laos and enters for business purposes, it is necessary to obtain business visa. The period is 3 months, 6 months, 1 year.
(1) Create necessary documents and apply for business visa at Laos Embassy in Japan.
The Embassy of Japan in Laos will send the documents to Laos and examine relevant agencies such as the Planning and Cooperation Committee, Immigration Bureau, Ministry of the Interior and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
(3) If approved, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs will issue a visa to the Embassy of Laos in Japan and a visa will be issued to him.
※ For enterprises with offices in Laos, you can apply for visa directly to relevant ministries and agencies and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
■ Conditions for Foreign Working Permit
(1) Foreign labor permission and alien registration
Users employing foreign workers apply for work permits to "Lao State Enterprise for Employment" (LaSE) to obtain permission from the Department of Labor and Social Welfare, and the Employment Promotion Division of the Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare Will accept applications (No. 749 / LSW "Agreement on Acceptance of Foreign Labor and Employment Management" Article 5).
In addition, the employer must submit a list of foreign workers employed by the Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare Labor Division within thirty days from the day foreign workers enter Laos (agreed by the Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare No. 749 / LSW "Acceptance of Foreign Labor and Agreement on Employment Management" No. 10).(2) Acquisition condition
Foreign workers who work in Laos must meet the following conditions. (Article 74 / LSW "Agreement on Acceptance of Foreign Labor and Employment Management" Article 4)
· Being healthy (not infected with infectious diseases)
· Be a skilled worker and have the necessary expertise
(3) Documents to be submitted
Documents to be submitted for work permits and alien registration are as follows.
(a) Documents for submitting work permits (No. 749 / LSW "Agreement on Acceptance of Foreign Labor and Employment Management" Article 6)
· Foreign Labor Import Application Form (Application form created by foreign workers' employers shall include the number of people, expertise, period and technology for Laotian workers so that Laotian workers can substitute for foreign workers The relocation plan must be clearly stated)
· Project Permit or Project Agreement (if available)
· Foreign workers plan (each term)
(b) Documents to be submitted for alien registration (Agreement on Acceptance of Foreign Labor and Employment Management No. 11, 749 / LSW of Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare)
· Registration Application Form (Signature of Foreign Worker Required)
· Foreign workers' import permit
· Legal visa
· Health certificate
· Academic certificate certifying expertise
· CV of foreign workers
Labor contract
· Photo (3 × 4 cm): 2 sheets
(4) Employment Extension Procedures for Foreign Workers
When prolonging the employment of foreign workers, it is necessary to submit the following documents to Laos state-run employment company as necessary application for extension of work permit (Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare Agreement No. 749 / LSW "Foreign Country Agreement on Acceptance of Human Labor and Employment Management "No. 12).
· Extension of Employment Period Application Form (Extension Reason Statement Described by User and Attachment of Residence of Foreign Worker Required)
· Employer's application form
· Applicant's income tax payment certificate
■ Employment obligation for local people and employment conditions for foreign workers
Companies must preferentially hire Laotians and hire foreign workers as necessary. In that case, it is necessary to prepare beforehand the procedures for alien registration. In addition, the ratio of the number of employees with local workers at that time must comply with the following criteria.
· For persons who have specific knowledge and perform physical labor, they do not exceed 10% of the total workers at the workplace
· For persons who have specific knowledge and who do brain labor, they do not exceed 20% of total workers at the workplace
In the case of hiring foreign workers beyond the above defined range, -
Salary design and calculation example of expatriate`s salary
In paying salaries to expatriates who are assigned to Laos, there is a difference in payroll method and applied tax rate between Japan and Laos, so even for that payment can not be said to be the same as Japan uniformly, Consideration of payment form etc. is necessary.
There is a difference in applicable tax rates between Japan and Laos, so if you pay the same salary as in Japan, the salary may be lower or higher.
The following progressive tax rates apply to the people of Laos. Currently, according to the Foreign Investment Promotion Act, individual income tax is imposed on the salary income of foreign workers including Japanese, with a uniform rate of 10%. However, in order to eliminate the differentiation of domestic and foreign capital, revisions have been made with respect to the uniform 10% tax rate, and the same rate as the local tax rate is applied.
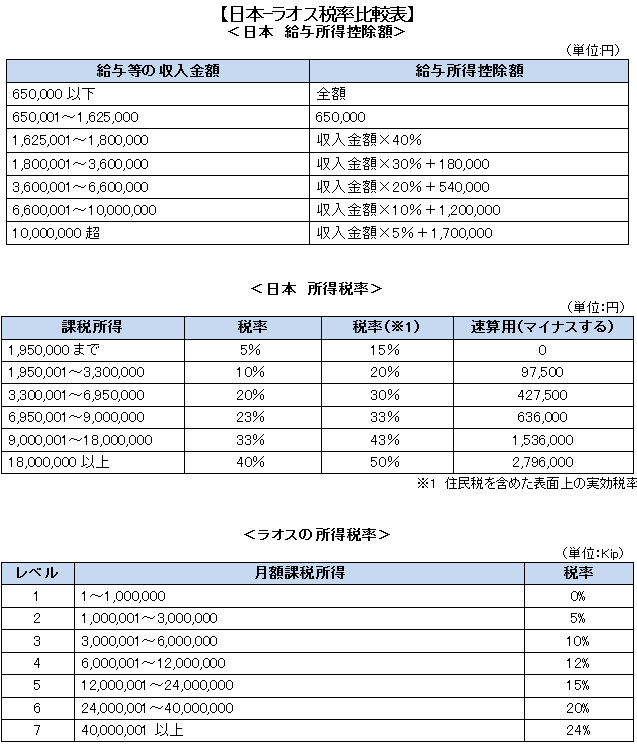
In paying salaries to Laotian expatriates, since there are differences in payroll method and applied tax rate between Japan and Laos, even when paying the salary is not equal to Japan uniformly, the salary amount setting and payment form We need to fully consider beforehand.
On the Japanese side, there are salary income deduction (650,000 yen) and basic deduction (380,000 yen), so income tax will not be applied if it is within 1,300,000 yen on an income basis. In Laos there is no deduction for salary income deduction and will be lower than in Japan. Therefore, gross up calculation for overseas assignees is needed in Laos.
Let's compare the taxable amount when Japanese expatriates actually receive salary in Laos against Japan.
■ Example of income tax calculation in Japan and Laos
(Preconditions)
40 year old man
Annual income in Japan: 6,480,000 yen
Dependent: None Estimated scheduled date of assignment: 3 years
* Social insurance fee will not be considered here.
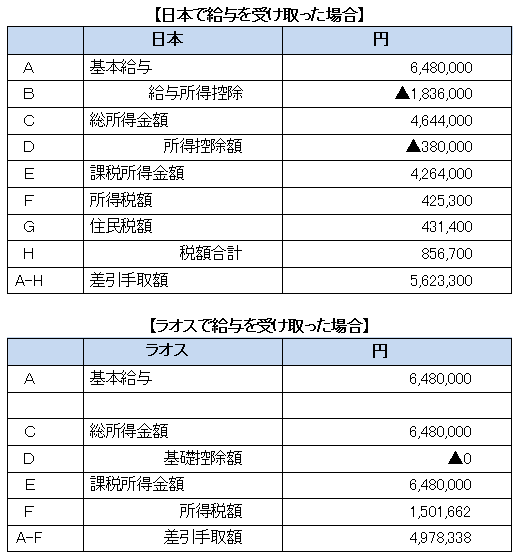 Thus, if an expatriate with an annual income of 6.48 million yen receives a salary in Laos, the amount of about 640,000 yen handover will be less.■ Gross Up Calculation Matching Committed AmountsAs mentioned earlier, due to the difference between the income tax rate of Japan and Laos, there are many cases where the takeover amount decreases by assigning to Laos as long as salary is not so expensive.Therefore, there are cases where gross-up calculation to compensate for the take-off amount received in Japan is made before assignment. Here, we will look at how much payment is needed to receive an amount equivalent to 5,623,300 yen for the amount of expatriate's expatriate in Japan with the annual income of 6,480,000 yen.
Thus, if an expatriate with an annual income of 6.48 million yen receives a salary in Laos, the amount of about 640,000 yen handover will be less.■ Gross Up Calculation Matching Committed AmountsAs mentioned earlier, due to the difference between the income tax rate of Japan and Laos, there are many cases where the takeover amount decreases by assigning to Laos as long as salary is not so expensive.Therefore, there are cases where gross-up calculation to compensate for the take-off amount received in Japan is made before assignment. Here, we will look at how much payment is needed to receive an amount equivalent to 5,623,300 yen for the amount of expatriate's expatriate in Japan with the annual income of 6,480,000 yen.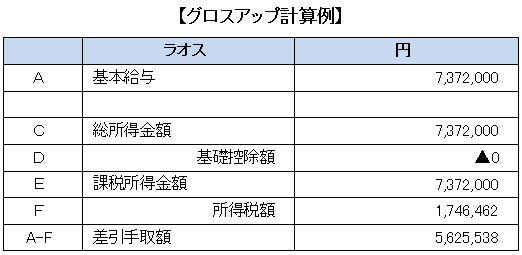 As shown in the table, in the case of a salary of 750 yen per year, the proceeds amount is 5,625,538 yen, which is almost the same amount. In other words, 7,372,000 - 6,480,000 = 8920,000 yen must be added and paid. The amount of money to be added varies depending on the amount of salary, but in most cases it will be necessary to add an additional amount of 1,020,000 yen or more, so it is necessary to consider the amount to be paid in advance.
As shown in the table, in the case of a salary of 750 yen per year, the proceeds amount is 5,625,538 yen, which is almost the same amount. In other words, 7,372,000 - 6,480,000 = 8920,000 yen must be added and paid. The amount of money to be added varies depending on the amount of salary, but in most cases it will be necessary to add an additional amount of 1,020,000 yen or more, so it is necessary to consider the amount to be paid in advance.
-
-
-
Websites
[1] 財団法人 海外職業訓練協会
[3] ラオス 雇用労働関係法令一覧 1.2 労働基準関係法令
[5] JOGMEC
[6] LAO PEOPLE’S DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC PEACE INDEPENDENCE DEMOCRACY UNITY PROSPERITY- LABOUR LAW(Amended)
[8] CAPITOL VISA SERVICES-Experts in obtaining visas and passports.
-
Other
[1] 保健省及び法務省法律公布部、「衛生、病気予防及び健康推進関連法」No. 04/ NA,(2001年4月10日公布)
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya