Malaysia
2 Chapter Investment Environment
-
-
1 Chapter Basic knowledge
1.3 Political regime and history of Malaysia
1.4 Education and education system in Malaysia
2 Chapter Investment Environment
3 Chapter Establishment
3.1 Characteristics of business base
3.2 Establishment of business base
3.3 Liquidation and withdrawal
4 Chapter M&A
4.2 Points to keep in mind when doing M & A
4.3 Laws and regulations concerning M & A
4.5 Other considerations in M & A
5 Chapter Corporate Law
5.2 Shareholders (shareholders meeting)
5.3 Director (Board of Directors)
6 Chapter Accounting
6.1 The accounting system of Malaysia
6.2 Malaysian Accounting Standards
6.4 Disclosure system in Malaysia
7 Chapter Tax
7.2 Domestic tax law in Malaysia
8 Chapter Labor
8.3 Social security system in Malaysia
8.4 Points to keep in mind while residing in Japan
9 Chapter Q&A
-
-
-
Latest News & Updates
【Regarding foreign currency capital restrictions on export companies】
It is anticipated that Malaysia, a trading country, will suffer a great deal of damage once Pres. Trump, the US new President, announced that it will abolish the TPP policy once again. Also, according to the IMF's announcement, Malaysia knows that the outlook for foreign currency reserves at the end of the year is $ 100 billion (about 11.3 trillion yen) and short - term foreign debt has deficit of 128.2 billion dollars. In the November foreign exchange market, the Malaysian Ringgit (Ringgit) performance against dollar is the worst among the emerging market currencies in Asia and its outflow of capital among emerging markets are reported to be the weakest.
Against this backdrop, the Malaysian Central Bank announced capital restrictions on foreign currency last December 2 in order to stop the ringgit depreciation. This regulation was being imposed from December 5 (Monday). Below is the Japanese translation of the content on the website of the Central Bank of Malaysia.
The outline of the regulation is as follows for eligible export companies:
1) Exporters must retain only up to 25% of export proceeds in foreign currency as against 100% done at the present. They may, however, hold high balances with approval from BNM to meet their obligations in foreign currency.
Presently exporters can possess 100% foreign currency money acquired from the exports. However because of the new regulation, the possession will be limited to as low as 25%. The possession of more than 25% is possible upon the permission of the Central Bank.
2) Payment by resident exporters for settlement of domestic trade of goods and services is now to be made fully in ringgit.
In the future, it is necessary to do all domestic transactions (goods and services) with ringgit. Exporters cannot use foreign currency.
Through the special accounts of all banks, the ringgit which the exporter acquired from export (after money exchange) will be applied an interest rate of 3.25% per year, which is higher than the market interest rate. This measure will be applied until December 31, 2017 but will be subject to further review.
4) Exporters are also able to hedge and unhedged up to six months of their foreign currency obligations.
Exporters can hedge foreign currency assets and liabilities up to six months.
The main point is that export companies will be able to hold up to 25% of foreign currency until that time will need to hold ringgit in domestic transactions. Government's intention is to stop the current situation where the value of ringgit will stop declining and capital out flows will be visible through.
【About the business license in Kuala Lumpur city】
The main purpose of mandating to secure business license in Kuala Lumpur is to crack down many illegal stalls that are built in the city.
Companies that acquire business license must meet either of the following requirements:
a) Investment of 50% or more from individual shareholders in Malaysia
b) Malaysian citizenship employees must be 50% or more of the total number of employees to be hired.
All companies Doing Business in KL.
However, if your company was approved as "Management Office", you do not have to fulfill this regulatory requirement.
* Although detailed definition of Management Office is not fixed and is supposed to be changed by the officer, basically, a Management Office should not buy or sell any goods in the site of business that they applied for. If they do so, their business office will be subject to inspection after receiving an "Appeal Letter".
Opinions of the officials are divided as to whether to apply this regulation when renewing a business license. For some officials the application of the regulation is unnecessary while others believe that it is a responsibility to apply the regulation. However, many officials approved to apply this regulation even at the time of renewal. So they also think of better direction or way in applying the regulation.
The following are the steps to be taken for first time application. It is said to be probable that upon using the new regulation, the same process of application will be followed.
1. Application
* Here, "Reject Letter" will be issued from DBKL if the above requirements are not satisfied.
2. Issue "Appeal Letter" for "Reject Letter"
※ In "Appeal Letter", fill in capital structure, business location, business purpose etc. Also, temporary business license will be issued after receiving "Appeal Letter". Because the main objective of the regulation is to prevent outdoor and small scale fraud caused by as street vendors, as per the official in charge, for the possibility of the approval of "Appeal Letter" received from restaurants and retail stores in shopping malls and hotels owners is strong.
3. Visit by DBKL official
Here, after submitting "Appeal Letter", inspection officers without prior notice will do the inspection if more than 50% of the total employees who applied in the office are Malaysian citizen and the business is located in the appropriate location.
4. After inspection, issue this business license
This is the issuance of a business license where application of new regulation starts.
However, due to the nature of Malaysia, I think it will take a long time for everyone to proceed in the same way. In addition, although we talked with several officials this time, we feel that further investigation is necessary for issues such as differences in opinions of each officer. -
Investment regulation
Malaysia is a multinational country where Malay, Chinese and Indian people live, and economic disparity among ethnic groups was a problem.
Malaysian individuals and indigenous people, as defined in the Federal Constitution, are called Bumiputera. The overall policy for preferential treatment and protection for Bumiputera is called "Bumiputra Policy". This policy has functioned not only to eliminate on Malays' economic disparities but also serves asr foreign capital regulation. The purpose of Bumiputra Policy is to support Bumiputera companies, to improve the educational environment of Bumiputera, and to support employment.
However, recently Bumiputra Policy regulating on the establishment of foreign capital enterprises have been greatly relaxed. This results in permitting a 100% foreign capital investment in most industries especially manufacturing to enter the country. However, the former regulation remains in the service industry, especially in the wholesale and retail sector, such as convenience stores. -
Prohibited industries
In the "Guidelines on Foreign Capital Entry into Malaysia Distribution Transactions and Services" announced in 2010, the lists of business related in distribution industry, retailing, wholesale industry stipulated as follows are not allowed to enter the market with foreign capital investment:
· Supermarket, mini market (Sales floor area is less than 3,000 m 2)
· Grocery store, general store
· Convenience store (open 24 hours)
· Newspaper dealerships, grocery stores
· Pharmacy (a pharmacy that sells traditional herbs and herbal medicines)
· Gas Station (Including Convenience Stores)
· Permanent market (wet market)
· Permanent walkway store
· Business related to the strategic interests of the state
· Cloth shop, restaurant (non-high-end shop), bistro, jewelry store etc.
-
Investment ratio · Capital regulation
Besides to prohibition in some industries, restrictions on investment ratio and minimum paid-in capital regulation are established for each industry.
① Business established for the benefits of national interests
For businesses related to national interests (areas related to national interests such as water, energy and electricity supply, broadcasting, defense, security, etc.), foreign capital entry is limited to 30%.
② Manufacturing industry
In the manufacturing industry, 100% foreign capital entry is permitted in most companies, no capital requirements are imposed. However, if you are going to enter the manufacturing industry you will need a license issued by the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI) and apply to the Malaysia Investment Development Authority (MIDA). Acquisition of this license is obligatory for manufacturing companies with shareholder's equity of 2.5 million ringgit and employees of more than 75 employees.
③ Service industry
For the service industry, except industries dealing with rendering service and selling goods at the same time like(petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, harmful substances, etc.) separate laws in the logistics industry, wholesale / retail industry and others being prescribed. The minimum paid-in capital amount for a pure service company is set as one million ringgit.
The jurisdiction body over the service industry is domestic trade, cooperative association and consumer Ministry (MDTCC).
Each industry will be described in details below.
(③.1) Logistics industry
In the logistics industry regulations are particularly strict, and capital regulations are set according to the type of industry. Refer to the table below..png)
(③.2) Wholesale and retail trade
Regarding the wholesale / retail industry, the capital requirement varies depending on the form of dealer. See as follows.
A hypermarket refers to a dealer with a sales floor area of 5,000 m 2 or more while a supermarket refers to a dealer with floor area that is over 3,000 m 2 but less than 4,999 m 2.
.png)
-
Other regulations
① ExchangeForeign exchange regulations are set forth in the Financial Service Act 2013 (Financial Service Act 2013) and the Islamic Financial Service Act 2013 (Islamic Financial Service Act 2013) as follows..png)
② Land ownership regulationIn the case of acquiring real estate property under the conditions falling under the following categories, it is necessary to apply to the Prime Minister's Economic Planning Agency based on the "Guidelines on Acquisition of Properties" (Guideline on the Acquisition of Properties).
.png)
① Restriction on employment of foreign representative
Foreign-affiliated companies are allowed to hire foreigners in areas where Malaysians with required expertise are not available. However, in order to protect the employment of Malaysian citizens, Malaysian are trained in various jobs and technical skills are being improved. Restrictions are being imposed on the number of foreign resident expatriates who can be dispatched by foreign-funded enterprises and the allowable period of their stay.
Categories of foreign resident staff who can be dispatched are according to job type, key post, time post, etc. The number of people accepted in each post depends on the business contents. In areas and businesses where training is the focus ofthe government, authorization of dispatch becomes easier (see table below)..png)
.png)
In addition, expatriates staying for more than two years must acquire a managerial position called Employment Pass and a work visa for professionals.
To obtain employment pass, there are conditions to be satisfied such as minimum salary of 5,000 ringgit per month, employment contract period minimum 2 years, minimum capital (see table below) etc..png)
④ About employment of localsIn addition, the Malaysian Employment Act (Employment Act 1955) prohibits the dismissal and reduction of local personnel to prioritize the employment of foreigners if the local personnel possessed the necessary abilities required by the company. (Article 60N of the same Act).
-
-
-
Incentives overview
■ Overview
Malaysia has a wide variety of investment incentives to encourage foreign investment. There are incentives such as preferential treatment by industry, tax incentive measures, bonded preferential treatment and tariff reduction at the time of importing capital goods. Pioneer status and investment tax credit are the pillars of investment incentives. Both of these are investment incentives given to companies who conduct businesses that fall under the incentive project and companies that manufacture promoted products.
■ Pioneer status (PIONEERSTATUS)
Pioneer status is a system established by the Investment Promotion Act 1986 and other laws. Whether the application of the company is approved or not will be judged by considering the level of value added, the technology used, the contribution to strengthen inter-industry cooperation, etc.
The applicant for pioneer status is the Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA).
■ Investment tax credit (Investment Tax Allowance (ITA))
As an alternative to pioneer status, companies can apply for investment tax deduction (Investment Tax Allowance (ITA)). Companies that have been approved with ITA will first be eligible for qualified capital expenditure incurred within 5 years from the date of qualified capital expenditure (expenditure on factories, plants, machinery and other equipment used in licensed projects). The company will get 60% deduction. This deductible amount can offset 70% of the statutory income of each year, and unused deductions can be carried forward in the following year until the full amount is used.
■ Selection of pioneer status and investment tax credit
As mentioned above, there are pioneer status and investment tax credit (ITA = Investment Tax Allowance) as the main preferential treatment, but which preferential treatment is to be taken into account is as follows. For an entering company, to apply for establishment of a local corporation. Selection of pioneer status or ITA will be selected at the beginning upon submission of approved "Manufacturing License" to Malaysia Investment Development Agency (MIDA).
Although the center of enterprises that are recognized as pioneer status is the manufacturing industry, investment companies for agriculture, tourism (including hotels), licensing services, research and development, training, environmental protection activities, etc. are also accepted. If the initial investment is large in the manufacturing industry and the deficit continues for several years after the start of operations apparently, the benefits of Pioneer status 'partly exempted income tax' cannot be enjoyed. Companies that invest heavily in plant facilities should be pleased if they were given the "investment tax credit (ITA)", not the pioneer status. A general manufacturing company that has been granted "investment tax credit" shall not exceed five years non-operated from the date of the first occurrence of "qualified capital expenditure" (expenditure on factories, plants, machinery and other equipment used in the approved project). A deduction frame equivalent to 60% of the total amount of "qualified capital expenditure" that occurred in the same period can be offset and as well as 70% of the statutory income of each year. The unutilized deduction frame can be carried over and use on the following year until the full amount was utilized. The company will only pay the excess corporate tax after offsetting the deduction facility during that period.
Capital deductions that are not yet utilized during the Pioneer status period can be carried over with cumulative losses and can be deducted from revenues after the Pioneer status period.
Below, we will explain the application of pioneer status and investment tax deduction for each type of industry. -
Incentives in the manufacturing sector
The encouraged industries in the manufacturing sector are categorized as follows.
① Hi-tech industry
② Strategic project
③ SME (manufacturing industry)
④ Specific machine equipment manufacturing industry
⑤ High added value automobile parts manufacturing industry and Hybrid vehicle manufacturing industry
⑥ Industries that manufacture using palm oil biomass
① Hi-tech industry
The industries that are considered high-tech are defined as follows.
· Development and design of computer industry
· Development and design of medical equipment, chemical equipment
· Biotechnology
· Advanced materials (polymers, biopolymers, nanoparticles)
· Alternative energy technology
Steel
Furthermore, in order to receive preferential treatment, (1) the proportion of R & D expenditure in total domestic sales is at least 1% per year (the company is given a three-year grace period from the start of the project until this condition is met), ② At least 15% of chemistry / technology staff who acquired diploma graduation qualifications or diploma (junior college or vocational school graduation) and have experience of more than 5 years in related field.
If these conditions are satisfied, you can receive exemption from investment tax or pioneer status for the following contents..png)
① Strategic project
"A strategic project is a project in which a long-term investment plan, a large amount of capital expenditure, advanced technology, together with a comprehensive and wide-ranging industry collaborate and has an important impact on the economy. It is defined as activities important for the whole state."
If it falls under a strategic project, you can choose to receive either of the following pioneer status or investment tax exemption.
① SME
Small and medium enterprises are defined as companies with capital of 60% or more in Malaysia with paid-in capital of 500 thousand ringgit or less, or companies with Malaysian capital of 100% and paid-up capital exceeding 500 thousand ringgit but below 2.5 million ringgit.
For the manufacturing sector, you need to be involved in manufacturing engaging in the following industries.
MIDA incentive target SME industry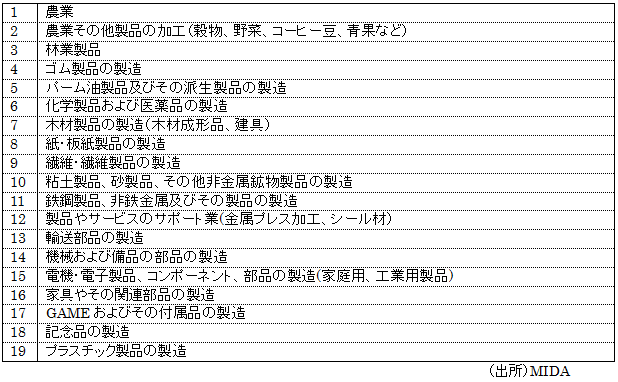
If the company falls under the category of SME in the manufacturing sector, it can choose from either of the following pioneer status or investment tax exemption.
Even in the case of individual companies and partnerships, this preferential treatment can be taken over by a newly established private limited company or limited company. At that time, the conditions that may be satisfied are (a) the added value is at least 15%, (b) the corporate activities contribute to the development of local society.
In addition to the incentives listed in the table above, corporate tax rates of 25% will be applied for the remaining income with a reduction tax rate of 20% for 500,000 ringgit of the taxable income in small and medium enterprises.
① Specific machine equipment manufacturing industry
For the machinery and equipment manufacturing industry, industries that can receive preferential treatment are specified.
(C) Palm Oil Biomass Equipment (d) Renewable Energy Equipment (e) Renewable Energy Equipment (a) Machinery Equipment (Machine Tools, Material Handling Equipment, etc.) (b) Specific Equipment and Supplies. Basically, they are the manufacturer of energy saving equipment.
Mechanical equipment manufacturing industry that meets the above conditions can receive following pioneer status or exemption from investment tax.
① High value added automobile parts manufacturing industry and Hybrid vehicle manufacturing industry
Companies that manufacture certain important and value-added automobile parts and components can receive preferential treatment.
Automobile parts subject to preferential treatment are (a) transmission system (b) brake system (c) air bag system (d) steering system, and hybrid vehicles and electric vehicle parts subject to preferential treatment are, (A) Electric motor (b) Electric battery (c) Battery management system (d) Impater (e) Electric air conditioner (f) Air compressor.
Enterprises manufacturing target parts can receive the following pioneer status or exemption from investment tax.
Companies that assemble and manufacture hybrid vehicles and electric vehicles can receive this preferential treatment as well as the vehicles assembled and manufactured in Malaysia and also, the excise duty exemption on industrial adjustment funds will increase by 50%.
⑥ Industries that manufacture using palm oil biomass
For companies that manufacture value added products such as particle boards, MDF boards, plywood, pulp and paper by utilizing palm oil biomass, the following incentives can be selected.
Even after the period of pioneer status and investment tax deduction is over, a company can enjoy additional incentive measures can be taken if certain conditions are satisfied as follows.
· Reinvestment deduction
In the case of additional investment aimed at automation, modernization, diversification of existing business, the company can receive reinvestment deduction (RA). Exemption of investment tax of 60% in capital expenditure may be enjoyed upon submitting the application to the National Tax Agency.
The company should be operating for more than 36 months as a condition of reinvestment deduction. The incentive will be granted for 15 years from the day of reinvestment.
In addition, the company cannot dispose assets subject to reinvestment deduction within five years from reinvestment.
· Accelerated depreciation
Even after the objective period of reinvestment deduction, privileged product manufacturers can further undergo accelerated depreciation on the tax system. By applying to the National Taxation Bureau, you can be given a capital expenditure deductions of 40% in the first year of application and three years' deduction of 20% annually thereafter.
Likewise, (a) within 2 years, (b) within 1 year, and (2) when installing (a) power stabilizing equipment, (b) security system equipment, and (c) industrial building system equipment, application of accelerated depreciation within 3 years is permitted.
· Group deduction
With respect to income of companies within the same group, we can offset the non-deductible loss for the current fiscal year from other companies in the group by 50% to 70%.
In order to receive this group deduction, it is necessary to meet the following criteria.
· The receiving company and the delivery company hold paid-up capital of ordinary shares of RM 2.5 million or more respectively
· The receiving company and the delivery company are in the same accounting period
· The direct or indirect shareholding of the receiving company and the delivery company by the group is not less than 70%
· 70% shareholding must be continuous throughout the previous year and the year
· Ownership and losses from acquisitions by foreign companies are not eligible for group deduction
However, companies subject to the following preferential treatment are not subject to group deduction.
· Pioneer Status
· Investment tax deduction / investment deduction
· Reinvestment deduction
· Exemption from shipping profit
· Income tax exemption under Article 127 of the 1967 Income Tax Act
· Investment preferential company -
Major investment incentives to agricultural production department
Agricultural cooperatives, agricultural associations and individual and partnerships engaged in agriculture that produce qualified items may possibly receive incentives.
The four major privileged industries in the agricultural production department are as follows.
① ① Agricultural production industry
For the agricultural production industry, companies that produce items indicated by LIST OF PROMOTED ACTIVITIES & PRODUCTS (APPENDIX IA) are eligible for preferential treatment. Among them, the items related to agricultural production are agricultural products from cultivation of plants, agricultural products from cultivation of fruits, vegetables, cacao, livestock products, aquatic products, medicines and cosmetics and supplements necessary to produce plants.
As for the agricultural production industry, you can receive preferential treatment as well as manufacturing industry.
② Food manufacturing industryThe food production industry is an activity to process agricultural products for further consumption.①. By setting preferential treatment in two stages of food-related industry, the ratio on the import of raw materials may be suppressed
In the food production industry, if there is a subsidiary engaged in processing production and a parent company investing, incentives are set up for both sides. (A) The parent company has an investment ratio of 70% or more (b) Production activities approved by the Ministry of Finance (cultivation of kenaf, vegetables, fruits, herbs, spices, aquaculture, cattle , breeding of goats and sheep, deep sea fishery) (c) The production business must start within one year from the day of grant of incentive measures.
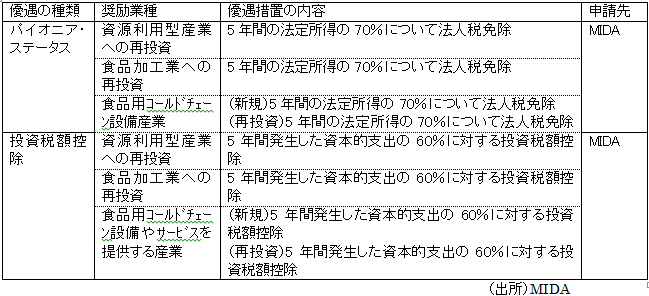
③ Halal food manufacturing industry (Appendix IV)Regarding Halal Food Production, in order to manufacture internationally compatible quality Halal foods, companies that produce Halal foods export products have preferential treatment so that modern facilities can be used. Companies that have acquired Halal certification by the Malaysia and Islamic Development Authority (JAKIM) can apply to MIDA and receive investment tax deduction of 100% of the total capital expenditures incurred for five years.
In addition, if it falls under the following projects, it is possible to receive separate preferential treatment.
· Special processed food· Pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, personal care products· Livestock Food, Meat Products· Halal raw material· Transportation industry·Warehousing business· Transportation industry
 ④ Industries providing cold chain equipment and services for food
④ Industries providing cold chain equipment and services for foodCold chain equipment for foods refers to frozen warehouses and frozen car equipment for fresh foods. Incentives are provided for companies that provide services related to this.
The contents of the incentive measures are as shown in the table below.
■ Additional incentives (agriculture)For the agricultural production department, additional incentives such as the following are set up.
(Reinvestment deduction)
Companies that produce main food (rice, corn, vegetables, root vegetables, livestock and fishery products) over 36 months since the establishment can receive investment tax deduction of[U1] % on s capital expenditure for over 15 years from the first year of reinvestment.
(Subject to investment tax credit on capital expenditure)
The agricultural production department subject to investment tax deduction for capital expenditure are as follows.
· Land clearing and preparation
· Crop planting
· Breeder stock for culturing
· Breeder stock of livestock
· Introduction of plants and machinery equipment used in Malaysia for cultivation of crops, pastoral farming, cultivation, inland fishery, deep sea fishery, other agriculture · animal husbandry
· Purchase of structures, lands, buildings, structures including bridges and structural improvements
Also, it is permitted to carry out accelerated depreciation after 15 years from the period of reinvestment deduction, and it is possible to deduct the 20% annual deduction in the first year of taxation and 40% capital expenditure deduction.
(Ministry of Finance approved agricultural project)
Furthermore, if a company is engaged in an agricultural business approved by the Treasury Department it can obtain a 100% deduction for capital expenditure. The target business is as follows and capital expenditure is the same as the object of reinvestment deduction.
· Cultivation of vegetables and fruits (papaya, banana, passion fruit, star fruit, guava, mangosteen)
· Cultivation of potatoes and root crops
· Cultivating herbs and spices
· Farming for grains for feeding and water cultivation
· Cultivation of ornamental fish
Fish and shrimp farming (pond cultivation, aquarium farming, marine cage farming, offshore ocean cage farming)
· Tragai, mushrooms, mussels and laver cultivation
· Small prawns · shrimp · fish hatchery
· Specific variety of forest plantation project
(Re-investment in resource utilization type industry, food processing industry)
If you reinvest in the resource utilization industry, food processing industry and food cold chain equipment industry related to the agricultural production department, it will be subject to preferential treatment. Industries in which reinvestment is encouraged are indicated in the LIST OF PROMOTED ACTIVITIES & PRODUCTS (APPENDIX IE). For companies whose capital from Malaysian exceeds 50% and are engaged in resource utilization type industries, industries using palm oil and rubber, preferential treatment is established,
Similarly, preferential treatment may also be applied to companies under food processing industry with 60% capital from Malaysian capital Regarding the cold chain equipment industry for food, there are preferential treatment even in the case of new investment, but it is limited to related services for perishable agricultural products.
[U1]No percentage indicated.
-
Major investment incentive measures to service sector
Various investment incentives are also set up for the service industry. The following four major industries are applying preferential treatment from MIDA.
① ① Tourism industry
The tourism industry includes eco-tourism and agro-tourism, and the privileged industries include hotel business, construction of holiday campgrounds, indoor and outdoor theme parks, recreation business, construction and operation of convention centers (Those that can accommodate people 3,000 people).
② ② Environmental management
For MIDA, the companies that will conduct environmental management activities for the following four industries as environmental management projects,: (a) forest plantation project, (b) hazardous waste storage, treatment and disposal project, (c) energy conservation service industry, and (d) waste recycling business will be given preferential treatment.
(A) Because the forest plantation project is a strategic project, (b) the storage, treatment and disposal of hazardous waste project is to promote the establishment of related facilities, (c) energy conservation service industry and (d) The waste recycling project is encouraged as it leads to the promotion of environmental protection.
In addition, (d) waste recycling business includes agricultural waste, agricultural byproduct, recycling of chemical substances, and manufacturing of regenerated wood.
For (c) Energy preservation service industry also gives incentives to companies that implement energy conservation projects within their own company.
③ ③ Research and Development
R & D is a systematic survey in the field of science and technology. It refers to activities aimed for the improvement of production and materials, equipment, products, products and processed goods.
The main preferential treatment is as follows.
In order to receive preferential treatment, the following conditions must be satisfied.
· Research to be conducted economically brings benefits to national interests
· More than 70% of revenue will be generated by this research activity
· If it is related to the manufacturing industry, more than 50% of all employees have proper qualification as a technical position
· In the case of agriculture related work, more than 5% of all employees have proper qualification as a technical position
However, the following activities are not included.
· Quality control of products, regular inspections of materials and equipment
· Survey of humanities and social science
· Regular collection of materials
· Efficiency survey and management research
· Marketing research and sales promotion activities
Regarding research and development, it is possible to deduct the profitable expenditure required for research and development for the business approved by the Ministry of Finance.
The following expenditures are deductibles:
· Payment to approved research organization
· Payment for services provided by contract research and development company
· Malaysian training expenses
④ ④ Training
The subjects that can be given preferential treatment at the personnel development institution are as follows:
-
Preferential treatment focused on the function of the company
① Capital deduction for promotion of automation of labor intensive industry
MIDA promotes early automation of industries with high labor intensive rate (especially natural rubber products, plastics, wood, furniture, textile etc). For these industries, company can get a 200% tax deduction for the first 4 million ringgit for expenditures incurred to promote automation, which occurred between 2015 and 2017.
② Preferential treatment for establishment of Principal Hub (Principal Hub)
Incentive measures for the establishment of major bases (companies that utilize Malaysia as a business base for domestic and overseas management and supervision) is an alternative to IPC, RDC, and OHQ. The corporate tax rate is reduced to 0 to 10% for companies recognized as the main bases.
-
Investment incentive measures focusing on the region
① Investment incentive measures for Multimedia Super Corridor (MSC)
The Multimedia Super Corridor is a site provided by the Malaysian government to create, sell and use multimedia products and services to become a base for IT development in Asia. The Malaysian Government provides a site of 15 km east to west and 50 km north / south extending from Kuala Lumpur region.
The MSC status is given by the Malaysian government through the Multimedia Development Corporation (MDeC) to companies engaged in information and communication technology business in MSC Malaysia. The following will be subject to preferential treatment upon obtaining MSC status.
② Iskandar · Malaysia and large-scale long-term development plan (corridor plan)
In addition to the above, the Malaysian government is promoting a large-scale long-term development plan (Iskandar · Malaysia, Northern Corridor Economic Area, East Coast Economic Area, Mackerel Development Corridor, Sarawak Renewable Energy Corridor) for the purpose of rectifying regional disparities.
As an incentive, exemption from corporate tax for accredited project for a certain period of time etc, will be given. However, details are different for each area.
③ Preferential treatment on low development area
Low development areas are areas with no specific designation and will be considered with investment promotion agencies.
If deemed eligible, you can receive 100% corporate tax exemption for 10 years, exemption from income tax on capital expenditure and exemption from stamp duties when expanding business or conducting a new business.
① ④ Preferential treatment on industrial area
Incentive measures concerning industrial areas aimed int expanding the infrastructure of the area thorough maintenance and management, and promoting its growth and development and its neighboring areas.
If it deemed qualified, you can receive 100% exemption from corporate tax for 5 years from the start of the project.
② ⑤ Incentive treatment on goods tax (GST)
From April 2015, excise taxes were also introduced in Malaysia and tax payment of 6% was obliged for trading transactions. But free areas (areas subject to exemption from import tax and excise tax imposed in the main customs area ) and in a bonded factory (a company that is located in an area other than free areas and manufactures export goods), sales transactions between free regional companies or bonded factories are exempt.
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya