DubaiAbuDhabi
5 Chapter M&A
-
-
1 Chapter Coming Soon
2 Chapter Basic knowledge
3 Chapter Investment Environment
3.1 Present state of business environment 2019.
4 Chapter Incorporation
4.1 How to open a company in Dubai
5 Chapter M&A
5.1 Trends in M & A in Dubai and Abu Dhabi
5.2 Laws and regulations concerning M & A
6 Chapter Company Law
6.1 Organization of the company
6.2 Free Zone Establishment (FZE)
6.3 Free zone · company (FZCO)
6.4 Limited Liability Company (LLC)
6.6 New commercial company law
7 Chapter Accounting
8 Chapter Tax
8.1 Tax relating to entry into Dubai / Abu Dhabi
8.2 Individual provision of international tax
8.3 Individual Issues of Domestic Tax Law
9 Chapter Labor
9.4 Points to keep in mind while having Japanese people in Japan
-
-
-
Trends in M & A in Dubai and Abu Dhabi
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is made up of seven emirates (Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Um Al Kai Wine, Fujairah, Ras al Hihma). Because of the large number of Japanese firms entering the country, this chapter mainly describes Abu Dhabi Emirate and Dubai Emirate, but with regard to the place which is described as UAE, it is common to all 7 emirates. There are not many M & A transactions in UAE. The following graph shows the number and amount of M & A published in UAE published between 1999 and 2013. The total number of M & A transactions in 2012 is over 160, which is quite small compared with the published M & A number of developed countries (about 10,000 in the United States, about 3,000 in the UK, about 1,800 in Japan) I will. Before Lehman shock in 2008, there was a trend of increase, but after that, both the number of cases and the amount of money decreased sharply.The number of acquisitions (In-Out) by Middle Eastern companies by Japanese companies is 6 in 2011, 4 in 2012 and 13 in 2013, of which the number of M & A for UAE is 3, 0, It is one case (RECOV survey). It can not be said that advancement to UAE by M & A of Japanese companies is progressing.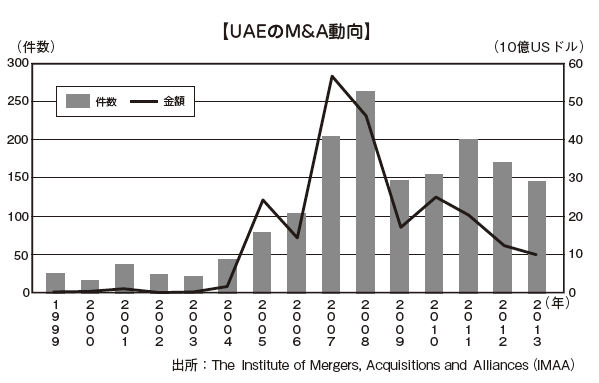
-
-
-
Laws and regulations concerning M & A
UAE's M & A market is not mature enough like the developed international market, but it is the most advanced in the Middle East and North Africa region. The law has been enacted to develop M & A transaction procedures, and ultimately the goal is to match UAE to the international market standards of developed countries. In M & A, there is a unique system between UAE and Dubai International Financial Center (DIFC: Dubai International Financial Center), respectively. Therefore, when doing M & A at UAE, it is one of the important issues which target company belongs to which jurisdiction. UAE legal regulation is almost useless in DIFC and vice versa. In each jurisdiction, there are investment regulation and commercial investment law as the main regulations concerning M & A.
-
Investment regulation
Companies founded at UAE must have one or more UAE co-investors holding 51% or more of their share capital and the UAE co-investors are employees of UAE citizens or corporations managed by UAE citizens It must be. However, some businesses (real estate brokers etc.) must possess 100% UAE. Meanwhile, there are no restrictions on holding shares of foreigners in DIFC, there is no minimum investment ratio by UAE citizens, as in UAE law. Foreign financial institutions can also launch their business without local co-investors.
■ Regulation by IndustryIn UAE, most industries are open to foreign investment except for some industries such as finance and medical institutions. However, careful attention is required because there is restriction by the investment ratio to establish a local corporation. Licenses for starting a business can be obtained from each emirate government. All foreign companies except companies in the free zone need to register with the Federal Ministry of Economy, and industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing industry and pharmaceutical industry are required federal government approval.
■ Regulation by ownership ratioIn establishing a subsidiary in UAE, the investment ratio of foreign capital is limited to 49% at maximum. In other words, it is the principle condition of establishment that UAE citizens contribute 51% or more, there are exceptions as in the following cases.
· In case of a branch office of a foreign company or a representative office※ UAE citizen or corporation with 100% UAE capital required sponsorship· Individual business entities (medical services, legal consultants etc.) of professional occupation※ The above sponsors are necessary· In cases where ownership by 100% UAE capital is required by law· 100% GulfCooperation Council (GCC) In the business field that is permitted to be owned by capital (GCC is the Gulf Cooperation Council to which the six Middle East / Saudi Arabia countries such as UAE, Saudi Arabia, etc. are members)· A company with 100% GCC capital partnership with the UAE citizen· When establishing a local corporation in the free zone* It is possible to establish a company with 100% foreign capital
■ Regulations on land ownershipThere are no federal laws that allow foreign owners to own land. However, each emirate country regulates land ownership of foreigners by its own law. In Dubai, you can own or hold 99 years long term lease for citizens of UAE and other GCC countries (or 100% owned company). Other foreigners will be available only in designated areas. In Abu Dhabi, in the case of UAE citizens, it is possible to own, the citizens of GCC countries can possess only within the designated area, and the other foreigners lease for only 99 years within the designated area or acquire the land use right for 50 years It is possible.
■ Regulations concerning laborThere are no regulations concerning the industries of foreign workers, 90% of the UAE's working population is foreigners. At UAE, we are promoting Employment Policies (Emiratization) of Labor Force, and outside the Free Zone there is a system that said that they hire citizens in the following industries.
In fact, it is operated flexibly, so far, punishment such as suspension of business has not been applied even if it does not meet employment obligations. Also, depending on the degree of diversity of employment form and nationality of employees, the fee incurred in various procedures during employment hiring will differ. In addition, although it is not clearly stated on the system, in the case of a company with more than 100 employees, it is necessary to make a foreign employee (PRO) who processes procedures such as issuing a visa to his / her nationals.
■ Regulations on Establishment of CompanyWhen establishing a subsidiary in UAE, the main company forms are as follows.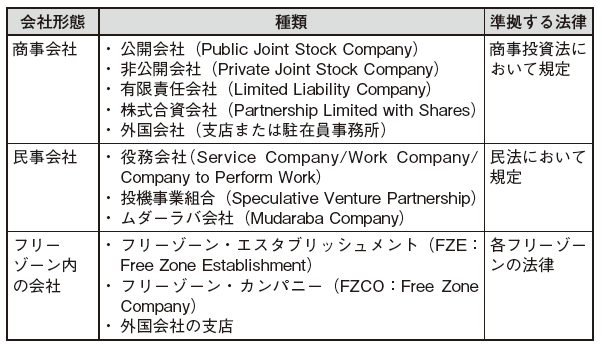
There is an offshore company form other than the company form mentioned above, but it is rarely used. The offshore company does not need to set up an office, it becomes a paper company. The main features of the offshore company are as follows.
· Establishment with 100% foreign capital is possible· Free zone · Inexpensive establishment cost than onshore company· Corporate tax and income tax will be exempted for 50 years after company establishment (renewal is also possible)· There is no regulation on paid-up capital· There is no regulation on foreign currency· Tax exemption on import of goods· You can remit the entire amount of profits and capital to your home country* Offshore company refers to a company established in the free zone. Basically, companies founded offshore have preferential treatment such as tax free. On the other hand, the free zone / onshore company refers to a company established outside the free zone
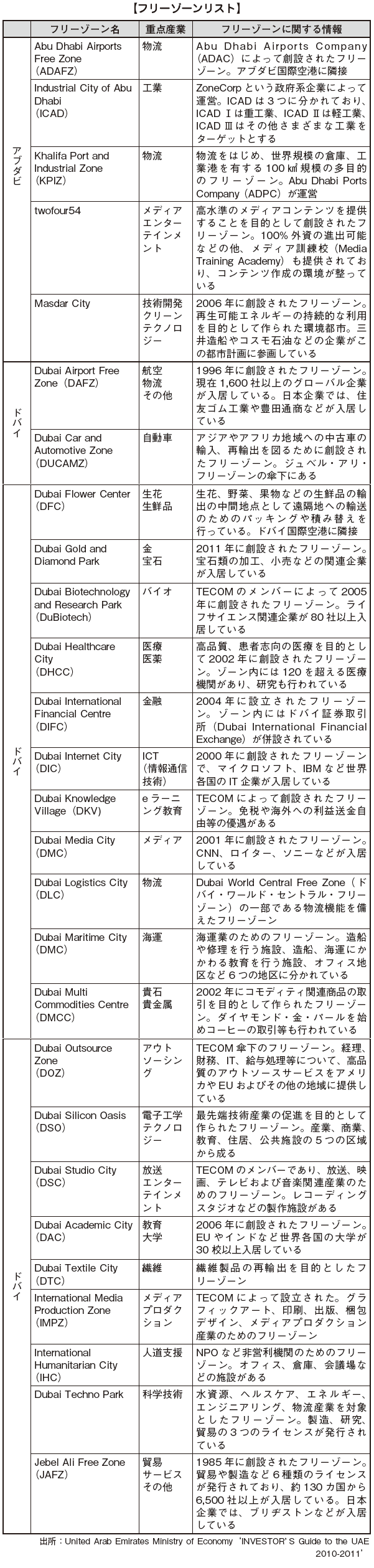
In corporate form, Japanese companies choose the most in a limited liability company, branch office or representative office and establish a company in the free zone. UAE has many free zones, and many Japanese companies have advanced. Most of the free zone is located in Dubai. The Commercial Investment Act also does not apply to each Free Zone as it defines its own laws, regulations, regulations and requirements. Therefore, we encourage you to compare many free zones and move forward. Although there is no regulation of shareholders' nationality, companies in the free zone can conduct only transactions or international transactions within the free zone, and do not do business with companies entering the UAE countries through local contractors or agents Be careful as it is not necessary.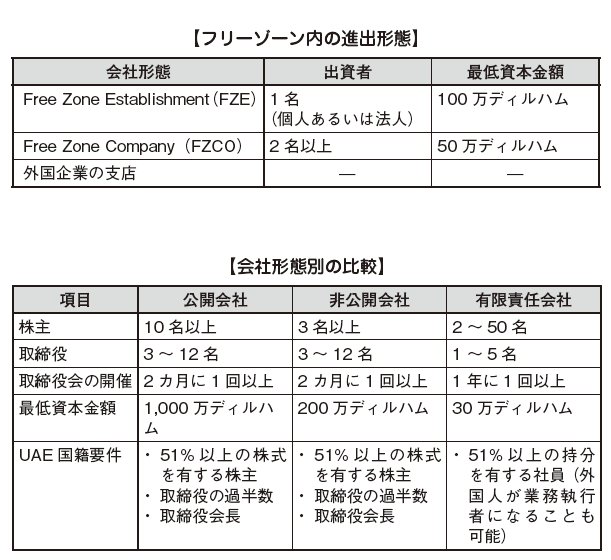
■ License Acquisition RegulationIn establishing a subsidiary to provide commercial or service, it is necessary to acquire a license regardless of company type. There are three kinds of licenses, it is necessary to acquire commercial licenses when conducting ordinary commercial transactions, industrial licenses in the case of manufacturing industry and industries, and specialized licenses when providing services by professionals and craftsmen. The requirements for issuing licenses vary from emirate country to country, but both are issued at DED (Dubai Government Economic Development Authority). Also, in the case of certain industries such as financial institutions, media companies, manufacturing companies, etc., it is necessary to obtain special approval before acquiring the license. Special approval is made by the management agency of each industry.On the other hand, regarding the license acquisition in the free zone, the type of license and its acquisition method are different depending on each free zone.
■ Regulations concerning exchange transactionsThere is no regulation on foreign exchange transactions at UAE, but transactions with Israel are prohibited. Revenues and royalty remittances are free, and the local currency has a fixed exchange rate system against the US dollar since 1980.
■ Free zone informationA free zone is an economic special zone existing in UAE. As of 2012, over 30 free zones are established in UAE. Each free zone has its business environment and preferential treatment according to the type of industry. As a preferential treatment common to most free zones, there is a possibility of establishing a company with 100% foreign capital, tax exemption for corporation tax, freedom of remittance to home country etc. Also, the inside of the free zone is regarded as a bonded area, and import duties are not imposed unless it is brought outside the free zone. As of May 2013, 396 Japanese companies have entered the UAE. By emirate, 294 companies in Dubai (increased by 11 companies from the previous year), 76 companies in Abu Dhabi (3 companies in comparison with the previous year) and 26 companies in the other five emirates (2 companies increased year on year). Looking at the breakdown of 294 companies located in Dubai, 209 companies are located in the free zone and 85 companies are in the city. According to information of companies entering the enterprise, there are many advances to free zones specializing in their business such as IT and high-tech technology, and free zones that are easy to access the airport and the city. In addition, there are an increasing number of companies establishing bases in multiple free zones.For example, the license in the Jebel Ali Free Zone is as follows.
[Commercial license]You can carry out import / export, sale and storage business, but if you do business outside this free zone you need to have a sales agent in mainland UAE.
[Industrial license]We can import raw materials, manufacture products and export finished products.
[Service / license]You can provide the designated service, but the type of service must comply with the license acquired by the parent company from the relevant emirate.
[Domestic industrial license]It is a license for manufacturing companies with citizens / citizens of the GCC countries possessing 51% or more and can have the same status as the company of the local or GCC countries within the UAE. In addition, as a requirement to acquire the license, there is a characteristic that the value added to the product within the Jebel Ali Free Zone is 40% or more.
■ Typical free zone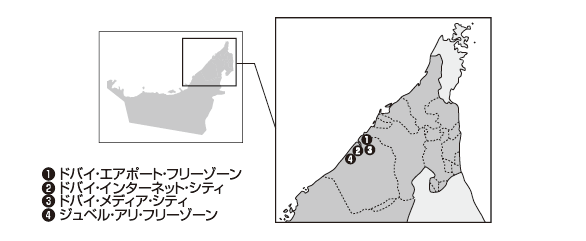
[Dubai · Airport · Free Zone]Established in 1996, Dubai Airport Free Zone (DAFZ) has over 1,600 companies (as of October 2013) in a variety of industries including aircraft, pharmaceutical, logistic, cargo, jewelry, IT, Companies are entering the market. The advantage of the Dubai airport free zone is located within Dubai International Airport (Duba iInternational Airport), and access to the cargo village (Cargo Village) capable of processing 1.5 million tons of cargo annually as well as the airport It is easy. Singapore (24%), Hong Kong (14%), China (13%), South Korea (9%), Asia companies that have 34% ) Has become.
[Dubai Internet City]Dubai Internet City (DIC: Dubai Internet City) is a member of Dubai Holding (Dubai Holding) of the Dubai government and was established under the umbrella of TECOM (Dubai Technology, Electronic Commerce and Media Free Zone Authority) established in 2000 It is a free zone.It has been established to attract ICT (Internet and Communications Technology) related companies. Microsoft, IBM, etc., which are major giants of IT business, are entering.
[Dubai Media City]Dubai Media City (DMC: Dubai Media City), like Dubai Internet City, is a member of Dubai Holding and is under the control of TECOM. At the end of 2012, more than 1,300 companies are registered. Business licenses issued by Dubai Media City include industries such as broadcasting, consulting, advertising-related, movie-related, music, entertainment, news, newspaper, media, publication, web production.
[Jebel Ali Free Zone]Founded in 1985, Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZ: JebelAliFreeZone) is located in the most Abu Dhabi place in Dubai, facing the Persian Gulf. As of 2012, more than 6,500 companies in 132 countries are in operation, of which 139 companies are dominated by Japanese companies. Although JAFZ, where only 19 companies existed in 1985, has grown rapidly until more than 300 times more companies were established in about 30 years.
-
UAE Commercial Investment Act
MergerAbsorption merger and consolidation merger are available as M & A methods prescribed in the UAE Commercial Investment Act (the Investment Act). Absorption merger is defined as "the dismissal of one or more enterprises and the transfer of rights and obligations of the dissolution company to existing companies". Under law the acquired company is deemed to have been extinguished and all assets and liabilities are transferred to the acquiring company. In addition, the merger is defined as "the dissolution of two or more companies and the transfer of all rights and obligations of the company to the new company". Legally, the two merging enterprises are deemed to have disappeared, and the newly-established enterprise has the rights and obligations of the expiring enterprise. In both cases, approval of the Emirates Securities and Commodities Authority (ESCA) is required when listed companies are involved. Under the Investment Law, it is not clearly stated about cases where each acquirer continues to exist without acquiring the acquired company when the acquiring company acquires the acquired company, but actually the acquired company acquires There are cases where it becomes a company subsidiary. Such acquisitions are generally accepted and can be made directly to shareholders of the target company through a tender offer. Acquisition consideration will be cash and shares, and acquisition is required for a certain period of disclosure. After publication, we will carry out the procedure prescribed by UAE Securities and Commodities Committee (SCA: Securities and Commodities Authority). In principle, the acquisition of shares of a public company by foreigners (people other than UAE citizens) is limited to 49%. If you have appropriate procedures and required approvals you can freely acquire up to 49%. -
DIFC
In DIFC, the DIFC Investment Act No. 2 (the DIFC Investment Law) enacted in 2009 has regulations on M & A. Regarding companies listed on the Nasdaq Dubai, there is a provision in the Take Over Module specified by the Dubai Financial Services Agency. Regarding M & A methods, neither the DIFC Investment Law nor the Acquisition Rule Module has clear provisions. However, as long as M & A methods that are accepted in countries that apply common law, such as the UK and the US, are also accepted in DIFC. This is because the legal system of DIFC follows the principle of common law. -
Business acquisition by business transfer
In each emirate country and free zone in UAE, it is possible to obtain business from UAE corporation. For example, on February 18, 2011, Sumitomo Corporation has a project with the Korea Electric Power Corporation to acquire a part of the interests of the thermal power generation project. -
Acquisition of listed companies
The UAE has three stock exchanges: Dubai Financial Market (Dubai Financial Market), Abu Dhabi Stock Exchange and Nasdaq Dubai. The M & A system of the Dubai financial market and the Abu Dhabi Stock Exchange are almost the same. On the other hand, the Nasdaq Dubai is quite different from the other two stock exchanges, rather it is similar to the British M & A system. ESCA is the main agency that has jurisdiction over companies listed on the Dubai financial market and the Abu Dhabi Stock Exchange. In addition, the Dubai financial market and the Abu Dhabi Stock Exchange each set rules for listing and disclosure. The Department of Economic Development in Dubai and Abu Dhabi has authority over certain procedures. The main agency that has jurisdiction over the companies listed on the Nasdaq Dubai is the Dubai Financial Services Authority.
■ How to acquire companies listed on the Dubai financial market and the Abu Dhabi Stock ExchangeThere are mergers, stock exchanges, cash tender offers as methods of acquiring companies listed on the Dubai financial market and the Abu Dhabi Stock Exchange.
[merger]merit· Since minority shareholders do not remain in the acquired company, the subsequent decision-making process for management will be smooth· There is a possibility that scale merit is accepted by expansion of company scale
Demerit· The price of the shares of the acquired company must be determined by a government-designated committee (the evaluation must be approved by the acquirer's shareholder)· As long as the new holding company is not the issuer, the acquiring company is obligated to grant a pre-right to shareholders of the previous acquired company· The creditors have the right to oppose the merger (In this case, the merger is postponed till resolution)· The merger will be approved only if the shareholder who holds voting rights has a votes of more than 75%· The assets / liabilities of the acquired company are transferred to the acquiring company, but it is highly likely that consent of the third party organization will be required· Issuance of new shares by the acquiring company is required for listing (In case the authority is not delegated from ESCA, preparation of the prospectus is required)
[Share exchange]merit· Creditors of acquired companies do not have authority to oppose mergers / acquisitions· Exchange does not transfer assets / liabilities and no third party institutional approval is required
Demerit· There are no compulsory provisions that will allow replacement proponents to acquire minority shares· The price of the shares of the acquired company shall be determined by a government-designated committee (the evaluation must be approved by the acquirer's shareholder)· As long as the new holding company is not the issuer, the acquiring company is obligated to grant a pre-right to shareholders of the previous acquired company· If the replacement proposer wishes to delist an acquired company, it is highly likely that the acquired company will be required to hold a general shareholders meeting· Issuance of new shares by the acquiring company is required for listing (In case the authority is not delegated from ESCA, preparation of the prospectus is required)
[Cash tender offer] Benefits· It is more convenient than legal merger or stock exchange· Creditors of acquired companies do not have authority to oppose mergers / acquisitions· Assets / liabilities will never be transferred due to the purchase and no approval by a third party organization is required
Demerit· There are no mandatory provisions that make it possible for the procurement proposer to acquire minority shares· There are no rules similar to merger rules that regulate the process of buying in the UK· If the proposer wants to delist the acquired company, the acquired company is likely to be required to hold a general shareholders meeting
■ Acquisition of companies listed on Nasdaq DubaiFor the acquisition of a company listed on the Nasdaq Dubai, the acquisition rule module specified by the Dubai Financial Services Agency is applied. Cash or stock is used for the purchase consideration. In the case of a company whose target was established under DIFC, if the buyer holds 90% of the shares by the purchase offer, the buyer has the right to purchase the shares of the remaining minority shareholders, the minority shareholders sell I have the right to do. There is no clear provision about the method of M & A by merger, as stipulated by the Dubai financial market and the Abu Dhabi Stock Exchange, but if it is a method of M & A that is accepted in countries that apply common law such as UK and USA, It is considered to be accepted also in DIFC. This is because the legal system of DIFC follows the principle of common law.
■ ConfidentialityFor companies listed on the Dubai Financial Market and the Abu Dhabi Stock Exchange, there is no obligation of confidentiality until the acquisition is made. The buyer and the target company agree with the confidentiality agreement that the secrecy will be kept until the point where information must be disclosed by the SCA regulations. However, in the case of companies listed on the Nasdaq Dubai, the parties (stakeholders) who are sensitive to confidential information must disclose confidential information concerning bids by all means until the bid is made public. The acquirers must take appropriate actions to minimize the possibility of information leakage by any chance.
■ Compulsory Tender Offer There is no mandatory tender offer provision for companies listed on the Dubai Financial Market and the Abu Dhabi Stock Exchange, but for the listed companies of Nasdaq Dubai the provision of mandatory tender offer there is. Shareholders who hold shares with a voting right of 30% or more must make a tender offer to all remaining shares outstanding. The purchase price must not be lower than the highest value of the past six months paid by the buyer. This rule prevents the acquirer from taking control of the target company and also prevents the remaining minority shareholders from being squeezed out without a sufficient public tender offer. Although there is no stipulation of the minimum amount of consideration for acquisition, market rates and stock prices must be reflected. -
Antitrust law
Under the UAE there is no antitrust law or equivalent regulation or regulation. If organization restructuring is completed and subsidiaries belong to other jurisdictions such as free zone, we will comply with the antitrust law etc. of that area. -
Local accounting standard (International Accounting Standard Convergence)
Accounting standards do not exist in UAE. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are recognized as de facto national accounting standards. In practice, IFRS (and previous accounting standards) has been applied in UAE for more than 20 years.
-
-
-
Tax on M & A
There is no tax regulation concerning M & A in the tax law. When corporations and corporations that are subject to corporate income tax at UAE conduct mergers and acquisitions, taxes on various funds such as borrowing money, ownership rights, collaboration between ownership rights and discount securities vary depending on each case I will. UAE's tax law is extremely concise. The UAE does not have a corporate tax law at the federal level. Of the seven emirates, the three emirates of Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Sharjah have established their own taxation system which is similar in nature and text. However, corporate tax theoretically covers all corporations, but in fact it is a foreign oil company (such as a company dealing with hydrocarbon materials produced by the emirate, which has oil digging right including crude oil) and foreign companies It is imposed only on the banks of Japan. Foreign oil companies need to sign a concession agreement under the rule of the emirate who miners and produces oil. The corporate income tax rate of oil companies is 55 to 85%. Each emirate country has issued its own corporate income tax on declaration tax payment to a branch of a foreign bank, and the corporate income tax is roughly estimated to be 20% of the taxable income.
■ Purchase of assets and stocks[Purchase of assets]There is no provision of tax law concerning the purchase of assets. In the case of corporations subject to corporate income tax at UAE, taxable subjects, allocation of tax of purchase price, handling of goodwill, tax attributes etc. will vary depending on each case.
[Value-added tax]As of 2014, there is no law concerning consumption tax and value added tax (VAT). The UAE Federal Government is positively considering the introduction of VAT, but concrete final decisions have yet to be made.
[Purchase of stock]Acquisition of shares by companies is subject to foreign investment restrictions.
[Comparison of assets and stock purchases]In the corporate income tax laws of each emirate such as Dubai and Abu Dhabi, profits arising from the sales or assignment of property and rights are subject to taxation. When a company subject to taxation of UAE conducts mergers and acquisitions, it is not legally permissive to transfer assets for accounting purposes for tax purposes without making a contract. Therefore, if an asset is sold at a book value, the tax bureau will examine the equality and check whether there was profit.
Selection of Capital AcquisitionUAE does not have any special undercapitalization or exchange control regulation concerning income tax law. Therefore, funds transfer to home country is relatively easy. In the case of a limited liability company, the UAE Commercial Investment Law stipulates that at least 10% of revenue shall be allocated as annual capital reserve. Such dividends need to continue until revenue of 50% of the share capital is reached.
[Withholding tax]There is no withholding tax on borrowings.
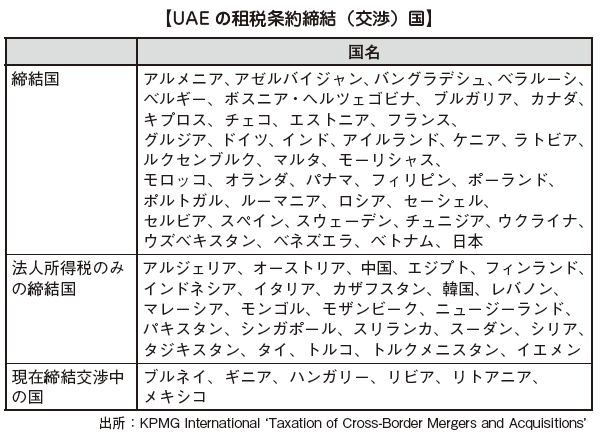
Tax TreatyUAE has a tax treaty on income and capital with other countries. A tax treaty was concluded between Japan and the UAE in May 2013 based on the closer economic relations between the two countries.
-
-
-
References
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya