Laos
5 Chapter Accounting
-
-
1 Chapter Basic Knowledge
2 Chapter Investment Environment
2.3 Investment regulation and incentives
2.4 Industrial park information
3 Chapter Establishment
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.2 Establishment of business base
3.3 Company liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter Corporate Laws
4.4 Regulatory Body/Bodies And Affiliated Institutions
5 Chapter Accounting
6 Chapter Tax
7 Chapter Labor
-
-
-
Accounting system
■ Outline of accounting system
In 1986, socialism reform has begun to focus on liberalization of politics, economy and culture in Laos.
This reform is called as "Chintanakan Mai" meaning "New Thinking". After at the aspect of economy the economical policy called New Economic Mechanism: MEM was executed to accelerate and promote an external opening and an economization of market
《Examples of MEM》
· Liberalization of price (except utility fee)
· Unification of multiple exchange rates
· Integration of national and local general budget
· Trade liberalization
· Establishment of dual banking systemAlong with this economic change, the national system of financial accounting of the Lao PDR was established in 1988, and also in 1990 the law on Enterprise Accounting was established.
These bylaws had fulfilled the role of accounting standards until Lao accounting law was enacted in 2007.
Lao accounting system was established in 1988 and Laos corporate accounting law was established in 1990 (hereinafter both referred to as accounting standards), but these were originally promulgated toward domestic enterprises in Laos; the source of capital is only collected in Lao. However, the range of applicable subject expanded to foreign companies after foreign investment promotion act was enacted in March 1994 to promote the wide opening of market..Finally, Laos completed its unification and integration of accounting for economic activities.
However, as these accounting standards were significantly different from international accounting standards foreign enterprises needed reporting the actual accounting situation like financial statements based on not Laos accounting standards but IFRS’s one to their own countriesIn October 2004 Foreign Investment Promotion Management Act was revised and stipulated “you can use the other authorized international accounting system if require it.”
However, in order to utilize other accounting standards, it is necessary to obtain an agreement of the Ministry of Finance of Laos and notify annual accounting report to FIMC: Foreign Investment Management Committee with a certain requirements. As long as you perform business in Laos, it is a basic requisite that you comply with Lao accounting standards.The entity of setting Lao accounting standards is the Ministry of Finance of Laos which elaborates bylaws and provisions including accounting standards. Accounting standards elaborated by the Ministry of Finance are proposed by the Minister of Finance and publicized to the people by the approval of the Prime Minister (Article 18 of Laos Accounting Act).
Period of Accounting
Since the year of taxable income under Income Tax Act is stipulated as one year from January 1st to December 31st, it is generally set in conjunction with the tax year of the tax law in general. However, as a requirement to continue its period, you can arrange another 12 months as accounting period.
■Accounting book
The company has an obligation to update and keep its accounting book recorded of the business activities. In addition, it is obligation that a company must keep the accounting books and the proofs related to them for at least 10 years.
■ Inconsistent and mismatch of law system
In Laos there are corporate laws, accounting laws, audit laws, and tax laws to regulate enterprises, but there are some contradictions.
For example, despite audit law prohibits shareholders from being auditors of a corporation but, article 154 of corporate law permits this act. Also, corporate law requires public corporations and some private companies to take an audit of financial statements, but provisions of tax law doesn’t require it, thus balance sheet submitted to tax authority these is not audited. According to the accounting law and audit law enacted later than tax law, the adjustment of mismatch and inconsistent is stipulated as stating “the provision of the law concerned is prohibited by the other provisions of other laws, the law concerned is taken as priority." However, it’s no wonder that each relevant law must be matched, revised and modificated as emergency.
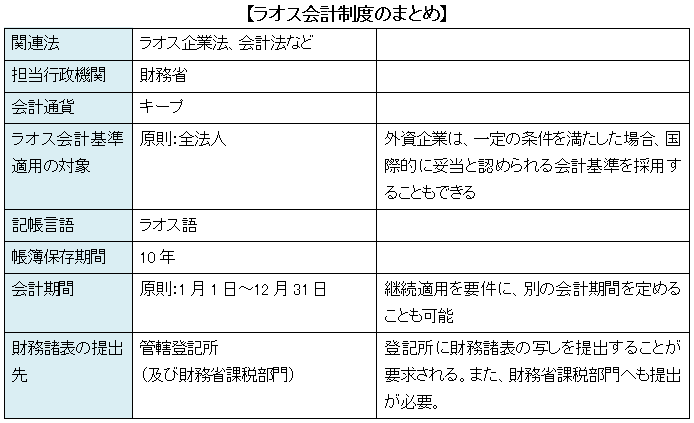
■ Laos Accounting Standards
[From home country standards to international ones]
The Laotian government had been unable to resolve the change with international accounting standards for a long time after adopting economic market shifting policy. But, after the conference of Laos Accounting Auditing Standards held in February 2006, Laos announced that they would introduce International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
With this announcement, Laos Accounting Law was enacted in 2007 as a first step of convergence with IFRS. The content conforms to IFRS and in principle, all corporations conducting business in Laos must comply with Laos's accounting law as the national standards of Laos.
Laos is supposed to achieve to comply with IFRS from 2016.
Problems of Laos’ accounting standards
According to World Bank's report and reviewing the financial statements of 28 companies in Laos including 4 commercial banks, 4 foreign-capital joint ventures, 3 companies with full foreign capitals and 5 airline companies, there were following differences from the required disclosure system of IFRS.

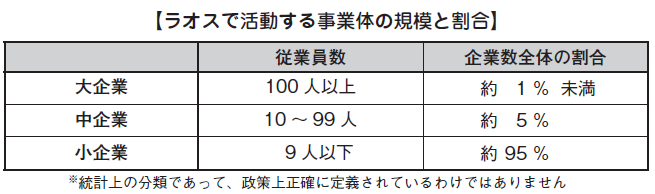
■ International accounting standards for small and middle enterprises: SMEs
As of 2011, nowadays, Laos doesn’t introduce IFRS toward SMEs of Laos. The reason is that SMEs are not yet able to reach the degree of IFSR at the point of management and accounting..
Approximately 80% of Laotian citizens are agricultural employees and in the case of such small enterprises, because most of them are domestic home industries and family management, they don’t reach the level that they can’t elaborate their accounting books and .financial statements finely.
-
-
-
Disclosure system
■ Disclosure schedule
All companies except the companies under the jurisdiction of Laos need to make disclosure procedures based on the provisions of general account.
Of companies applying general accounts, all companies except banks and insurance companies are obligated to prepare for financial statements within two months after the settlement date and submit the annual financial statements to taxation department of the Ministry of Finance (Article 37 of Laos Accounting Law). However, the extension of three months is accepted by applying..
By Requesting for disclosure to the notary of the company, the public can use the financial statements (Article 239 of the Corporate Law).
【Disclosure Schedule of General Accounting Applicable Company (Except for Banks and Insurance Companies)】
Disclosure document
The characteristic of the Lao accounting law is that it is obliged to prepare a monthly trial calculation chart by Article 15. All companies are required to compile monthly and quarterly trial tables and prepare financial statements and income statements.
Also, during the fiscal year, you are required to elaborate a balance sheet, a profit and loss statement, a calculating statement of change of shareholders' equity, cash flow statement, and note. However, according to the accounting law, quite a small company is approved to elaborate only income and outcome reports described of profits and losses of the company..
■ Penalty of violation of disclosure system
Some penalties are imposed on you accordance with the provisions of Article 161 of the Lao People's Punishment Act (2005) if there is any fraud or tampering in the disclosed information. Likewise if there are an illegal dividend of unjustified shareholders and a delay of submitting financial documents to the authority concerned.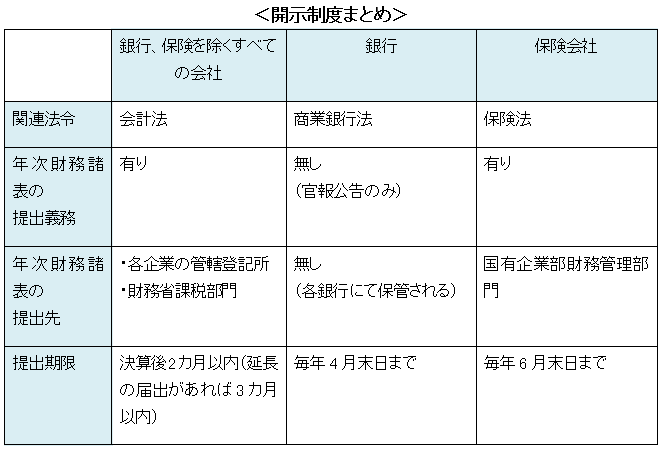 .
.
-
-
-
Audit system
■ Companies to be audited
Laos’ corporate law separately prescribes the audit of three different companies; a private company, a public company, and a state-owned company.
[Private company]
In private company, the establishment of the accounting auditor is, in principle, optional. However, in the case of a company whose asset value exceeds more than 50 billion kips, it is mandatory to establish an auditor (Article 153 of Corporate Law).
Therefore, if the asset value exceeds more than 50 billion kips, you must appoint an accounting auditor at the General Meeting of Shareholders and take an accounting audit of the annual financial statements every year.
[Public company]
From the date of company establishment, you must set an auditor (Article 179 of Corporate Law).
[State-owned company]
In this description, a state-owned company means the company established with full investment of the government, or the one whose 50% of shares sold to the private company up to 50% of total shares.
In principle, you have to establish an accounting auditor, but if you do not set up an accounting auditor, you’re required to audit the financial statements before the date of general shareholders' meeting once a year Act 216).
■ Qualification requirements of the auditor
Auditors perform for the external audit of corporation after passing the exam of certified public accountant: CPA prescribed by the Association of Laos’ CPAs and being registered as a certificated public accountant after experience of the audit corporation. The certified public accountants are allowed to act on the tax side as well and can also become liquidators when a company is closed down.
In Laos, the existence of certified public accountants has appeared since 1998. The association of Laos CPAs has been established, whose role and responsibility was stipulated on from Article 66 to 68 of Accounting Law and Articles from 54 to 57 of Audit Law.
Currently, while more than 2,000 companies are registered in Laos, there are only about 150 CPAs of Laos. The shortage of accountants is a serious problem. Especially large corporations require the appropriate numbers of CPAs for auditing, therefore they use an international accountant firm.
There are local small-sized 40 accountant offices in Laos, however, you can say they are mainly engaged in advisory and support of taxes and accounting rather than audit task.
-
-
-
Websites
[1] Audit&LAS
-
Other
[1] ビジネスガイド
[2] GLS ビジネスフォーラム
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya