Colombia
4 Chapter Economic Environment
-
-
1 Chapter Coming Soon
2 Chapter Basic knowledge
2.2 Political regime and history
2.3 Colombian education system
3 Chapter Investment Environment
4 Chapter Economic Environment
5 Chapter Corporate Laws
5.1 Kinds of Corporate Systems
6 Chapter Tax Laws
-
-
-
Economic trend
Colombia is a regional power in South America, with the second largest population after Brazil, the economic scale is the third largest after Brazil and Argentina. The economy was stagnant for a long time due to terrorism by anti-government armed guerrillas and struggle by drug cartels, but since the Uribe administration in 2002 entered into an economic growth period, it was taken over by the Santos administration in 2010 .Under both governments, we continued a favorable economy due to expanding exports of oil and strong domestic consumption, but since 2014, we will be able to maintain a world economy, including international oil prices crash, US monetary easing, We are facing negative negative factors. However, due to stable fiscal and macroeconomic management, strong domestic demand, the Colombian economy is also showing firmness, and it is one of the most noteworthy countries among emerging countries that are stagnant.
■ GDP and Economic Growth RateThe Colombian economy from the latter half of the 1990s to the early 2000s was sluggish due to terrorist attacks by anti-government armed guerrillas. However, since the establishment of the Uribe regime in 2002, a full-scale sweeping operation of anti-government armed guerrillas has been successful, dramatically improving security. In addition, regulatory reform such as privatization of state-owned enterprises was promoted. Along with that, foreign investment and private consumption will become active, and the economy will head towards growth trajectory.In 2006 and 2007, we achieved high growth of 6% range. Although it temporarily slowed down due to the impact of the Lehman shock, the increase in production of mineral resources such as oil and coal advanced by active investment and the soaring global price of resources have overlapped, and again in 2011 high growth of 6% Marked.After that, we have continued steady growth of around 4% in 2012 - 2014 when global recession continues. However, international crude oil prices plunged in late 2014, the economy is getting cold sharply. The Colombian economy has a high degree of dependence on primary products, and oil and petroleum related products account for 50% of exports and 20% of revenue, so its impact is very large.The growth rate in 2015 is supposed to be 3.1% (preliminary value of the Central Bank of Colombia), 2.5% (forecast value of IMF), which is a low forecast of 2.8% (Central Bank of Colombia) and 2.8% (IMF) in 2016 It is. It is expected that the future trend of crude oil price and progress of industrial development other than mineral resources will be key..png)
* Forecasted IMF in 2015Source: IMF "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2015"
Per capita GDP is about tripled in the past 10 years, it exceeds 8,000 US dollars in 2013,You can say that you have joined the ranks of middle-ranking countries next to Chile and Brazil. In addition, the middle income group has doubled from 30% to 60% over 10 years, not only export of resources, but also vital domestic consumption is a driving force driving economic growth.Meanwhile, Colombia is said to be the country with the largest disparity gap in South America, and the Gini coefficient is the lowest 53.5 in South America (the World Bank in 2013), and the current unemployment rate is high. Along with the expansion of the middle class, raising the low income group can be said to be a necessary matter for paying out social unrest..png)
* Forecasted IMF in 2015Source: IMF "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2015"
■InflationEven though the economy of Colombia is in a growth trajectory, the inflation rate has been relatively stable. In the 1980s and 1990s, there was no hyperinflation that many of the Central and South American countries like Brazil and Argentina experienced.In 1999, central banks have set inflation targets of 3% ± 1%, and solid monetary policy will be taken around this. In the first half of the 2000s I exceeded the target limit, but after that it became stable within the target.However, since the beginning of 2015, the rise in import prices due to the declining peso against the backdrop of the easing of monetary easing in the US and the rise in the price of agricultural products due to the El Niño phenomenon have meant to exceed the target limit again. In response, the central bank gradually increases the policy interest rate from 3.25% to 6.25%. In line with the trend of foreign exchange and the slowdown of the economy, it seems that it has entered a phase where increasingly delicate monetary policy is required from now on..png) * Forecasted IMF in 2015* Consumer price index: Index at the end of December 2008 as 100 (annual average)Source: IMF "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2015"
* Forecasted IMF in 2015* Consumer price index: Index at the end of December 2008 as 100 (annual average)Source: IMF "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2015"
■ FinanceThe finance of Colombia is relatively healthy. Colombia finance is said to be an honors student along with Chile etc. in Central and South America where there are many countries with bad financial situation such as Brazil which is rapidly expanding the budget deficit and Argentina which repeats the default.The primary balance is exceptionally deficit in the three years from 2009 to 2011 where the economic stimulus measures after the Lehman shock and massive floods had occurred, but all other things are in surplus. You can see that the Colombian government has not maintained popular relaxation finance and has maintained sound fiscal discipline. For this reason, the ratio of fiscal balance to GDP has been under 3% for the past 12 consecutive years since 2003.However, due to the fall in crude oil prices in the second half of 2014, the national treasury payment due to the state-owned enterprise "Eco Petrol" which accounts for about 20% of the revenue has decreased sharply. In Fiscal 2015, although the fiscal austerity measures were taken, the primary balance was in the red and the ratio of the fiscal deficit to GDP was 3%. For the time being, it is expected that the stimulus and fiscal discipline will be difficult and difficult..png)
* Forecasted IMF in 2015Source: IMF "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2015" -
Trade
The amount of trade in Colombia was 4.5 times for exports and 4.3 times for imports during the decade from 2003 to 2013 when security restored and economic growth was on track. Although the effect slowed somewhat in 2009 after the Lehman shock, the impact was minor and it can be said that we have continued to expand trade strongly.As background, the successive Colombian government has inherited the free trade orientation. It is located in the center of the Americas and has been active in liberalizing trade and investment in order to make full use of the geopolitical advantage facing both the Caribbean and Pacific Ocean. The ROHAS commerce and industry tourism minister, who took office in 2013, is seen as a somewhat cautious faction, but the basic policy is not changed.Secondly, in the latter half of the 2000s and early 2010s, there is a sharp rise in oil production due to the recovery of security in Colombia and a surge in international crude oil prices due to tightening of energy demand in emerging countries. Colombia became the third largest oil producing country in Latin America in 10 years, becoming a major exporter of resources.However, international crude oil prices plunged in the second half of 2014 and dark clouds hang in trade expansion that was smooth. In the following 2015 the trade deficit doubled the previous year. In addition, the major export destination, the US, was converted to a petroleum net exporter by the "Cher revolution", and in China, which was also the main export destination, the energy demand has been drastically reduced due to the economic slowdown. While not expected to early recovery of crude oil prices, is an urgent need to improve the competitiveness of strong domestic consumption and domestic industry infrastructure demand was traction, it says that the big challenge of breaking away of resource dependence on exports has been confronted..png)
Source: Colombia Republic of Statistics Office
Source: Colombia Republic of Statistics Office
[Free Trade Area, Free Trade Agreement]Colombia is one of the countries aggressively promoting free trade. Bilateral and regional free trade agreements (FTAs) with the United States, Mexico, Canada, the EU and major Latin American countries have been in effect and have many tariff elimination items with 45 countries. In addition, I am waiting for ratification with Korea and Panama, and I am also negotiating with Japan, Turkey and others.In addition, active in establishing joint economic zone in Latin America, the Andean Community (Bolivia, Ecuador, Peru, Colombia), Pacific Ocean Alliance (Mexico, Chile, Peru, Colombia) is a member of the Mercosur (Brazil, Argentina, Venezuela , Uruguay, Paraguay) has also entered into a trade agreement.In particular, in recent years a popular movement to the economic integration of Alliance Pacific Ocean, has been launched to clear the cooperation attitude of the Asia Pacific Ocean region, and a protective-trade of Mercosur has been said to have a clear distinction.[Imports and exports by country / region]Colombia is the country with the most trade with the United States in South America, and has occupied more than 30% of trade value for many years. This is due not only to the geographical conditions of being located at the northern end of the continental South America and having a good port in the Caribbean, but also due to the fact that the political power has continued, and that free trade has been proactively promoted It can be said that things are big. In that sense, it shows a different trade situation with other South American countries, especially Mercosur countries such as Brazil and Argentina.If you look at the export value of 2015 by country, 27.6 percent largest export destination in the United States, followed by Panama 6.7%, China 6.3%, Ecuador 4.0%, Brazil 3.3%, it has become a Peru 3.2%. In the United States, it was an overwhelming rate of 42.2% in 2010, but both the amount and the ratio have declined at the peak of 2011. The biggest reason is that shale revolution greatly reduced oil exports to the US. In addition, the export value to China has also declined by half since 2014, and the decline in energy demand has been greatly affected as well.Meanwhile, the total Latin American Union of 2015 (the ten major countries of South America + Mexico, Cuba) totaled 26.0%, which is comparable to the United States. Exports itself by the decline of crude oil price has decreased, Panama, Ecuador, a lively border transactions with neighboring countries such as Peru, are considered the effect of the progress of economic cooperation of the Latin America region is out..png)
Looking at imports by country again, the United States will continue at 28.7%, followed by 18.6% in China, 7.1% in Mexico, 4.2% in Germany and 3.9% in Brazil. From the United States, it is characteristic that many imported petroleum products. Colombia is an oil producing country, but because the capacity of the refinery is insufficient, we import petroleum products such as gasoline from the United States. There are many imports of automobiles from China, such as electronics and electric products, from Mexico. The fact that FTA between Mexico and Colombia was concluded in 2011 is the background of the elimination of tariffs on finished vehicles and poses a threat to Colombia's automobile industry.The future, FTA ratification with South Korea, some such as the progress of the EPA negotiations with Japan, Asia Pacific Ocean trade with the region has been considered that there is a possibility to expand dramatically, of the Pacific Ocean side port, road infrastructure development , It will be the key to future diversification of trade.
.png)
[Import / export by item]Looking at exports by item, the overwhelming majority of petroleum and its petroleum-related items are overwhelmingly 40.1%, followed by coal 12.8, with energy resource exports accounting for more than half of the total. As a result, it is susceptible to trends in supply and demand of international resources and price fluctuations, especially since the second half of 2014, the amount of exports has decreased significantly.Next, 7.2% of coffee and tea, 4.0% of plastics raw materials, 3.7% of precious metals / jewelry and 3.7% of horticultural crops. Coffee was a flower-shaped export item that accounted for half of the export value until the late 1980s. After that, the ratio fell by the rise of energy resources, but Colombia is now the third largest coffee exporter of the world after Brazil and Vietnam, and it is one of the main items. Precious metals and jewelry have gold and emeralds produced, and horticultural crops have cut flowers such as roses and carnations whose exports are increasing rapidly, mainly in North America. In recent years, light industrial products for adjacent Ecuador and Panama are also promising exports.
.png)
Regarding imports, import of industrial goods such as boiler · generator by 12.8%, machinery · electronic equipment 10.3%, vehicle and vehicle parts 7.8% are drawing attention. In addition, 9.5% of mineral fuels and petroleum products resulting from the refinery shortage, various raw materials, intermediate goods are also being actively imported. In recent years, due to the expansion of the middle class, imports for personal consumption such as automobiles, home appliances, mobile phones and other electronic appliances are also expanding, and it seems to reflect the expansion of the domestic market. Although the import value has started to decline in 2015 from the downturn of the economy, domestic consumption is solid, and further consumption will be expected to diversify and expand over the medium to long term.
.png) Source: Colombia Republic of Statistics Office
Source: Colombia Republic of Statistics Office -
Industry trends
Looking at the industrial composition of Colombia as a percentage of GDP, the primary industry is 6.4%, the secondary industry 36.9%, and the tertiary industry 56.7%.Although the primary industry is only 6.4% in GDP, it is one of the key industries playing a part in major export goods, as the production of cash crops such as coffee and cut flowers is prosperous. Regarding the secondary industry, mining such as energy resources (petroleum and coal), construction that is growing rapidly due to active infrastructure development, labor-intensive light industry in the region, automobiles as a production base of the global industry in the northern part of South America We are widely located, including the motorcycle industry. It can be said that industrialization is relatively advanced in this area. The tertiary industry is developing as 56.7% as developed countries, and the service industry such as wholesale and retail trade has also developed. More noteworthy is that the financial industry in Colombia has become one of the most reliable and thick business in South America..png)
■ AgricultureFarmers' urban inflows advanced rapidly, as rural populations, which occupied more than 60% of the population, had anti-government guerrilla activities mainly based on rural areas. Although the rural population has fallen below 20% in the early 2000s, it is said that the rural regression is progressing with the recovery of security in recent years.In Colombia, the agricultural land area is only about 3% of the national land, and the proportion of agriculture in GDP is not as large as 6.4%. However, coffee, cut flowers, bananas and other export competitive cash crops are actively being produced, so if we maintain security, the position as one of the important industries will remain unchanged.In addition, in recent years, the production of sugar cane as a raw material of ethanol and oil palm which becomes biodiesel fuel is also increasing.
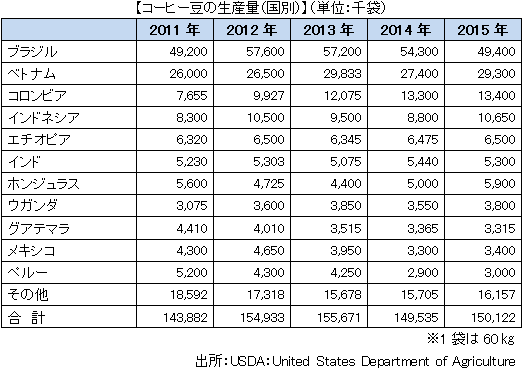
[coffee]Coffee is the major export item of Colombia, following oil and coal, and boasts the third largest export volume both in Brazil and Vietnam, both in production and export volume. It is characterized by the fact that most of the production species are high class species of Arabica species and has advantages different from inexpensive robusta species such as Vietnam and Indonesia which have increased production in recent years. Coffee accounts for 60% of exports to Japan.Highlands with an altitude of 1,000 m above sea level in northern Andean, such as Antioquia and Caldas, are suitable for production, production is mainly from slopes, so production by small farmers is large, and cost competitiveness is an issue as mechanization is not progressed I will. Therefore, the National Federation of Coffee Producers (FEDECAFE) promotes various incentives for small-scale farmers by promoting incentives for new planting trees and fair trade initiatives.
[Horticultural crops]In Colombia, cut flower production became popular in the 1970s, and many varieties were produced for export such as carnations, roses, chrysanthemums, etc. It is close to the equator and the sunshine time is long, but the highland area with the temperate and moderate rainfall is the production suitable land, Bogoda and the suburbs of Medellin are exported from major production areas and also to the West, Japan by air mail. The largest export destination accounts for approximately 70% in the United States. In recent years exports to Japan have also increased, and 70% of Japan's imported carnations are from Colombia.In recent years, we have expanded the production of secondary processed products such as essential oils made from roses etc., and the development of industries of high value added products is underway
■ Oil industryColombia's energy resources have been made state-owned through Colombian state-owned oil "Eco Petrol", but in the 2000s, regulatory reforms such as partial privatization enabled foreign investment by foreign companies It was.In addition, Columbia became a net exporter of petroleum, as anti-government armed guerrilla countermeasures have taken effect at the same time and oil production has turned to an increase. Especially foreign investment in the upstream sector is thriving, exploration and mining are actively carried out, Ecopetrol is only about 60% of Colombian oil production.On the other hand, there are many issues such as lack of refinery facilities, lack of transport capacity of pipeline, low reserves. There are only a few refineries, such as Cartagena facing the Caribbean Sea and the Magdalena River in the northeastern, and the refining capacity is not catching up with domestic demand. In addition, due to the lack of capacity to transport pipelines from inland oil fields, circumstances such as the inability to raise production volume are overlapping. For this reason, despite being a petroleum net exporter, the situation continues to be importing diesel oil etc. mainly from the United States. Ecopetrol is proceeding with construction of 20,000 BPD from 80,000 BPD to 165 thousand BPD, which is progressing to increase the capacity of the Barrancabermeja-Santander refinery along the Magdalena River from 20.5 thousand BPD to 300 thousand BPD, and will be completed in 2016.Although the attack by the anti-government guerrillas is somewhat reduced due to the restoration of security, progress due to the peace process in the future is significant, and ensuring the safety of petroleum facilities will continue to be an important issue.Furthermore, the oil reserves in Colombia are 2.4 billion barrels (33rd in the world) and the number of years that can be taken is as short as 6.8 years as of 2013, so the progress of exploring new oil fields is expected not only in the future oil industry but also in the Colombian energy It is the key to our strategy. In the new exploration, heavy oil and shale oil · gas reserves are confirmed. Motivation for investing in these new types of oil field extraction depends on trends in international crude oil prices, so it is attracting attention as a global issue..png) Source: US Energy Information Administration
Source: US Energy Information Administration
-
-
-
参考文献
・コロンビア統計庁DANE: National Administrative Department of Statistics・農林水産省・IMF・世界銀行・EIA・USDA (United States Department of Agriculture)・BP・三菱UFJリサーチ&コンサルティング・国際通貨研究所・国際金融情報センター 新興国 カントリーフォーキャスト・日立総合研究所コモディティスーパーサイクル終えんに伴う資源国経済の変容・JETRO「世界貿易投資報告(コロンビア」」・JPEC(石油エネルギー技術センター)JOGMC
-



 Japan
Japan UnitedStates
UnitedStates China
China Hong Kong
Hong Kong Mongolia
Mongolia Russia
Russia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Laos
Laos Cambodia
Cambodia Myanmar
Myanmar Indonesia
Indonesia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia India
India Bangladesh
Bangladesh Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil Peru
Peru Colombia
Colombia Chile
Chile Argentina
Argentina DubaiAbuDhabi
DubaiAbuDhabi Turkey
Turkey South Africa
South Africa Nigeria
Nigeria Egypt
Egypt Morocco
Morocco Kenya
Kenya